![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
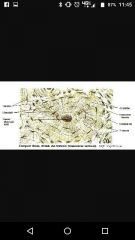
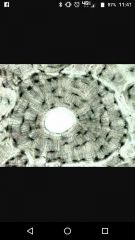
Osteon Central canal Lamella Lacuna Osteocytes Canaliculi |
|
|
|
Name 6 epithelial tissue and 6 connective |
Simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified, stratified keratinized squamous, stratified non keratinized squamous Bone, blood, cartilage, adipose, loose areolar connective tissue, dense regular connective tissue |
|
|
|
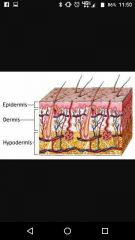
|
|
|
|
Four primary tissue |
Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous |
|
|
|
Simple epithelial Found? Characteristics? Function? |
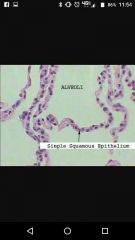
One layer thick, not exposed to outside, all cells contact with basement membrane one layer sick, not exposed to outside, all souls contact with basement membrane, for minimum stress, probably for filtration absorption and secretion. Found in lung |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal - found/ look
|
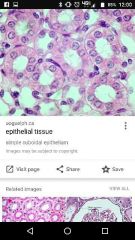
Gut/ small intestine Kidneys!!! Lining exocrine glands
|
|
|
|
Simple sqamous Found/ look |
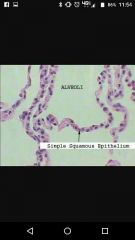
Blood vessels Olveoli ! (Threachia)
Kidney,eyes,alveoli |
|
|
|
Simple columnar |
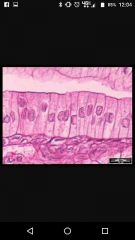
Increase surface area! Microvilli Small/large intestine
|
|
|
|
Stratified squamous keratinized vs non keratinized |
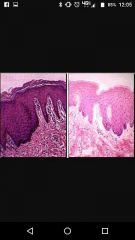
Keritinized found on skin surface Non karitzised found in vagina,anus,etc. |
|
|
|
Study this sight ! |
https://quizlet.com/4376472/ch-04-tissue-level-flash-cards/
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified columnar |
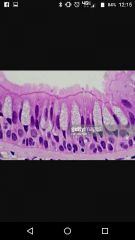
Nasal cavity Simple. But looks funked up |
|
|
|
Characteristics of connective tissue |
Loosely packed cells, they have a ground substance contained of non-living stuff and proteins. |
|
|
|
Look at pics of blood, adipose,cartilage, loose(areolar) and dense |
Do it |
|
|
|
Endocrine gland vs. Exocrine gland |
Endocrine glands release hormones, they like ducks and drop directly into the bloodstream
Exocrine glands have ducts and they secrete material to the surface examples being digestive, sweat glands ,and tears merocrine |
|
|
|
Four types of membrane and location |
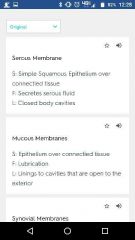
|
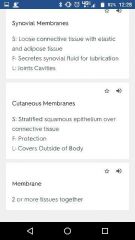
|
|
|
Apoptosis |
the death of cells that occurs as a normal and controlled part of an organism's growth or development. |
|
|
|
Hyperplasia , hypertrophy, neoplasia |
Hyperplasia: the enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the reproduction rate of its cells, often as an initial stage in the development of cancer Hypertrophy: the enlargement of an organ or tissue from the increase in size of its cells Neoplasia: the formation or presence of a new, abnormal growth of tissue. |
|
|
|
Differentation |
cellular differentiation is the process where a cell changes from one cell type to another. |
|
|
|
4 type of cell Junctions |
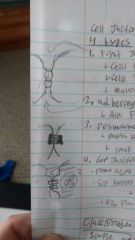
Tight junction- thread like top Adhering Junction- thread like bot Desmosomes- button strap Gap junction- protein connection Glucose, amino acidd, and ions travel |
|
|
|
Mode of gland secretion |
Merocrine or eccine gland. - watery Hokocrine- releases self cells (pimples) Apocrine -( middle, breast milk) |
|
|
|
Three types of gland |

|
|
|
|
Three types of ground fiber |
Collagen, strength Elastic, stretchy Reticular fibers, Network |
|
|
|
6 types of tissue change |

|
|

