![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Excitability |
Plasma membranes can change their electrical states (polarized to depolarized) and send an electrical wave called an action potential along the length of the membrane. |
|
|
Aponeuroses |
Flat tendon sheet |
|
|
Elasticity is a quality of muscle tissue that... |
Can return to its original length when relaxed due to elastic fibers |
|
|
Extensibility |
Stretch or extend |
|
|
Contractility |
Allows muscle tissue to pull on its attachment points and shorten with force |
|
|
Differences among 3 muscle types are organization of contractile proteins...? |
Actin and myosin
•These proteins are arranged in lines (striations) in cytoplasm of skeletal and cardiac muscle. •In smooth muscle, the cytoplasm of muscle fiber (which has single nucleus) has a smooth appearance |
|
|
Sarcolemma |
Plasma membrane of muscle fibers |
|
|
Sarcoplasm |
The cytoplasm in a muscle fiber |
|
|
How many myofibrils are in a muscle fiber ? |
Hundreds to thousands |
|
|
Sliding filament model of contraction |
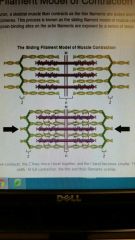
•The process of which a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slid past the thick filaments within a sarcomere. •The sliding can only occur when myosin-binding sites on the actin filaments are exposed by a series of steps that begin with Ca++ entry into sarcoplasm |
|
|
Myogram |
An instrument that measures the amount of tension produced by a twitch over time. |
|
|
3 phases each twitch undergoes |

•Latent period- the action potential is being propagated along the sarcolemma and Ca++ is released from the SR (excitation & contraction are being coupled) •Contraction phase- Ca++ in the sarcoplasm have bound to troponin, tropomyosin shifted, cross bridges formed, and sarcomeres actively shorten to peak tension. •Relaxation phase- When tension decreases as contraction stops. Ca++ is pumped out of sarcoplasm into SR, cross bridgs cycling stops, and muscle fibers return to relaxed state. |
|
|
Graded muscle response |
Contraction of a muscle with varying degrees of force dependent on the circumstance. •They do this through wave summation -Wave summation is an increase in muscle contraction strength based on how rapidly a muscle is stimulated. This occurs because muscles that are rapidly stimulated are not able to relax between repeated stimulations. |
|
|
Tetanus |

During tetanus, the concentration of Ca++ in the sarcoplasm allows virtually all of the sarcomeres to form cross bridges and shorten, so that a contraction can continue uninterrupted (until muscle fatigue) |
|
|
Treppe |
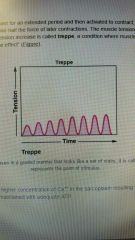
(Staircase effect) A condition where muscle contractions become more efficient. - Treppe results from a higher concentration of Ca++ in sarcoplasm resulting from steady stream of signals from motor neuron. |
|
|
Hypotonia |
The absence of low level contractions that lead to muscle tone (atrophy) and can result from damage to parts of the CNS (cerebellum), or from loss of innervations to a skeleton muscle (poliomyelitis) |
|
|
Hypotonic muscles have what kind of appearance |
Flaccid and they display weak reflexes |
|
|
Hypertonia |
Excessive muscle tone, accompanied by hyperreflexia (excessive reflex response). •often result of damage to upper motor neurons in the CNS |
|
|
Hypertonia is characterized by... |
Muscle rigidity (Parkinson's) or spasticity (some strokes) |
|
|
3 main types of skeletal muscle fibers |
•Slow Oxidative (SO): fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP.
•Fast Oxidative (FO): fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration, can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
•Fast Glycolytic (FG): fibers have fast contractions and primarily use anaerobic glycoIysis. The FG fibers fatigue more quickly than others. |
|
|
If a fiber primarily produces ATP through aerobic pathways it is... |
Oxidative |
|
|
The Oxidative fibers contain many more _____ than Glycolytic fibers because aerobic metabolism (which uses oxygen in the metabolic pathway) occurs in this. |
Mitochondria |
|
|
SO fibers contain a large number of ____, _____, and _____ |
Mitochondria, blood Capillaries, and myoglobin |
|
|
Maintaining posture, producing Isometric contractions, stabilizing bones and joints, and making small movements that do not require large amounts of energy are due to what fibers? |
SO fibers |
|
|
FO fibers are sometimes called what? |
Intermediate fibers- they possessed characteristics that are Intermediate between fast fibers and slow fibers |
|
|
FO fibers are primarily used for what? |
Movements (walking) that require more energy than posture control but less energy than an explosive movement (sprinting) |
|
|
FO fibers produce ____ tension than SO fibers but are ____ fatigue resistant than FG fibers |
More tension and more fatigue |
|
|
FG fibers are useful for? |
Rapid, forceful contractions to make powerful movements. •These fatigue quickly however and can only be used for short periods |
|
|
What happens to muscles cells when they grow in strength? |
New cells are not formed when muscles grow, instead structural proteins are added to muscle fibers in a process called hypertrophy (cell diameter increases) |
|
|
Age related muscle atrophy is called what? |
Sarcopenia |
|
|
What type of training modifies slow fibers to make them more efficient by producing more mitochondria to enable more aerobic metabolism and more ATP production. |
Endurance training |
|
|
Endurance exercise can increase ____ in a cell |
Myoglobin |
|
|
Myoglobin is found where? |
In the sarcoplasm and acts as an oxygen storage supply for mitochondria |
|
|
Angiogenesis |
Endurance training can trigger the formation of more extensive capillary networks around the fiber to supply O2 and remove waste |
|
|
Resistance exercises require what type of fibers ____? |
Large amounts of FG fibers - Causes increased amount of myofibrils |
|
|
Resistance training increases development of what tissues? |
Connective tissues and tendons become stronger |
|
|
Resistance training involves a lifter to weights in what pattern? |
Gradual increase of heavier weights |
|
|
Anabolic steroids |
A form of male testosterone |
|
|
Endurance athletes will what substance to increase aerobic respiration? |
Erythropoietin (EPO)- a hormone normally produced in the kidneys, which triggers production of red blood cells. |
|
|
Human growth hormone (hGH) |
It's main role is to promote healing of muscle and other tissues after strenuous exercise. |
|
|
Dangerous side affects of Anabolic steroids |
Infertility, aggressive behavior, cardiovascular disease, and brain cancer |
|
|
As muscles age, muscle fibers die and are replaced by what ? |
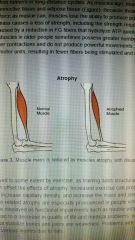
Connective tissue and adipose tissue |
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
•Shorter than skeletal and have 1 nucleus •Possess many mitochondria and myoglobin, ATP produced by aerobic respiration |
|
|
Intercalated disc |
Cardiac muscle cells are connected to one another by these. They allow the cardiac muscle to contract in a wave pattern so the heart can work as a pump |
|
|
Intercalated discs are part of the _____ |
Sarcolemma |
|
|
What are the two important structures of intercalated discs |
•Gap Junctions- forms a channel between adjacent cardiac muscle fibers that allow the depolarizing current produced by cations to flow from one cardiac muscle cell to the next. •Desmosomes- a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting. |
|
|
Syncytium |
The network of electrically connected cardiac muscle cells that creates a functional unit of contraction |
|
|
Contractions of the heart (heartbeat) are controlled by what cells? |
Pacemaker cells- they directly control heart rate. |
|
|
Pacemaker cells respond to signals from what to speed up or slow down |
Autonomic nervous system (ANS) •They can also respond to hormones that model a heart rate to control blood pressure |
|
|
Autorhythmicity |
The group of pacemaker cells are self excitable and are able to depolarize to threshold and fire action potentials on their own (they do this at set intervals) |
|
|
More features of cardiac muscle: |
•Long action potentials, having a sustained depolarization "plateau". •The plateau is produced by Ca++ entry through voltage gated calcium channels in sarcolemma of muscle fibers. •Large % of Ca++ that initiates contraction comes from outside the cell rather than from SR. |
|
|
Smooth muscle is found where ? |
Hollow organs and in the eyes and skin |
|
|
How much shorter are smooth muscle fibers to skeletal muscles? |
Thousands of times shorter |
|
|
Smooth muscle fibers contain... |
•Actin •Myosin contractile proteins •Thick filaments •Thin filaments |
|
|
a Dense Body |
Similar to the Z-discs of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle fibers and is fasted by the sarcolemma |
|
|
Calmodulin |
Allows smooth muscle to activate an enzyme called myosin (light chain) kinase which in turn activates the myosin heads by phosphorylating them. Then the heads can attach and pull on thin filament |
|
|
Photo of smooth muscle contraction |

The middle is bulged in a corkscrew motion |
|
|
Smooth muscle is able to function for long periods without rest through what? |
Latch bridges- keep the thick and thin filaments together for a prolonged period and without need for ATP |
|
|
Trigger for smooth muscle contraction |
Hormones, neural stimulation by ANS, and local factors |
|
|
Varicosity |
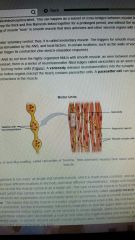
Releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft -Visceral muscle in the walls of the hollow organs (except heart) contain pacesetter cells |
|
|
Pacesetter cell |
Can spontaneously trigger action potentials and contraction in the muscle |
|
|
Single unit muscle (smooth muscle) |
Visceral Muscle •Muscle fibers join by gap Junction so that the muscle contracts a single unit. •Found in the walls of all visceral organs except the heart |
|
|
Stress-relaxation response of Visceral muscle |
As the muscle of a hollow organ is stretched when it fills, the mechanical stress of the stretching will trigger contraction, this is immediately followed by relaxation so that the organ does not empties contents prematurely |
|
|
Multiunit smooth muscle |
•Rarely possess gap junctions. •Stimuli for these muscles come from autonomic nerves or hormones. •Found around large blood vessels, in respiratory airways, and in eyes. |
|
|
Hyperplasia |
Smooth muscle can divide to produce more cells. -Uterus at puberty (producing more uterine smooth muscle fibers) |
|
|
Somites |
Paraxial mesoderm cells adjacent to the neural tube form these blocks of cells •Skeletal muscles (not head or limbs) develope from these |
|
|
Somites give rise to____ |
Myoblasts- a muscle forming stem cell that migrates to different regions of the body and then fuses to form a myotube |
|
|
Satellite cell |
(Help repair skeletal muscle cells) Similar to a myoblast because it is a type of stem cell; However, satellite cells are incorporated into muscle cells and facilitate the protein synthesis required for repair and growth |
|
|
Fibrosis |
A process in which muscle fibers are replaced by scar tissue if they cannot be repaired by satellite cells |
|
|
Pericyte |
A type of stem cell that smooth muscle can regenerate from (found in some small blood vessels) |

