![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Big Data
|
It is defined by the
- Volume - Variety - Velocity - Veracity - Variability - Value |
|
|
Architecture for Big Data Solutions
|
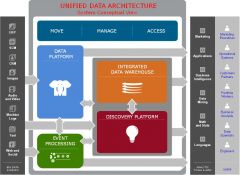
|
|
|
What slows BD initiatives
|
- Limitations of your current platform's processing power.
- Data sources does not comply with the data storage schema - Need the freshest data on the reporting - You want to work with a schema-on-demand data storage paradigm because of the variety of data types involved. - The data is arriving so fast at your organization’s doorstep that your traditional analytics platform cannot handle it. |
|
|
Critical Success Factors for BD Analytics
|
- A clear business need
- Strong, committed sponsorship - Alignment between the business and IT strategy - A fact-based decision-making culture - A strong data infrastructure - The right analytics tools - Right people with right skills |
|
|
BD Analytics Enablers
|
- In-memory analytics: Storing and processing the complete data set in RAM
- In-database analytics:Placing analytic procedures close to where data is stored - MPP:Use of many machines and processors in parallel (MPP - massively parallel processing) - Appliances:Combining hardware, software, and storage in a single unit for performance and scalability |
|
|
Challenges of DB Analytics
|
- Data volumeThe ability to capture, store, and process the huge volume of data in a timely manner
- Data integrationThe ability to combine data quickly and at reasonable cost - Processing capabilitiesThe ability to process the data quickly, as it is captured (i.e., stream analytics) - Data governance (… security, privacy, access)- Skill availability (… data scientist) - Solution cost (ROI) |
|
|
Business Problems Addressed by BD Analytics
|
- Business Process efficiency and cost reduction
- Brand managementRevenue maximization, cross-selling/up-selling - Enhanced customer experienceChurn identification, customer recruitingImproved customer service - Identifying new products and market opportunities - Risk management (especially banks and education) - Regulatory complianceEnhanced security capabilities |
|
|
MapReduce - Definition
|
MapReduce distributes the processing of very large multi-structured data files across a large cluster of ordinary machines/processors
|
|
|
MapReduce - Goal
|
Achieving high performance with “simple” computers usually running Windows or Linux.
|
|
|
MapReduce - Background
|
Developed and popularized by Google
Good at processing and analyzing large volumes of multi-structured data in a timely manner |
|
|
MapReduce - Sample Application
|
Indexing the Web for search, graph analysis, text analysis, machine learning
|
|
|
Hadoop - Definition
|
Hadoop is an open source framework for storing and analyzing massive amounts of distributed, unstructured data
|
|
|
Hadoop - Background
|
Originally created by Doug Cutting at Yahoo!
Hadoop is now part of Apache Software Foundation |
|
|
Hadoop -How it works
|
Hadoop clusters run on inexpensive commodity hardware so projects can scale-out inexpensively
|
|
|
How Does Hadoop Work?
|
- Access unstructured & semi-structured data
- Break data into “parts,” load them into a file system made up of multiple nodes running on commodity hardware using HDFS - Each “part” is replicated multiple times & loaded into the file system for replication & failsafe processing - node acts as the Facilitator & another as Job Tracker - Jobs distributed 2 clients, & once complete, results r collected using MapReduce |
|
|
Demystifying Hadoop
|
- Is about data diversity, not just data volume
- Hadoop complements a DW; it’s rarely a replacement - Hadoop enables many types of analytics, not just Web analytics |
|
|
HDFS, Hive and MapReduce Demystifying
|
- HDFS is a file system, not a DBMS
- Hive resembles SQL but is not standard SQL - MapReduce provides control for analytics, not analytics |
|
|
Data Scientist Skill
|
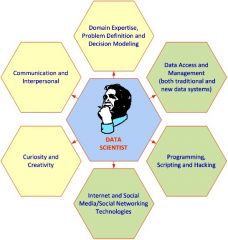
|
|
|
BD and DW
|
Big Data and RDBMS do not go nicely together
Will Hadoop replace DW/RDBMS? |
|
|
Use Cases for Hadoop
|
Hadoop as the repository and refinery
Hadoop as the active archive |
|
|
Use Cases for Data Warehousing
|
Data warehouse performance
Integrating data that provides business value Interactive BI tools |
|
|
When to Use Hadoop vs. DW
|

|
|
|
Big Data & Stream Analytics - Definition
|
Analytic process of extracting actionable information from continuously flowing/streaming data
|
|
|
Why Stream Analytics
|
It may not be feasible to store the data, or may lose its value
|
|
|
Stream Analytics Applications
|
- e-Commerce
- Telecommunication - Law Enforcement and Cyber Security - Power Industry - Financial Services - Health Services - Government |

