![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the commonly used method to measure hemoglobin?
(what do you convert it to, with what, how is is specifically measured) |
Lyse blood
add cyanide (heme --> metheme (Hi)--> HiCN) Measure absorbance (540 nm) |
|
|
What type of hemoglobin cannot be measured using the commonly used laboratory method?
|
Sulfhemoglobin (SHb)
nitrates, sulfonamides, sulfasalazine |
|
|
Y x Z = hematocrit
What are Y and Z? |
MCV and RBC
|
|
|
Hb/hct x 100 =?
|
MCHC
|
|
|
What gives reticulocytes their speckled look?
|
ribosomal RNA
|
|
|
How do the two chemical tests for detecting hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin work?
|
Acid buffer- HbA elutes, HbF stays --> check for persistence of color
alkali denaturation- HbF does not denature, HbA does. Measure resulting optical density |
|
|
For the purposes of interpreting Hb electrophoresis, what is the normal order of hemoglobins on cellulose from cathode to anode?
Citrate |
(-) I C S F A (+) pH = 8.6
(-) F A I S C (+) pH = 6.2 I = origin |
|
|
Where do all the "odd" hemoglobins (D, G, E, A2, M) travel in citrate agar?
What are the 2 major exceptions and where do they travel? |
They travel with A.
C harlem travels with S, O stays on the origin. |
|
|
Where do the "odd" hemoglobins (D, G, E, A2, M O, C harlem) travel in cellulose?
|
C - Vowels + C harlem
S - D, G, Lepore A- M |
|
|
Osteoblasts and plasma cells can appear similary; what is one characteristic that helps differentiate the two?
|
The nucleus of an osteoblast typically extends beyond the cell border
|
|
|
What disease show a Leukocyte Alkaline phasphatase score under 15?
|
CML
n= 40-120 |
|
|
What are the first two antigens, after CD34, Tdt and HLA-DR, to be expressed in B and T cells differentiating the two cell lines.
|
B cells - CD19 and CD10
T cells- CD2 and CD7 |
|
|
CD59 is normally expressed on what cells? Absence of CD59 is seen in what disorder?
|
Nearly all human cells
PNH (also CD55) |
|
|
The Ig heavy chain has 4 regions (VDJC); the kappa light chain and lambda light chain regions have 3. What region is not found?
|
D
|
|
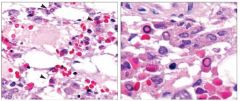
What is this?
|
Parvo virus inclusions.
|
|
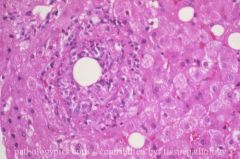
What is this?
|
A ring granuloma, seen in patients with Q fever from Rickettsial infection (Coxiella burnetii). This is non-specific. Also causes myelosuppression and hemophagocytosis.
|
|
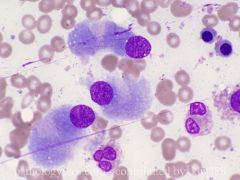
what is going on here?
|
These are osteoblasts. They appear similar to plasma cells, but are larger in size, and the nuclei may appear to "pop out" of the cytoplasm, rather than merely tethered to the side.
|
|
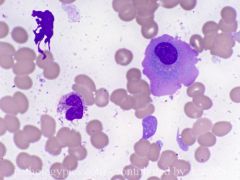
what is this cell and what is it associate with?
|
Flame cell. Flame cells are a morphologic variant of plasma cells associated with IgA myeloma.
|
|
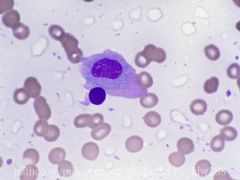
What is this cell and what is it associated with?
|
Flame cells are a morphologic variant of plasma cells associated with IgA myeloma.
|
|
|
In the cyanmethemoglobin method, what is the absorbence of the product (HiCN)?
|
540nm
|
|
|
Which of these hemoglobin types is not measured by cyanmethemoglobin method?
A. Hb-O2 B. Hb-CO C. Hb-S D. Hi |
C. Hb-S, more commonly written as SHb or sulfhemoglobin. Hi is methemoglobin.
|
|
|
What is a common interference when measuring Hb with cyanmethemoglobin method?
A. Hemolysis B. High WBC C. Cold agglutinins D. Clumped platelets |
B. This has something to do with turbidity??
|
|
|
What molecule is defective in hereditary spherocytosis?
Hereditary eliptocytosis? |
Ankyrin
Spectrin |
|
|
Which of the following does not produce stomatocytes?
A. Alcohol B. Phenothizine C. Rh null D. liver disease E. Uremia |
E. Uremia
|
|
|
How is G6PD tested for?
|
Measure NADPH levels at 340nm
|
|
|
Patients with PK deficiency show what RBC abnormality in the peripheral blood?
|
Burr cells
-also seen in Uremia and burns PK deficient patients have elevated levels of 2,3 DPG to compensate |
|
|
Name three diseases that show acanthocytes in the peripheral blood?
|
Mcleod
abetalipoproteinemia liver disease |
|
|
What hemoglobin should be present during fetal life but should disappear by age 6 mos?
|
Hemoglobin F (gamma-alpha)
|
|
|
What type of RBC is prominently seen in hemoglobin C disease?
|
Target cell
|
|
|
Gel with apparent hemoglobin S at 12%. What is this disease?
|
Hb Lepore. Clue is the 12%. Hemoglobin S is always higher.
S trait is 35-45%. |
|
|
How do you interpret a gel showing hemoglobin S between 25-35%?
|
Combined alpha thalassemia and hb S. Normal S trait is 35-45%
|
|
|
How do you interpret a gel showing hemoglobin S between 50-80%?
|
Likely S - b thalassemia.
Normal S trait is 35-45% Normal SS is >80% |
|
|
Since E and C run together on gel, how can one easily determine when dealing with a hemoglobin E?
|
Hemoglobin E shows thalassemic indices.
|
|
|
Both the pulse oximetry and arterial blood gas analyzer will show a normal O2 sat in a patient with what kind of Hb problem?
|
HbCO
1/2 life in room are = 6 hours 1/2 life on 100% O2 = 1 hour Methemoglobin (Hi) will show a pulse oximetry aroudn 85% This real level vs. measured level is the 02 saturation gap. A Co-oximeter should be used to measure these when suspected. |
|
|
Zone 1 PAS positive globules in the liver but not alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency. What is it?
|
Afibrinoginemia
|
|
|
What is Hb barts and when is it seen?
|
gamma tetramers that are formed in utero in patients with alpha thalassemia
|
|
|
What is Hb H and when is it seen?
|
Beta tetramers that are formed after birth in patients with alpha thalassemia
|
|
|
A2 levels are increased in patients with beta thalasemmia except in what senerio?
|
In a beta thal. patient with iron deficiency.
|
|
|
What is the "normal" MCV in a patient with alpha thal?
beta thal? |
Alpha = 65-75
Beta= 55-65 Note: There is also RBC > 5.5 Also, to differentiate form iron def. anemia. Iron def. shows increased RDW. |
|
|
What does alpha thalasemmia look like on gel or HPLC?
Beta thal? |
Alpha thal looks normal
Beta shows increased A2 and F (unless iron def.) |
|
|
What is hb CS (constant spring)?
|
extra long alpha gene due to mutation in stop codon.
This results in 4 bands in the cellulose gel in adults (6 in kids) |
|
|
Which organ is spared in type 1 Gaucher's disease?
|
The brain (CNS) is not affected in type 1 Gaucher's.
|
|
|
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria is caused by an antibody to what antigen?
Cold agglutinin disease antigen? |
Anti-P
Anti I, Anti i, or anti H |
|
|
What is the most common cause of cryoglobulinemia?
|
HCV
This is type 2 (mixed) cryoglobulinemia |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria and how do you test for PCH?
|
Viruses. It used to be syphilis
Test with Donath-Landsteiner test |
|
|
What is the peripheral blood finding in a patient with paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria PCH?
|
Neutrophils eating RBCs
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of PNH?
What other disease also shows a Decreased LAP score |
Clone of RBC's with mutation in PIG-A (which encodes GPI protein). Cell can't turn of complement resulting in intravascular hemolysis. Associated with aplastic anemia
LAP score is low; also seen in CML |
|
|
How is PNH diagnosed?
|
Sucrose hemolysis test- incubate serum with sucrose and check for hemolysis due to complement binding
Ham's test- acidify serum (activating complement) and look for lysis (in BOTH autologous and heterologous sera) vs. congenital dyserythropoietic anemia where autologous lysis does not occur (lysis in patients own serum). Decreased CD55 and CD59 on monocytes |
|
|
What is congenital dyserythropoietic anemia?
|
Has high density of i and I antigens
Positive HAM test (acidified serum) except only with another persons serum. |
|
|
Most common cause of neutropenia?
|
Drugs
|

