![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define: Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
-deficiency of? -presents with? -Dx made with? -tx? |
21-hydroxylase deficiency that leads to
1) ambiguous genitalia 2) hyperandrogenism (excess sex steroids) 3) salt wasting --> hyperkalemia / hypotension (no Aldosterone) Dx: 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone, decreased serum cortisol ---> *all steroid precursors (cortisol, aldo) are being shunted into sex hormones!* tx: cortisol, this will inhibit ACTH release and stop the adrenal gland from producing more sex steroids |
|
|
Labial fusion is most commonly associated with?
-2 common causes |
excess androgens
mcc: *exogenous androgen exposure* mcc inborn: *21 hydroxylase deficiency* leading to *Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia* |
|
|
Define: imperforate hymen
|
-obstruction of outflow tract of reproduction system, leads to buildup of vaginal secretions
|
|
|
Define: transverse vaginal septum
|
improper canalization of the mullerian tubercle
-- the mullerian tubercle is the junction point between the mullerian system (upper vagina) and the sinovaginal bulb/UG sinus (lower vagina) the result is a stretch of skin that goes across the vaginal canal tx: surgery |
|
|
Define: vaginal atresia
|
agenesis of lower vagina
-ovaries, uterus, cervix, upper vagina are normal but UG sinus fails to contribute to lower portion |
|
|
Primary amennorhea could be a number of benign gyn disorders, including
|
vaginal atresia
imperforate hymen transverse vaginal septum |
|
|
Define: Lichen Sclerosis
|
benign epithelial disorder of the vulva. no mech known. associated with labial fusion and contracture and shrinkage and thin white epithelium.
|
|
|
Define: Squamous Cell Hyperplasia AKA Atopic Eczema
|
Benign epithelial disorder due to scratching and rubbing 2/2 vulvar irritation. hyperkeratosis. raised white lesions
|
|
|
Define: Lichen Planus
|
Eruption of purple, pruritic, papules with *white straie on mucosal membrane surfaces*
|
|
|
Define: vulvar psoriasis
|
Seborrheic dermatitis --- inflammation of areas w/ sebaceous glands. red, moist.
|
|
|
Define: Lichen simplex chronicus
|
inflammatory process 2/2 to reactive changes (scratching and rubbing)
|
|
|
Define: Vaginal Adenosis
|
Benign lesion of the vaginal mucosa. Associated with DES exposure in utero. spots are palpable.
|
|
|
How are benign epithelial vaginal/vulvar disorders diagnosed?
|
histologically - so do biopsies!
|
|
|
Tx for benign epithelial disorders of vag/vulva?
|
Topical steroids
|
|
|
most common cause of vulvular tumors?
-type -what is the definition? |
epidermal inclusion cysts
occluded pilosebaceous duct/ blocked hair follicle |
|
|
Where is skene's gland located?
|
skene's glands are located next to the urethral meatus.
|
|
|
Where are bartholin's glands located?
|
"4 and 8 oclock" on the posterior aspect of the vaginal orifice. mucus secreting glands.
|
|
|
What are Gartner's Ducts?
|
Gartner's Duct can encyst..they are remnants of the mesonephric ducts of the Wolffian system (degenerated in females). Found anterolaterally in vagina.
|
|
|
Name 3 types of benign solid tumors of the vulva/vagina
|
1) lipoma: mature fat cells
2) hemangioma: most will bleed w/ trauma 3) urethral caruncles: small fleshy tumors at distal uretrhal meatus |
|
|
how do you treat benign solid tumors of vulva?
|
no need to treat because asymptomatic
|
|
|
A dilated retention cyst on the cervix is called...
-name -cause? -sx? |
...a *nabothian cyst*
-caused by blockage of endocervical glands -asx! |
|
|
Define: Cervical polyp
-defintion -sx -tx |
benign growth of the cervix.
sx:asx generally, but can be associated with intermenstrual spotting tx: removed because they can mask other irregular bleeding |
|
|
Define: Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome
|
Vaginal agenesis in genetic females. normal ovarian function. normal secondary sex characteristics.
|
|
|
tx for cysts?
|
typically only if needed - if they become infected or symptomatic. if so you, you do an incision and drainage.
|
|
|
Define: Hidradenitis supparativa
|
result of abscess formation from superinfection of apocrine sweat glands and cysts
|
|
|
What is the instrument used to treat an infected, large bartholin's cyst?
|
A word catheter
|
|
|
Name the parts of the reproductive system derived from the mullerian system (paramesonpehric ducts)
name 2 exceptions |
-superior vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes
-exceptions: lower vagina, ovaries |
|
|
The rate of uterine anomalies increasing can be attributed to what?
|
DES exposure in utero. it's very rare otherwise. DES exposure increases the chance of mullerian abnormalities
|
|
|
Define: septate uterus
-definition -assocaited w/? |
collagenous, fibrous septum that usually extends vertically downwards from the to pf the uterus
associated with pregnancy loss b/c often the septum of the uterus doesn't have an adequate blood supply to keep pregnancy going |
|
|
What are the differences btw/ septate uterus and bicornuate uterus w/r/t/ mechanism of pregnancy loss?
-mechanism -differential presentations |
bicornuate uterus: limited by *size* of uterine horn, rather than blood supply, which is the limiting factor for septated uteri.
-so...bicornuate nuclues leads to 2nd trimester pregnancy loss and PTL, whereas septated uterus leads to 1st term pregnancy loss |
|
|
What is the difference between unicornuate, bicornuate, and didelphys uteri?
|
Unicornuate: only connects to one tube
Bicornuate: connects to both tubes, but the two ends connect to themselves very low down in the uterus Didelphys: both fallopian tubes have uterine attachments/connections, but they never fuse and thus there are two separate openings to the vagina |
|
|
How are kidney and uterine anomalies related?
|
the mullerian system is responsible for both their developments, so a defect in this system can produce:
-renal agenesis -rudimentary fallopian tube -unicornuate (on the other side) uterus) |
|
|
Tx: Uterine anomalies?
|
most require none
|
|
|
Define: Uterine Leiomyoma
|
Fibroids! Benign proliferations of smooth muscle cells of the myometrium that occur in women of childbearing age and regress during menopause.
|
|
|
the most common indication for surgery for women in the US is?
|
fibroids
|
|
|
What are the three types of fibroids?'
-most common type? |
-submucosal (beneath endometrium)
-intramural (muscular wall)* most common -subserosal (beneath uterine serosa) |
|
|
define: parasitic leiomyoma
|
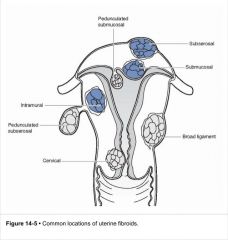
pedunculated fibroid that attaches to pelvic viscera an develops its own blood supply
|
|
|
Discuss the risk of getting fibroids
-overall risk -racial differences |
overall risk: 30% of american women
50% of african american women, with larger fibroids, heavier bleeding, and more severe anemia |
|
|
effect of smoking on endometrial cancer risk?
|
actually decreases it...
|
|
|
most common symptom of fibroids?
|
abnormal uterine bleeding
|
|
|
a woman in her late 30's presents with dysmenorrhea, pelvic pressure and bloating, and abnormal uterine bleeding. she has been unable to become pregnant. also, her periods are longer and heavier than usual. what is this, probably?
|
fibroids!
|
|
|
define: dysfunctional uterine bleeding
|
abnormal bleeding that is due to changes in hormone levels
|
|
|
List the Ddx for abnormal uterine bleeding
|
-fibroids
-adenomyosis -endometrial polyps -endometrial hyperplasia -endometrial cancer -dysfunctional uterin bleeding |
|
|
List the Ddx for pelvic mass/uterine enlargement
|
-fibroids (leiomyoma)
-pregnancy -leiomyosarcoma -ovarian cyst/cancer -fallopian tube abscess -adenomyosis - |
|
|
Estrogen makes fibroids ____, which is why ______ therapies are used to treat them by effectively __________
|
grow
GnRH agonist or progesterone decreasing circulating estrogen levels |
|
|
Describe: Uterine Artery Embolization
|
treatment method for symptomatic fibroids
|
|
|
What are some treatment options for fibroids
|
-myomectomy: for pts who want to remain fertile
-medical therapy -high intensity ultrasound -hysterectomy -expectant management |
|
|
define: endometrial polyp
|
overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma
|
|
|
define: metrorrhagia
|
bleeding between periods
|
|
|
What is the cause of endometrial hyperplasia?
-cause -symptoms |
-cause is continuous endogenous (peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens by aromatase in adipocytes) or exogenous (hormone replacement) estrogen stimulation without progesterone
-symptoms: *common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding* |
|
|
What is the Penny, nickel, dime, quarter rule?
|
progression of endometrial hyperplasia to endometrial cancer
simple- 1% complex 5% simple w/ atypia 10% complex w/ atypla 25% |
|
|
Define: simple vs. complex hyperplasia
|
simple: proliferation of glands and stroma
complex: proliferation of just the glands, with crowding |
|
|
a patient with long periods of oligomenorrhea followed by irregular/excessive uterine bleeding in a postmenopausal women is highly suspicious for?
|
endometrial hyperplasia/carcinoma
|
|
|
How does one dx endometrial hyperplasia?
|
EMB
|
|
|
Typical treament of endometrial hyperplasia includes?
|
progesterone therapy, whihc reverses the hyperplasia by inducing stromal decidualization and a thinning of the endometrium.
|
|
|
Define: Functional ovarian cyst
|
an ovarian mass that derives from normal physiologic fxning of the ovaries (as opposed to neoplastic growth)
|
|
|
Define: follicular cyst
|
most common type of ovarian cyst. arise after failure of follicle to rupture during follicular maturation phase.
|
|
|
Define: Corpus luteum cyst
|
occur during luteal phase of menstrual cycle. formed when corpus luteum fails to regress after 14 days, and becomes enlarged and/or hemorrhagic
|
|
|
Define: theca lutein cyst
|
large bilateral cysts filled with fluid that result from stimulation by abnormally high beta-HCG (from molar pregnancy/choriocarcinoma)
|
|
|
What is the Ddx for ovarian cysts?
|
ectopic pregnancy
PID torsed adnexa tuboovarian abscess endometriosis fibroids ovarian neoplasm |
|
|
you palpate an ovarian/adnexal mass suggestive of an ovarian neoplasm. next step?
|
investiage w/ exploratory laparoscopy
|
|
|
cysts that don't spontaneously resolve 60-90 days after (like most do) require...?
|
cysteoctomy, oophorectomy via laparoscope
|

