![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between deoxyribose and ribose?
|
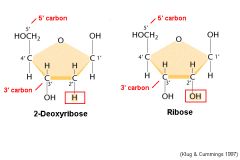
Replacement of the hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon with a hydrogen atom
|
|
|
Generic purine.
|
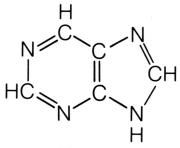
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Generic pyrimidine.
|
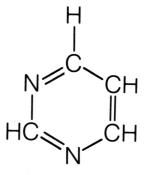
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Adenine.
|
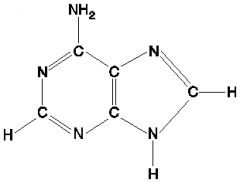
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Cytosine.
|
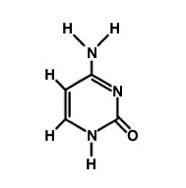
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Guanine.
|
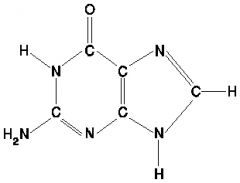
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Thymine.
|
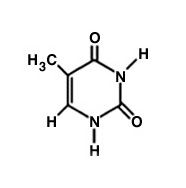
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
Uracil.
|
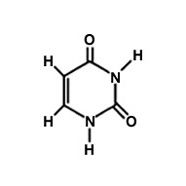
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
What is the difference between thymine and uracil?
|
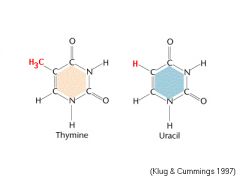
Thymine has an extra methyl group in place of a hydrogen.
|
|
|
Uracil.
|
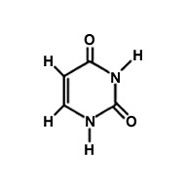
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
What is an anomeric carbon?
|
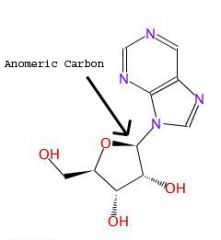
The anomeric carbon is the location of the glycosidic bond.
|
|
|
How are carbons numbered in a nucleoside?
|
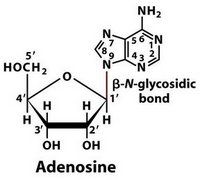
The carbon and nitrogen participating in the glycosidic bond are both 1'.
|
|
|
What is a generic description of all of the nitrogenous bases?
|
Heterocyclic aromatic bases
|
|
|
A nucleoside.
|
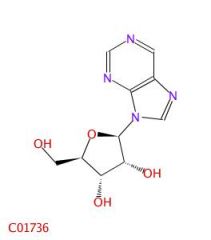
What is this molecule?
|
|
|
What is a nucleoside?
|
A nitrogenous base bonded to a sugar.
|
|
|
What are the names of the nucleosides?
|
Cytodine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine.
|
|
|
Phosphoester bond.
|
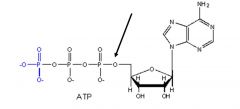
What type of bond is this?
|
|
|
How are phosphate groups labeled in a NTP?
|
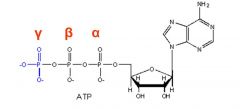
Phosphates are labeled using Greek letters beginning at the 5' end of the sugar.
|
|
|
Pyrophosphate bond.
|
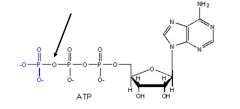
What type of bond is this?
|
|
|
What is ATP used for?
|
General metabolism.
|
|
|
What is GTP used for?
|
Protein synthesis.
|
|
|
What is CTP used for?
|
Phospholipid biosynthesis.
|
|
|
What is UTP used for?
|
Carbohydrate biosynthesis.
|
|
|
Phosphodiester bonds.
|
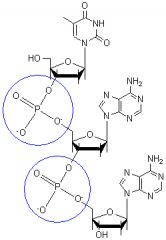
What type of bonds are these?
|
|
|
Linking sugars in a RNA or DNA backbone.
|
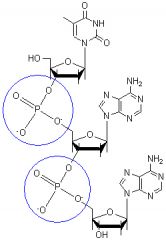
Where would you find these types of bonds?
|
|
|
In which direction are bases generally listed?
|
5' to 3'.
|
|
|
How many hydrogen bonds do adenine and thymine form?
|
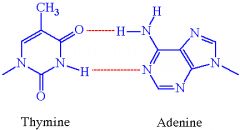
2
|
|
|
How many bonds to cytosine and guanine form?
|
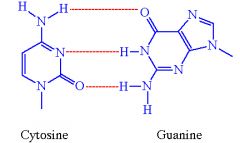
3
|
|
|
The minor groove.
|
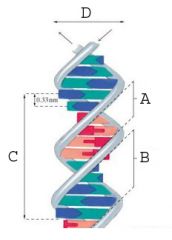
What is A called?
|
|
|
The major groove.
|
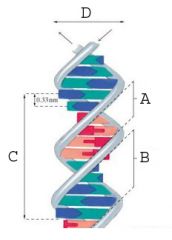
What is B called?
|
|
|
35.7 A
|

What is the measurement of the area marked "C" (full turn of DNA)?
|
|
|
20 A
|
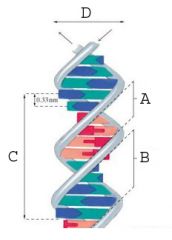
What is the measurement of the area marked "D" (diameter of DNA)?
|
|
|
What is the twist angle of DNA?
|
34.3 degrees per turn.
|
|
|
What is the number of base pairs per turn of a molecule of DNA?
|
10.5 bp per turn
|
|
|
What are the major forces stabilizing nucleic acid helices?
|
Hydrophobic effects (non-polar bases forced to center, polar sugar-phosphates outward) and base stacking interactions (bases stacked at Van der Waals contact distance).
|
|
|
What factors affect helix stability?
|
Hydrophobic effects (base non-polar/backbone polar), base stacking (Van der Waals), hydrogen bonds (purine/pyrimidine), ionic interactions (cations shield neg. charged phosphate groups), sugar phosphate chain constraints (angles of backbone).
|

