![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
|
Anti-RBC
Triad: Warm-- severe anemia, splenomegaly, high MCHC cold- anemia, raynauds, acrocyanosis |
|
|
Bullous Pemphigoid
|
Anti-epidermal basement membrane
Triad: Bullae, pruritis, elderly |
|
|
Type I DM (insulin dependent DM)
|
Anti-islet cell (beta cell)
Triad: Hyperglycemia, DKA risk [in a stage of no insulin because there is no inhibitory reponse to hormone senstiive lipase-which makes FA-> Ketone bodies when in excess], infections later you see: retinopathy, nephropathy, and atherosclerosis |
|
|
Pempigus
|
Anti-Keratinocyte Junction--loosens up tight junctions
Triad: Nikolsky's sign (light brush can rub skin off), oral and skin erosions, older |
|
|
Pernicious anemia
|
Anti-IF, anti- patietal cell
Triad: Megaloblastic anemia, gastritis (chronic type A), vitamin B12 deficiency |
|
|
Microscopic Polyangitis (in capillaries)
|
P-ANCA (peri-nuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasm)
Triad: Hemopytsis, hematuria, palpable purpura (with glomerulonephritis) |
|
|
Polymyositis
|
Speckled ANA (anti-nuclear antibody) 20% also have anti-jo-1
Triad: proximal muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, elevated myoglobin |
|
|
Progressive Systemic sclerosis (PSS: scleroderma)
|
Anti-scl 70
Triad: Visceral organ fibrosis, facial tightening, sclerodacyly |
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome
|
Anti- SS A (anti-RO) and anti- SS B (anti-La)
Triad: Xerostomia (dry mouth), keratoconjuctivitis sicca, arthritis |
|
|
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (adult form)
***childhood one is not autoimmune *** |
Anti-structural platelet
Triad: thrombocytopenia, Petechiae, and purpura, muscosal bleeding |
|
|
Vitiligo
|
Anti-melanocyte
Triad: hypopigmented area of skin, white hair in areas of affected skin, sun burns Think creula from 101 dalmations |
|
|
polyarteritis nodosa (medium sized blood vessels effected(
|
Tetrad: fever, hypertension, abdominal pain, and renal disease (without glomerulonephritis)
|
|
|
Rhematoid Arthritis
|
Anti- IgG (rheumatoid factor)
4/7 to diagnose: Morning stiffness > 1 hr , Arthritis in 3 or more joints simultanously, Arthritis in hand joints, symmetrical arthritis, rheumatoid nodules, Serum rheumatoid factor (anti-IgG), Erosions or bony decalcification on x-ray |
|
|
SLE
|
Anti- nuclear antibodies (ANA) for screening; Anti-ds DNA for confirmation
Triad: Malar rash (butterfly), lupus nephropathy, arthritis |
|
|
Drug- induced lupus
(hydralazine and procanomide) |
Anti-histone
Triad: Arthralagia, fever, serositis |
|
|
CREST
*** |
Anti-centromere
PENTAD: calcinosis, Raynauds, esophageal dymotilty, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia (small dilated BV near surface of skin) |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis
|
Anti- Ach receptor
post use episodic muscle weakness, ptosis, thymus gland pathologies |
|
|
Grave's disease
|
Anti-TSH receptor
Triad: symtomatic hyperthyroidism, exopthalmos, pretibial myxedema (non-pitting edema) |
|
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
Anti-microsomal
Triad: Nontender goiter, typically female, hypothyroidism (which becomes symptomatic) |
|
|
Wegener's granulomatosis
|
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm (ANCA)
Triad: sinusitis, glomerulonephritis, lung lesions (cavitary) |
|
|
Celiac Sprue
|
Anti-Gliadin
Triad: malabsorption (ofte with diarrhea), dermatitis herpetiformis, short stature |
|
|
Good Pasture's syndrome
|
Anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM)
Triad: severe glomerulonephritis, pulmonary hemorrahage, dyspnea |
|
|
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
|
Anti- Mitochondrial
Triad: pruritis (after hot showers and sleep), female, jaundice |
|
|
amyloid-beta protein is deposited where and what does it cause?
|
produced by a gene located on chrosome 21 and deposits in brain to cause Alzheimer's disease
|
|
|
What is always a beta-pleated sheet of protein?
|
Amyloid
|
|
|
amyloid light chain (AL) is associated with what?
What about amyloid associated protein or AA |
multiple myeloma and waldenstorms
chronic inflammation and aging |
|
|
Allergens: pollen, insect venom, animal dander
examples: allergic rhinitis, eczema, hives , allergic gastroenteopathy, ASTHMA, systemic anahylaxis |
Type I hypersenstivity
Ig-E mediated ; usually 2nd exposure is the problem due to pre-formed Ab |
|
|
Blood antigens during transfusions, the Rh factor issue, quinine, hydralazine, infectious agents and MOLECULAR MIMICRY, autoimmunity
examples: ABO transfusions, erythroblastosis fetalis, rhematic fever......AUTOIMMUNE diseases |
Type II hypersensitivity
antibody-mediated cytotoxicity |
|
|
Erythroblastosis fetalis
|
Mom rh - , fetus rh+ --- delivery and blood mixture---mom develops antibodies against rh.
second preganancy...mom now has Rh + antibodies and ofcourse IgG ones.. so those through placenta and mess up the fetus's RBC, which was sadly Rh + |
|
|
Drugs (penicillin) VACCINES, inhaled antigens such as fungus
examples: Arthus reaction, SERUM SICKNESS, Post- strep glomerulonephritis, rheumatoid arthritis, SLE |
Type III hypersenstivity
immune complex depostions |
|
|
What is the culprit for the sequale of not treating a strep throat?
|
Our body makes antibodoes towards it which deposit in the heart (which looks our mouth apparently) and you get Acute rheumatic fever.
|
|
|
Delated type: poison ivy, mycobacterial infection, transplanted tissue, T cell medaited cytoxicity and macrocphages involved
examples: contact dermatitis, acute graft rejection, positive PPD test, TB, viral infections, neoplasia, tuberculoid leprosy |
Type IV hypersentivity
Cell- mediated Granulomas are type IV that never ended. |
|
|
Prefomed antibodies bind to antigen on tissue that was transplanted. Withing minutes ot hours.
|
Hyperacute rejection
Type II hypersensitivty |
|
|
Memory T cells recognize antigen; CD8 destro graft. Takes days to months
|
Acute rejection
Type IV (T cell mediated) |
|
|
Antibodies develop over time and damage graft vasculature; months to years
|
Chronic rejection
Type II and III hypersensitivity |
|
|
T cells in transplanted tissue attach host; days to weeks
|
Graft vs Host
Type IV (T- cell mediated ) |
|
|
c-myc- 1
|
Burkitt's lymphoma
|
|
|
c-abl
|
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
|
|
|
ras
|
colon carcinoma
|
|
|
BRCA-1
|
breast and ovarain cancer
|
|
|
p53
|
breast, colon, and lung carcinoma
|
|
|
tumor marker for adenocarcinomas
|
CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen
|
|
|
Alpha-fetoprotein
other uses? |
hepatocellular carcinoma
used for screening of fetus. If high means nueral tube defects or twins/triplets. If low means downs |
|
|
PSA and acid phosphatase
|
Prostate cancer.
PSA is also for screening of prostate cancer |
|
|
Alkaline phosphatase
|
diagnose non-neoplastic diseases as well.
produced normally in bone, kidney, placenta **, biliary system |
|
|
5` HIAA (5`-hydroxyindole acetic acid)
|
Carcinoid
|
|
|
CA-19-9
|
COLON, pancreatic, or breast CA
|
|
|
CA-125
|
Ovarian cancer
|
|
|
CD-25
|
hairy cell leukemia, adult T cell leukemia
|
|
|
CD-30
|
hodgkin's disease
|
|
|
neuron- specific enolase
|
small cell lung ca, neuroblastoma
|
|
|
B-hcG
|
prego, gestational trophoblastic disease, choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
Metastasis
|
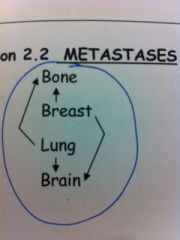
Breast --- to bone and brain
Lung--- to brain and bone Bone---to breast and lung Brain---to lung and breast |
|
|
hypophosphatemic rickets and incontinetia pigmenti have what type of inheritance
|
X-linked dominant
|
|
|
Leber's optic neuropatgy (bilateral blindness) can occur at any age in people who have this inherited disease. What is the inheritance pattern?
|
Mitochondrial inheritance
From mother to kids |
|
|
clinical findings: meconium ileus, viscous mucus, recurrent respiratory infections, postiive sweat test, chronic pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, malnutrition
|
Cystic fibrosis: mutation in CFTR gene
Autosomal recessive |
|
|
Unable to metabolize phenylalanine causing a buildup. Inability to make melanin, NE and dopamine
|
Phenylketonuria
mutation in phenylalanine hydroxylase autosomal recessive |
|
|
Inability to make melanin
|
Albinism.
Mutation of the tyrosinase enzyme Autosomal recessive |
|
|
alpha 1-antitypsin deficiency causes what?
|
inability to inhibit elastase (breaks down elastin).
You get destruction of lung, resulting in emphysema because lung looses elastic recoil |
|
|
Metabolic diseases usually have what inheritance pattern?
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
Thalassemia, inheritance pattern?
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
Von Gierke , pompe. MdArdle diseases are examples of what?
|
Glycogen storage disease.
inabability to utlitize glycogen normally. |
|
|
with what two diseases you see hypoglycemia during meals?
|
Von Gierke and pompe
|
|
|
unable to metabolize glycosaminoglycans; critical component of CT tissue is what type of disease?
--mental retardation and corneal clouding Give some examples |
lysosomal storage disease
examples: Hurler, Scheie, Hunter (X-linked recessive) others are autosomal recessive |
|
|
inability to metabolize sphingolipids, molecules involved in myelin and the CNS is what?
examples? |
sphingolipidoses
Major types: Niemann picks, Gaucher's, Krabbe's, Tay- Sachs, Metochrimatic dystrophy, Fabry (x-linked recessive) |

