![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an agonist? |
Enhance the activity of a neurotransmitter |
|
|
What is an antagonist? |
Reduces the activity of a neurotransmitter |
|
|
Increasing activity does not equal |
EPSP |
|
|
Reducing activity does not equal |
IPSP |
|
|
What is a double blind experiment? |
neither participant nor researcher are aware of treatment groups |
|
|
Withdrawal |
occurs when a substance is reduced or discontinued
withdrawal is the complement to the drug's effect
due to tolerance adaptations
not all drugs associated with withdrawal |
|
|
tolerance |
decrease in the response to a drug over time
metabolic tolerance: changes in metabolic enzymes (ALDH levels increased in drinkers)
cellular tolerance: changes in brain cells (decreased receptor density)
learned tolerance: changes in behavior (alcohol use and beam walking in rats; heroine users and overdosing) |
|
|
The Autonomic Nervous System |
1) Sympathetic Nervous System
2) Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|
|
Sympathetic Nervous System |
arouses body for action
fight or flight response
i.e. mugger in the alley |
|
|
Parasympathetic Nervous System |
rest and digest response
opposes the sympathetic response
i.e. Thanksgiving dinner |
|
|
Basic Divisions of the CNS |
The Spinal Chord
The Brain |
|
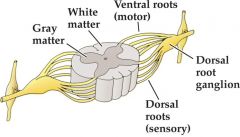
The Spinal Chord |
superhighway
dorsal portion = sensory info; body to brain
ventral portion = motor info; brain to body
spinal reflexes = can act independently of the brain |
|
|
The Brain |
the hindbrain
the midbrain
the forebrain |
|
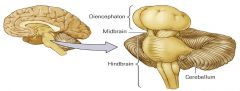
the hindbrain |
medulla
cerebellum
pons |
|
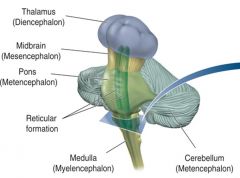
the medulla |
contains several nuclei
controls vital functions (breathing, heart rate, why snapping someone's neck can be fatal)
oldest part of the brain |
|
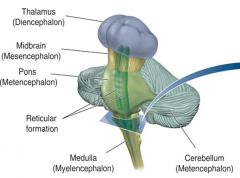
the cerebellum |
little brain (but contains the most neurons)
role in movement (coordinates voluntary movements; maintains muscle tone; regulates balance)
cognitive role?
i.e. sobriety tests |
|
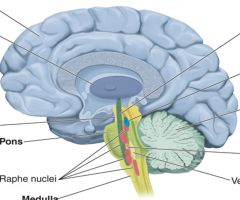
the pons |
bridge
connects the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
contains several nuclei (raphe nuclei = serotonin cell bodies) (locus coeruleus = norephinephrine cell bodies) |
|
|
the midbrain |
tectum
tegmentum |
|
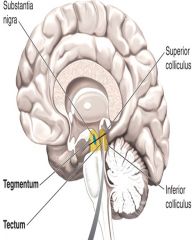
the tectum |
the roof
involved in orienting movements to stimuli (for vision: super colliculi) (for sound: inferior colliculi) |
|
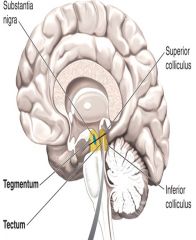
the tegmentum |
the floor
contains numerous nuclei (substantia nigra = dopamine) (ventral tegmental area = dopamine) |
|
|
the forebrain |
diencephalon (hypothalamus; thalamus)
telencephalon (basal ganglia; limbic system; cortex) |
|
|
diencephalon |
hypothalamus
thalamus |
|
|
telencephalon |
basal ganglia
limbic system
cortex |
|
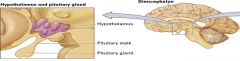
the hypothalamus |
directs the autonomic nervous system
contains regulatory centers for (eating, drinking, sexual behavior, sleep, temperature)
direct link with blood supply via the pituitary gland |
|
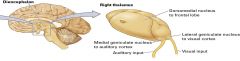
the thalamus |
contains several nuclei
the brain's greyhound station
director of sensory information (most sensory information stops here, filters information, integrates information) |
|
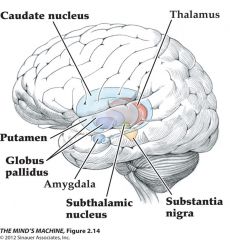
the basal ganglia |
contains several nuclei (caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus)
involved in the planning and execution of voluntary movement (dysfunctional in Parkinson's disease)
important for procedural memory (piano playing) |
|
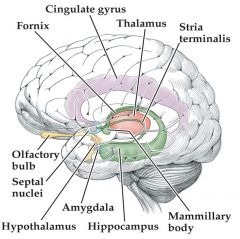
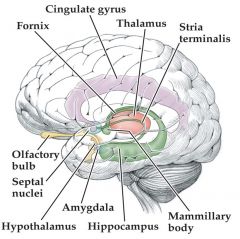
the limbic system |
paleocortex (3-4 layers) and nuclei
contains numerous structures
involved in controlling emotions and in learning and memory (amygdala=emotion, fear) (hippocampus = learning and memory) |
|
|
the cerebral cortex |
neocortex (6 layers)
involved in sensation and movement (sensory cortices, motor cortices, association cortices)
involved in higher order processing (prefrontal cortex) |
|
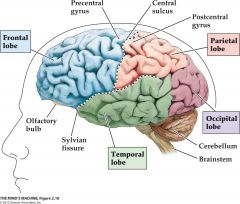
4 lobes of the cerebral cortex |
frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal |
|
|
grey matter |
cell bodies |
|
|
white matter |
cell fibers |
|
|
superior colliculi |
involved in orienting movements to visual stimuli |
|
|
inferior colliculi |
involved in orienting movements to sound stimuli |
|
|
structures of the limbic system |
|

