![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Watt's steam engine
|
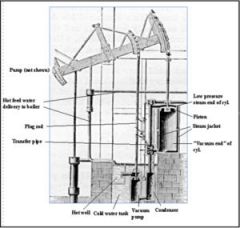
engines that burned coal to power boilers where steam was generated allowing the pressure to turn wheels and power machines
|
|

Luddites
|
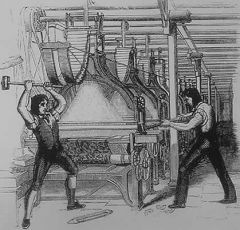
Luddites were displaced craftsmen who held violent protests and destroyed machines at night. The English government hung fourteen of them in 1813.
|
|
|
Capitalism
|
An economic system with origins in early modern Europe in which private parties make their goods and services available on a free market
|
|

Eli Whitney
|

inventor of the cotton gin
|
|
|
monopolies, trusts, cartels
|
Attempts to eliminate all other competitors by vertical organization ie. they purchased companies that fed into and out of their prime business or horizontal integration in which the owner of one company purchased all other competitors
|
|
|
demographic transition
|
fertility rates began to drop leading to a slower population increase as countries industrialized
|
|
|
utopian socialists
|
socialists that believed it was possible to construct a factory system out of a model community with non inequities
|
|

Count Sergei Witte
|

finance minister who promoted industrialization in Russia
|
|
|
factory system
|
system of specialized new machines requiring a new form of industrial organization in which each laborer produced one component of a final work
|
|

Adam Smith
|

writer of The Wealth of Nations and advocate of an individually focused free-market system in which labor is highly divided to increase prosperity and productivity
|
|

Josiah Wedgewood
|

potter, advocate of social reform, and factory owner who built villages next to factories to promote good living conditions of workers
|
|
|
corporation
|
joint-stock companies that were developed to fund new industries
|
|
|
Crystal Palace Exhibition
|
first exhibition taking place in London that showed displays from many industrialized nations with the point of showing nations' superiority in technology and economics
|
|

Thomas Malthus
|

English economist best known for theories on population growth (the high rate of population growth would eventually become unsustainable)
|
|
|
The Communist Manifesto
|
written by Freidrich Engels and Karl Marx advocating the abolition of private property and the capitalist system
|
|
|
Zaibatsu
|
large industrial business resulting from business sold from the government to private businessmen
|
|

Henry Ford
|

added the idea of an assembly line to automobile production;conveyor belts brought the parts to the workers and the car was assembled as it moved down the line
|
|
|
Agricultural density
|
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
|
|
|
Agricultural revolution
|
Time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering
|
|
|
Arithmetic density
|
total number of people divided by total land area
|
|
|
Census
|
A complete enumeration of a population
|
|
|
Crude birth rate
|
the total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people
|
|
|
Crude death rate
|
the total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people
|
|
|
Demographic transition
|
The process of change in country population that takes place in four stages: Low growth, high growth, moderate growth, and low growth again
|
|
|
Demography
|
the scientific study of population characteristics
|
|
|
Dependency ratio
|
the number of people who are too young or too old to work compared to the number of people in their productive years
|
|
|
Doubling time
|
the amount of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase
|
|
|
Epidemiologic transition
|
Distinctive causes of death in each stage of demographic transition
|
|
|
Epidemiology
|
Branch of medical science concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases that affect large numbers of people
|
|
|
Ecumene
|
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement
|
|
|
Industrial Revolution
|
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods
|
|
|
Infant mortality rate
|
the total number of deaths in a year among infants under one year old for every 1,000 live births in a society
|
|
|
Life expectancy
|
the average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions.
|
|
|
Medical Revolution
|
Medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to the poorer countries of Latin America, Asia and Africa. Improved practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death.
|
|
|
Natural increase rate
|
the percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate
|
|
|
Overpopulation
|

the number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living
|
|
|
Pandemic
|
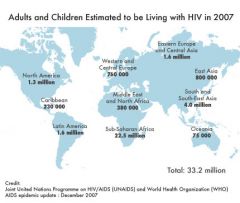
Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population
|
|
|
Physiological density
|
the number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture
|
|
|
Population pyramid
|
a bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex
|
|
|
Sex ratio
|
the number of males per 100 females in the population
|
|
|
Total fertility rate
|
the average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years
|
|
|
Zero population growth
|
a decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero
|

