![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Muhammad Ali
|

took control of Egypt with his European-modeled army after Napoleon attempted to defeat and hold Egypt
|
|

Napoleon
|

absolute leader of France who conquered most of Europe and was defeated in 1815
|
|
|
Capitulations
|
treaties between nations Ex. Ottoman Empire Capitulations were contracts between the Ottoman Empire and European nations
|
|

Mahmud II
|

Only relative of Sultan Selim III not to be assassinated by the Janissaries. Attempted to institute reforms but couched them in traditional terms leading to another revolt by the Janissaries. He massacred them to end revolt. Also known for European-modeled military, institution of postal, telegraph systems, and ministry-divided government.
|
|
|
Young Ottomans
|
nationalistic group that favoured converting the Turkish-dominated multinational Ottoman Empire into a more purely Turkish state and called for the creation of a constitutional government
|
|
|
Constitution of 1876
|
the first Ottoman constitution and the first in any Islamic country. It was derived from the will of the ruler, who retained their executive power . Ministers were responsible to him.Set rights of rulers and ruled.
|
|

Alexander III
|

became czar after the assassination of Alexander II. Criticized attempts at political reform
|
|
|
Crimean War
|
War between Russia, Turkey, Great Britain, France,and Piedmont-Sardinia lasting from 1853-1856. It was fought in the Crimea, Asia Minor, the Baltic, the White Sea and on Russia's Pacific coast.
|
|
|
emancipation
|
term used to describe efforts to obtain political rights or equality
|
|

Sergei Witte
|

finance minister who promoted industrialization in Russia
|
|
|
Russo-Japanese War
|
1905 war led by Nicholas II who favored expansion into Manchuria and Korea. Resulted in Russian loss and destruction of their navy.
|
|
|
Duma
|
national legislature in Russia with little power. Was symbolic as a concession on part of the tsar.
|
|
|
Opium War
|
1839-1842 war between British and Chinese. Showed the military prowess of European forces especially in terms of the British navy.
|
|
|
Unequal treaties
|
European nations forced China to sign them. Unequal peace treaties followed the example of the Treaty of Nanjing (1842) which ceded Hong Kong to British, opened five Chinese ports to trade, installed Britain with favored nation status, and granted extraterritoriality status to British citizens.
|
|
|
Tributary Empire
|
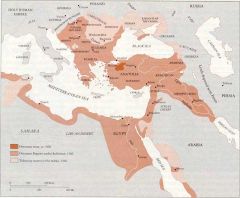
Vassal states of the Ottoman Empire serving as a buffer against Christendom including but not limited to Khanate of Crimea, Wallachia, Moldavia, Transylvania, and the Kurdish Emirates.
|
|

Hong Xiuquan
|

religious schoolteacher in China calling for the destruction of the Qing dynasty and multiple radical reforms. Was a leader in the Taiping rebellion of 1850
|
|

Empress Cixi
|

Royal concubine to Emperor Xianfeng. She was the only concubine to bear him a son so when he died her son became emperor.
|
|

Admiral Perry
|

American admiral that started the array of unequal treaties with Japan. Resulted in the samurai, daimyo, and emperor's officials banding together to push out the government. Resulted in the reign of Matsuhito and the Meiji rule.
|
|

Janissaries
|

elite corps under the Ottoman Empire composed primarily of war captives and Christian youths forced into service and Islam. Originally started by Sultan Murad I
|
|
|
Tanzimat Reforms
|
reorganization period with military, legal, and education reforms. Ideas were garnered from the European Enlightenment.
|
|
|
Young Turks
|
Nationalistic group that used newspapers to publicize their positions on universal suffrage, free public education, equal treatment under the law, secularization of the state and emancipation of women. Inspired army coup in 1908 resulting in puppet rulers. Tried to institute Turkish as the national language of the empire but backfired.
|
|

Tsar Alexander II
|

the reformist tsar, abolished serfs under conditions that were more favorable to landowners than former serfs. Also instituted regional assemblies to deal with social issues, reformed legal system along the lines of European courts with trial by jury, and economic reform to enhance military power.
|
|

Nicholas II
|

championed further police control and oppression, favored expansion into Manchuria and Korea
|
|
|
Zemstvos
|
county institution for self-government that existed in most of the territorial units of Russia until the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917
|
|
|
Pogroms
|
anti-Jewish riots in Russian lands
|
|
|
Bloody Sunday
|

After the defeat in the Russo-Japanese War there was increased social and political unrest. Soldiers shot into a crowd killing 130 workers caused rebellions, naval mutinies and student demonstrations to push for economic reform. The event became known as Bloody Sunday.
|
|
|
Cohongs
|
official merchants who were under strict control of the Chinese government
|
|
|
Treaty of Nanjing
|

Set the trend for unequal peace treaties. It ceded Hong Kong to Britain, opened five Chinese ports to trade, installed Britain with favored nation status, and granted extraterritoriality status to British citizens.
|
|
|
Hong Kong
|
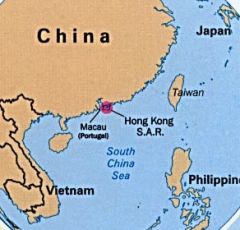
one of two administrative regions in China. Belonged to the UK until the ceding of sovereignty to the People's Republic of China.
|
|
|
Taiping Rebellion
|

1850 rebellion affecting most of China called for reforms such as the abolition of private property and a shared wealth plan to alleviate the distress of peasants. It called for equality of men and women and the prohibition of footbinding and concubinage (Taiping leaders maintained large harems)
|
|
|
Self-strengthening movement
|
movement with imperial permission to act as regional governments as they sought to blend Chinese tradition with European industrial technology. They built railroads, shipyards, and steel factories, and founded technological institutes.
|
|
|
Boxer Rebellion
|

violent anti-foreigner group that rampaged through norther China, killing foreigners, Chinese Christians, and those who had business with foreigners. They besieged foreign embassies and were defeated by the British, French, German, U.S., and Japanese forces. Chinese revolutionaries rose up against Empress Cixi for her complicity.
|
|

Tokugawa
|

Japanese government that incurred conservative reforms such as canceling debts and forcing return of peasants to the countryside, headed by shogun Tokugawa
|

