![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
NCS |
|
|
|
Seddon |
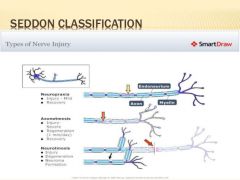
|
|
|
Seddon |
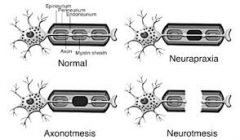
Wallerian degeneration occurs distal to injury. |
|
|
Anatomy of a nerve |
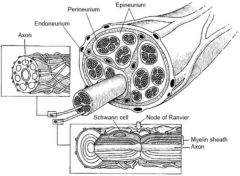
|
|
|
Sensory V Motor nerve |
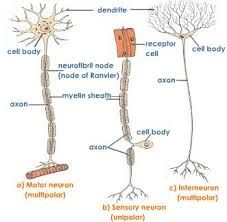
|
|
|
Muscle cell |
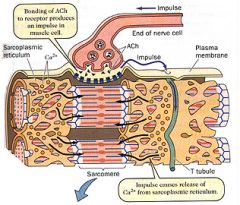
|
|
|
Microstructure muscle cell |
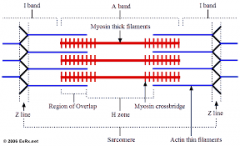
In contraction.
|
|
|
Muscle physiology |
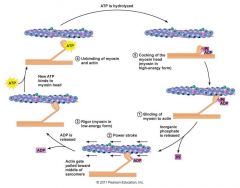
|
|
|
Muscle physiology |
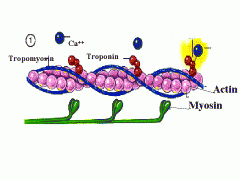
|
|
|
Motor end plate receptors |
Acetylcholine neuro transmitter Nicotinic receptor Ach is broken down by Cholinesterase. Electrical and mechanical maximum response doesnt occur simultaneously. |
|
|
Sequence in muscle contraction |
|
|
|
Vitamin D metabolism |
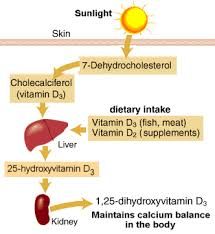
|
|
|
Calcitonin |
Stimulate by High Ca2+ Lowers serum Ca2+ Parafollicular or C cells (thyroid gland) response to high Ca levels. Inhibits osteoclast activity Increase excretion in Kidney Not involved in Phosphate homeostasis. |
|
|
Calcium |
99% in bone. Clotting, muscle contraction, nerve, 2nd mess plasma Ca 50% free 50% bound. pH plays role in % there need to know corrected. Absorbed in Duo (active 1,25(OH)2D3) jejunum passive. 98% reabsorbed in PCT. Intake 750mg/day >25yo. 600 < 10yo. 1400 10-25 or pregcor # healing. |
|
|
PTH |
Low levels of Ca2+ act directly on parathyoid. Increase Pi indirectly act (lowering level of Ca). Leads to increase Ca2+, decrease in Pi. Chief cells
|
|
|
Hypercalcemia of Malignancy |
|
|
|
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins |
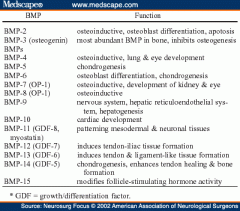
BMP 2, 7 known as OP1 (osteogenic protein 1). Clinically induce bone regeneration. Sub family of TGF-beta. |
|
|
Clotting |
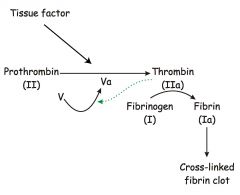
Antithrombin III combined with heparin like cofactor inactivates thrombin. |
|
|
Growth factors and cytokines |
Insulin like GF (IGF's).
IL-1, IL-6, TNF Alpha. Pro inflam. Also play role in OC recruitment from macrophage lineage. IL-4, IL-10 down regulate immune response. TGF-Beta - causes profli of mesenchymal cells. secreted in latent form (can be stored) clevage for activation. |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Haemotopoietic macrophage linage. Mutlinucleated attach via Integrins Ruffle border, proton pumps. Resorb in Pit (Howships Lacunae). Live 10-14 Days PTH increase activation Via OB the IL6 then OC. TNF alpha potent stimulator. |
|
|
Osteocytes |
Trapped OB connect to each other via long CP via canaliculi play role in Ca2+ and Pi metabolism. Respond to stimuli
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
From Mesenchymal stem cells Produces osteoid contain T1 collagen. Deposites it on mineralised surf. It then gets mineralised. Line surface of bone. High Alkaline Phosphatase activity. Cell diff by BMPS, GF, Cytokines. 3 fates. boneliner, ocytes, apoptosis. Secrete;
|
|
|
Chondrocytes |
From Mesenchymal stem cells produce abuntant extracellular matrix. Differentiation into one or two pathway
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
From Mesenchymal stem cells Type 1 and 3 collagen. used in generation of T/L Respond to mechanical stress Spindle shape cell |
|
|
Inflamation |
Rubor, Calor(heat), dolor(pain), tumour(swelling), functio laesa (LOF). 3 possible out come from acute inflam
Chronic inflam - key cell is mononuclear cell (macrophages). |
|
|
Stabilty |
Able withstand normal physiological forces without deformity. |
|
|
Wolfs Laws |
German Anatomist "Bone ins a healthy person woll adapt to the load it is placed under." |
|
|
JRF Hip |
JRF made from abduct force and body weight (5/6BW). Decrease JRF decreases pain. Decrease JRF by 1. Reduce BW moment
2. Help Abductors
|
|
|
Principles for tendon transfer |
Joint must be suble Gain of function must be greater than loss of function Motor must have sufficient power and excursion. (usually loss one grade with TF) Ideally
|
|
|
Orthotics |
device external applied to segment that facilitates or improves function for skeletal deformity or weakness. Dynamic or static. Functional characteristics
|
|
|
VACTERL |
Vertebra Cardiac Anal Atresia Tachy-oesophageal fistula Renal Limb Common with Radial Deficiency. |
|
|
Null Hypothesis |
the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error. prob that any different seen did occur by chance. Ortho usually accepts 5 % probability that it was due to chance therefore p=0.05 |
|
|
Power |
determines the n of subjects to show a difference if one exists or correctly reject the Null hypothesis. 1-beta. Factors affecting size of difference, p value, sample size data types. |
|
|
Statistical error |
Type 1. Alpha. False positives. NH rejected incorrectly. protect by reducing significance levels. Risk of type 1 decreases as p value is decreased. Type 2. Beta. False negatives. NH acceped incorrectly. Usually small sample size. need power study. Common. Type 1 and 2 inversely related. |
|
|
Sensitivity |
Ability to exclude False negatives. ie ability to pick up all cases of the disease. |
|
|
Specificity |
Ability to exclude False Positives. ie ability to exclude the disease. |
|
|
Positive predictive value |
Probability that some one who has a Positive test has the disease. i.e significance of the positive test. |
|
|
Negative predicted value |
Probability that some one who has a Negative test is true negative. i.e significance of the neg test. |
|
|
Levels of Evidence NHMRC |
1 - A systematic review of level IIstudies 2 - A randomised controlled trial 3.1 - A pseudorandomised controlled trial(i.e. alternate allocation or someother method) 3.2 - A comparative study withconcurrent controls: Cohort study, Case-control study. 3.3 - A comparative study withoutconcurrent controls. 4 - Case series. |
|
|
Grades of recomendation NHMRC |
A - Body of evidence can be trusted to guide practice B - Body of evidence can be trusted to guide practice in mostsituations C - Body of evidence provides some support forrecommendation(s) but care should be taken in itsapplication D - Body of evidence is weak and recommendation must be appliedwith caution |
|
|
Visco-elastic materials |
Exhib stress and strain behaviour that is time and rate dependant. Viscous - Fluid like tissue, constant load results in progressive deformity over time. (Creep). Elastic - Solid like tissue, returns to its original shape and length after load removed and its stress/ strain behaviour remains unchanged. |
|
|
Visco-elastic T/L |
Capacity for both viscous and elastic responses. Low loads = viscous behaviour dominates. High loads = elastic behaviour dominates. When L/T repetitively loaded stress strain curve shifts right less stiff more compliant When increase strain curve becomes steeper and more energy storage. |
|
|
Visco-elastic Bone |
Properties change with rate of application. Rapid application = bone stiffer, stronger and brittle. Able to absorb more energy. More likely comminuted. Also Rate of application of force determines energy transferred. Newtons laws increase velocity increase energy. |
|
|
Cortical bone |
Stiffer (Tolerates less strain) than cancellous bone. Anisotrophic
|
|
|
Titanium |
Titanium 64 used in ortho. 6%Aluminium, 4% Vanadium, 89% titanium Alloy precipates from moltn 2 forms HCC and BCC which improves fatigue resistance. Oxide layer forms on outside which protects. Youngs modulus 200 (half of SS). Notch sensitive. Less resistant to wear. Excellent resistance to corrosion, good biocompatibility, ductily, less Stress sheilding. |
|
|
Polymers |
Made from many Monomers (Carbon back bone) Fromed by addition or condensation. Long polymners held together by weak vonder woals force (no crossslinked) two methods of strengthening (cross link)
|
|
|
Ceramics |
Compunds of a metal bonded with non metallic elements. e.g Aluminium oxide. Ions bonds (free e). Strong. Properties depend on grain size. small better. Chemically inert, insoluble. V resistant to wear. High elastic modulus. No plastic deformity (Brittle) Ceramics osteoconductive. |
|
|
Mechanical wear modes |
1. generation of debris bw to primary surfaces. 2. primary surface against non primary surface. 3. two primary surfaces with 3rd body bw them. 4. two non bearing surfaces rubbing. Mode 1 is majority of wear. |
|
|
Corrosion |
Unwanted dissolution of metal in a solution resulting in continue degradation. Anode and cathode. Decrease structural integrity, release products. Metal forms a thin oxidies layer on it. Galvanic - 2 metals. anything with SS. Crevice Fretting Piting Stress |
|
|
Stainless steel |
Stainless Steel = carbon + iron + chromium (18%) Orthopaedic is 316L, 3% molybdenium, 16% Nickel, L is low carbon (<0.03%). Nickel helps structure. SS is cold worked by 30%. Strong, ductile, cheap |
|
|
Cobolt Chrome |
Cobolt with chromium. Also Carbon, nickel and molybdenum. Manufactured by powder. Form FCC structure. Main advan resistant to corrosion. Strongest Expensive. |
|
|
Bone Cement |
Polymethylmethacrylate. Liquid. Monomer, Accelerator, inhibitor Powder. PMMA co polymer, barium, initiator. |
|
|
Youngs modulus |
As increase so does the stiffness of the material (more resistant to deformation). |
|
|
3 main factors of visco-elastic behaviour |
|
|
|
Elasticity |
If material returns to its original shape after stress removed material considered elastic. |
|
|
Stress strain curve |
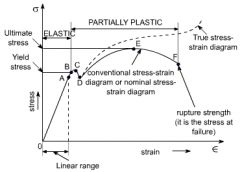
|
|
|
Stress |
Stress = force / total area. |
|
|
Strain |
Strain = Change length / total length |
|
|
Tendon transfers Rule of 13 S's |
Patient- Sensible Tendon- Strong, Sacrificeable, Synergistic, Sufficient excursion Surgery- Straight, Subcutaneous, Straight pull, Secure distally, Single function Joint- Supple, Sensate, Scarless |
|
|
CRPS diagnostic criteria clinical
|
unexplaineddiffuse pain that was not normal in relation to thestage of fracture treatment.
a difference in skin color relativeto the other hand and wrist diffuse edema a differencein skin temperature relative to the other hand andwrist limited active range of motion of the wrist andfingers that was unrelated to the stage of fracture treatment |
|
|
Vitamin C Wrist #
|
JBJS 2007 Zollinger
No Vit C CRPS 10% 500mg Vit C 1.7% Start on day of #. Benefits mostly seen in non op gp. Rx for 50days. |
|
|
"complaints related to the use of the plastercast were strongly predictive of the development of .......? "
|
complex regional pain syndrome
|

