![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Economics
|
Economics is the study of how man allocates scarce resources, which have alternative uses to achieve given or goals
|
Define
|
|
|
Define the term economy
|
The economy is the mechanism through which these scarce resources are organized for the production of goods and services
|
|
|
|
Sectors in an economy
|
Households, firms and government
|
|
|
|
What's the basic economic problem
|
Mans wants are unlimited, where as economic resources are limited. This means there are not enough resources to produce all the goods and services desired.
|
The imbalance between unlimited wants and limited resources
|
|
|
Scarcity
|
Scarcity is the economic condition where all goods and services are not sufficient for those who desire them.
|
|
|
|
Choice
|
Choice is the range of options available to the individual, firms are or government when making a decision
|
|
|
|
Opportunity cost
|
Opportunity cost is the cost of the alternative forgone
|
|
|
|
Money cost
|
This involves what was actually paid for the inputs used to produce a given good or service
|
|
|
|
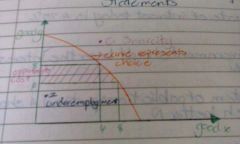
The production possibility frontier
|
A graph showing the various combination of two goods that an economy is able to produce with fixed resources
|
|
|
|
The ppf assumes
|
The economy only produces teo goods. The amt of resources is fixed. Each of the goods can be produced using changing ratios of the factors of production
|
|
|
|
A shift in the ppc outwards
|
Is caused by economic growth, discovery of new natural resources, growth in population, technological progress and improvements in labour productivity.
|
|
|
|
A pivot in the ppf
|
Assume that industry for one good uses a labour intensive industry and the industry for the other good uses a capital intensive industry. There is an improvement in technology and this benefits the capital intensive industry more than the labor intensive industry.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Normative statement
|
Involves an opinion or valued judgment
|
|
|
|
Positive statement
|
Can be verified
|
|
|
|
Subsidies
|
Government grants to suppliers of goods and services.
|
may be intended to keep prices down
|
|
|
Capital good
|
Goes into the production of other goods example goods and raw materials
|
|
|
|
Consumer goods
|
One which satisfies a person's immediate needs
|
|

