![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the antibacterial substances in oral secretions that contribute to innate immunity?
|
Lysozyme and Lactoferrin
(also low pH of the stomach for that region) |
|
|
What is the most important component in the innate immunity realm according to Dr. Weinberg?
|
Alternate Complement Pathway
|
|
|
Where are TLRs located?
|
Found on all cells, especially epithelial cells
|
|
|
What are some PAMPs that TLRs recognize?
|
1. LPS
2. Peptidoglycan 3. Lipoteichoic acid 4. Flagella 5. Mannans 6. Bacterial DNA 7. Glucans |
|
|
What TLR recognizes peptidoglycan and lipoprotein?
|

TLR-2
|
|
|
What TLR recognizes LPS?
|

TLR-4
|
|
|
What TLR recognizes bacterial DNA?
|
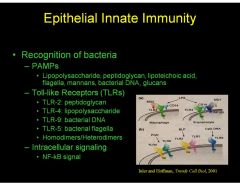
TLR-9
|
|
|
What TLR recognizes Bacterial Flagella?
|

TLR-5
|
|
|
What does the transcription factor NF-kB do?
|
NF-kB activates genes for inflammation reaction
|
|
|
Does TLR-2 work alone?
|

No it dimerizes with TLR-1 or TLR-6
|
|
|
What happens when TLR-2 binds to its ligand?
|
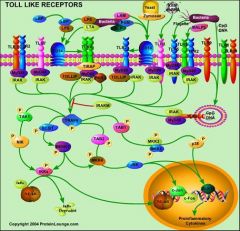
Activates pathway leading to NK-kB
|
|
|
How is NF-kB activated?
|

a) TLR-2 binds its ligand
b) I-kB binds to NF-kB constantly in the cytoplasm c) I-kB kinase cleaves off I-kB d) NF-kB is activated and enters the nucleus to act as a transcription factor. |
|
|
What is only associated with epithelial cells, protects against candida albicans, is expressed in macrophages and lymphocytes?
|

Dectin-1
|
|
|
What type of cells in Dectin-1 only associated with?
|

Epithelial cells
|
|
|
What is this sequence for?
1. Infection 2. Recognition by preformed, nonspecific effectors 3. Removal of infectious agent |

Innate immunity
|
|
|
What is this sequence for?
1. Infection 2. Recognition of microbial-associated molecular patterns 3. Inflammation recruitment and activation of effector cells 4. Removal of infectious agent |

Early Induced response
|
|
|
What is this sequence for?
1) Infection 2) Transport of antigen to lymphoid organs 3) Recognition by naive B and T cells 4) Clonal expansion and differentiation to effector cells 5) Removal of infectious agent |

Adaptive Immune Response
|
|
|
Where is a natural gradient of IL-8 located in the body?
|
The oral cavity
Anywhere else would be considered a sign of infection but this chemokine is normal here |
|
|
What are dendritic cells in the oral cavity called?
|
Langerhans cells
|
|
|
What is the bacteria in your saliva that is the Good Guy, which antagonizes the bad guys like A.A.?
|
Streptococcus Sanguis
|
|
|
T/F
Streptococcus Mutans has bacteriocin that can kill AA |

True
|
|

What does EAP stand for?
|
Epithelial Antimicrobial Peptide
|
|

What has the ability to cross talk with cells in the adaptive immunity system, can cause chemo-attraction activating APCs, and can activate Langerhans cells bringing in lymphocytes?
|
EAPs
|
|
|
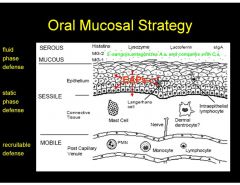
What are the different layers in the oral mucosal strategy?
|

1. Fluid phase defense
2. Static phase defense 3. Recruitable defense |
|
|
What has antiviral, antifungal, and antibacterial properties in saliva?
|
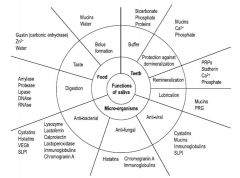
Defensins
|
|
|
What salivary factor binds bacteria, neutralizes and inactivates viral particles?
|

Antibodies
|
|
|
What salivary factor performs general antimicrobial activity and inhibit cysteine proteases
|

Cystatins
|
|
|
What salivary factor performs general antimicrobial activityl carry out charge mediated disruption of bacterial membranes?
|

Defensins
|
|
|
What salivary factor serves as an antifungal?
|

Histatins
|
|
|
What salivary factor binds iron to inhibit bacterial growth?
|

Lactoferrin
|
|
|
What salivary factor lyses bacteria?
|

Lysozyme
|
|
|
What salivary factor entraps and aggregates microbial particles?
|

Mucins
|
|
|
What salivary factor Binds bacteria?
|

Proline Rich Peptides and Statherin
|
|
|
What oral organisms need iron to survive?
|

Porphyromonas gingivalis
Lactoferrin binds iron needed by PG |
|
|
What salivary factor is very important against candidias?
|

Histatins
|
|
|
What salivary factor causes transglycolization (cleavage) of the peptidoglycan cytoskeleton of the organism (NAM-NAG)
|

Lysozyme
|
|
|
What salivary factor is anionic (can bind to cationic agents), can carry stuff electrostatically and bring these agents to the site better than if it wasn't there?
|

Mucins
|
|
|
What are mucins made up of?
|

Made up of Glycoproteins
|
|
|
What gives the mucin molecule its net negative charge?
|

Sialic Acid
|
|
|
What protects the underlying mucosa and tooth surfaces from chemical and physical harm and is important in formation of biofilm?
|

Mucins
|
|
|
What mucin comes from mucous acini?
|

MG1
|
|
|
What mucin comes from serous acinar cells?
|

MG2
|
|
|
Which mucin type plays a major role in pellicle formation?
|

MG1
|
|
|
Which mucin is often thought to be more important in bacterial clearance?
|

MG2
|
|
|
Where is MG1 and MG2 located in the pellicle?
|

MG2 covers outer layers
MG1 is more inside Paper is wrong |
|
|
Why is pellicle formation so important?
|

Colonization of first line of bacteria --- the good guys
|
|
|
Which mucin prevents bacterial colonization of the pellicle coated tooth by presenting identical surface carbohydrates in the fluid phase?
|

MG2
|
|
|
Which mucin acts as a decoy for bacterial colonization?
|

MG2
|
|
|
What cleaves beta-1,4 linkages between NAM-NAG in bacterial wall peptidoglycan?
|
Lysozyme
|
|
|
Where does lysozyme come from?
|
Myeloid cells (neutrophils) and glandular epithelium
|
|
|
How do lysozymes affect invaders?
|
It is a cationic protein that binds to anionicly charged membranes then defensins create holes in the membrane. Cleaves beta-1,4 link in NAM-NAG in bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan
|
|
|
What blocks growth of iron dependent organisms like candida albicans and PG?
|
Lactoferrin
|
|
|
What serous secretion in the mouth catalyzes the reduction of hydrogen peroxides to water and hypothiocyanite?
|
Salivary peroxidases
|
|
|
Why don't we get ulceration of the gingiva?
|
because of salivary peroxidases
|
|
|
What is the most important antifungal agent in saliva?
|
Histatins
|
|
|
Why does Denture Stomatitis occur?
|
Dentures cover palate and prevent access of parotid saliva, which contains Histatins.
Basically histatins can't get to the fungus |
|
|
How does Statherin in saliva affect invaders?
|
Like PRPs it maintains salivary calcium phosphate in a supersaturates state
INVOLVED IN MICROBIAL ATTACHMENT (like anchoring proteins found in the pellicle that bacteria know to bind to) |
|
|
What are two components of serous saliva that are important in dictating microbial attachment to the acquired pellicle?
|

Proline-rich proteins and Statherin
|
|
|
Why does strep sauga not bind in solution, but it will bind to teeth (pleomorphism)?
|

PRPs and Statherin are important in microbial attachment
|
|
|
What are the components of Serous secretions that contribute to adaptive immunity?
|
Secretory IgA
|
|
|
What are the components of Serous secretions that contribute to innate immunity?
|
Lysozyme
Histatins Salivary Peroxidase Lactoferrin Cystatins PRPs Calprotectin |
|
|
What are the major anchoring proteins in the pellicle for the early colonizers?
|

Statherin and PRPs
|
|
|
Everything that is directly attached to the pellicle is a ______________.
|

Streptococcus organism
|
|
|
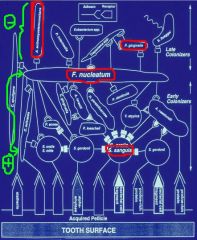
What is the primary organism that attaches to the pellicle?
|

S. Sanguis
|
|
|
T/F
F. Nucleatum is pathogenic |

False
He is a good guy who can bind tissue and teeth. He has the moost receptors and adhesions of any organism known. |
|
|
What is the bridging organism between the early and late colonizers?
|

F. Nucleatum
(note that it is right in the middle) |
|
|
Are the late colonizers good guys or bad guys?
|

BAD GUYS
(AA and PG) |
|
|
What organism is the host of enzymes that can break down the periodontium?
|

P gingivalis
|
|
|
What is the most important enzyme that p. gingivalis releases?
|
gingipain a cysteine protease that can break down tissue very well
|
|
|
Which organism leads to adult periodontitis?
|

p. gingivalis
|
|
|
Which organism leads to Juvenile Periodontitis?
|

Actinomycetemcomitans Serotype B (kills WBCs)
|
|
|
What part of the saliva is an inhibitor of cysteine proteinases?
|
Cystatins (come from myeloid cells)
|
|
|
Why does Cystatin C increase in saliva from periodontitis and gingivitis cases?
|
Because there are more myeloid cells when these are occurring
|
|
|
What very important microbial-derived cysteine proteinases do Cystatins neutralize?
|
Gingipain (from p. gingivalis)
|
|
|
Why is the mouth so healthy in spite of constant trauma occurring in a very septic environment?
|
Maginin - an alpha helical protein that protects the site from the surrounding bacteria (found in frogs)
|
|
|
Which hBD is constituatively expressed in all tisses?
|
hBD-1
|
|
|
T/F
FN can and will stimulate hBD-2 and PG cannot |
T
|
|
|
What are the Cytien bonds in all defensins?
|
1-5 2-4 3-6
|

