![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the stages of herpes?
|

Acquisition of disease
Asymptomatic phase Prodromal phase Symptomatic phase Healing/Convalescence |
|
|
What are the members of the HHV family?
|

HSV-1 & HSV-2
VZV EBV-burkitt's lymphoma and mono CMV |
|
|
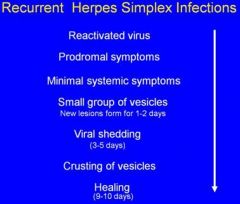
When does viral shedding occur during a recurrent HHV infection?
|
Viral shedding 3-5 days after the prodromal symptoms
|
|
|
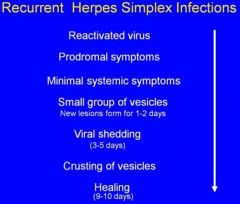
What are the stages of a recurrent HHV infection?
|
Reactivated virus
Prodromal symptoms Minimal systemic symptoms Small group of vesicles Viral shedding Crusting of vesicles Healing |
|
|
What are the 3 Phases of HSV Replication?
|

1. Immediate Early Proteins (alpha) gene transcription
2. Early Proteins (beta) DNA polymerase 3. Late Proteins (gamma) structural proteins |
|
|
What are the stages of Shingles?
|

Incubation period
Prodrome Lesions Rash Crusting and shedding |
|
|
What are the main HHV antiviral medications?
|

Acyclovir
Famciclovir Valcyclovir |
|
|
How soon can you begin to show prodromal signs after being exposed to chicken pox?
|

14 days after exposure
|
|
|
What is the difference between Primary VZV (chicken pox) and Herpes Zoster (shingles), regarding prodromal phases?
|

Chicken pox: prodrom is 1-3 days, rare in children, adolescents and adults experience headache, back ache, sore throat
Shingles: prodromal lasts 4-5 days, pain, tenderness and parathesia in the dermatome. Fever, headache, malaise □ Prodrome: pre-eruptive pain, itching, burning localized in dermatome, precedes eruptions by 4-6 days, pain can mimic MI pain, migraine etc. difficult to dx. , malaise, fever, regional lymphadenopathy |
|
|
T/F
HHV is responsible for shingles |
True
VZV is a member of the human herpes virus family |
|
|
When does DNA uncoat when replicating?
|

When it joins the nuclear membrane
|
|
|
Where does RNA uncoating occur?
|
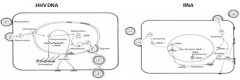
In the Cytoplasm
|
|
|
Where does assembly occur in DNA viruses?
|

In the nucleus
|
|
|
Where does RNA virus assembly occur?
|
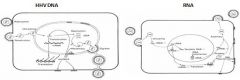
In the cytoplasm
|
|
|
Where does DNA virus assembly occur?
|
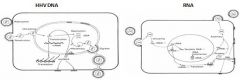
In the nucleus
|
|
|
What diseases are associated with EBV?
|
Mono, B cell lymphoma, Hodgkins, HOL (hairy oral leukoplakia), Lymphoproliferative disorders
|
|
|
What areas do Herpes Zoster Affect?
|
Follows dermatome and nerve distribution 2/3 of cases affect trunk, also can follow CN V
|
|
|
Is HIV an RNA or DNA virus?
|
HIV is a ssRNA virus
|
|
|
How does HIV enter cells?
|
HIV is a Retrovirus that enters Th cells
HIV envelope binds to M type CCR5 and T type CXCR4 Uses Reverse Transcriptase of RNA genome |
|
|
T/F
Replication of HIV occurs by fusion with host T cell, unraveling, and are expressed? |
True
|
|
|
What drugs are used to manage HIV?
|
HAART
|
|
|
How are mothers with HIV treated to prevent vertical transmission to infant?
|
Mothers who are HIV+ are given a protease inhibitor before delivery to prevent the vertical transmission of HIV
|
|
|
What is SLPI?
|
Secreted Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor
Protein found in saliva that protects against HIV |
|
|
What proteins are necessary for HIV to enter into the cell?
|
Gp120
CCR5 CXCR4 |
|
|
What is the disease course for HIV?
|
1) Initial transmission stage
2) Acute retroviral syndrome (2-3 weeks) 3) Recovery and sero-conversion (within 6 weeks) 4) Asymptomatic chronic HIV stage 5) AIDS (1-2 years prior to death) 6) HAART prolongs length of stages |
|
|
What is used in most treatment regimens for HIV?
|
Most drugs are either protease inhibitors or nucleoside reverse transcriptase
|
|
|
What are the cell walls of Candida albicans composed of?
|
Cell wall comprised of glucans, mannans, chitins (basically complexes of carbohydrates)
|
|
|
What factors affect growth of fungi?
|
Environment dictates growth and morphology
Temperature pH Inoculum size Nutrient source Scaffolding or site of attachment |
|
|
T/F
Fungal cell walls contain β1-3 and β1-6 glucans |
True
|
|
|
How does candida emerge?
|
Carriage - colonization - cadidiasis
|
|
|
Why are some patients more susceptible to fungal infections than others?
|

See above
|
|
|
T/F
Hyphal wall proteins HWP are virulence factors |
True
|
|
|
How many chromosomes do candida albicans have?
|
8
|
|
|
What is the 4th leading cause for all blood stream infections?
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
What is Stachybotrys?
|
Black mold that can cause anaphylaxis
|
|
|
What is dimorphism?
|
Multiple shapes, pseudohyphae for budding
|
|
|
T/F
Mycelium is a bowl of spaghetti. It has finger like hyphae and reproduces via spores |
True
|
|
|
What is an example of a dimorphic fungus?
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
What causes dimorphic changes in candida albicans?
|
pH
Temperature Metabolic substrates |
|
|
Are candida species haploid or diploid?
|
diploid
|
|
|
What does aphthous mean?
|
Apthous = Burning
|
|
|
What are the effects of loss or disruption of mucosal barrier function?
|
Salivary glands & saliva
Changes in epithelium Microbial insult (bacteria, fungal, and viral translocation) Alteration of Host Immune System (T&B cells) Iatrogenic Challenges (meds) |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of mucositis?
|
1. Initiation phase
2. Primary damage 3. Signal amplification 4. Ulceration 5. Healing phase |
|
|
What kind of specimens should you obtain for culturing Adenovirus, Influenza virus, enterovirus, rhinovirus, paramyxovirus, rubella virus, & HSV?
|
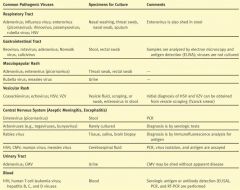
Nasal washing, throat swab, nasal swab, sputum
|
|
|
What kind of cultures would you want to take for Reovirus, rotavirus, adenovirus, norwalk virus, and calicivirus?
|
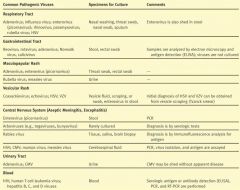
Stool, rectal swab
|
|
|
What kind of tests would you want to perform for Reovirus, rotavirus, adenovirus, norwalk virus, and calicivirus?
|
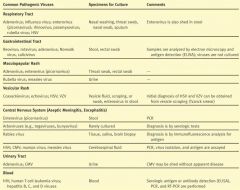
Electron microscopy and antigen detection (ELISA), VIRUSES ARE NOT CULTURED
|
|
|
If you have a patient with a maculopapular rash, what specimens do you take?
|
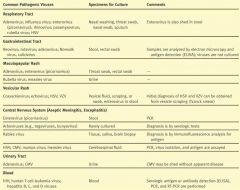
Throat swab or rectal swab
|
|
|
If you have a maculopapular rash and you suspect Rubella virus or measles, what specimen would you take?
|
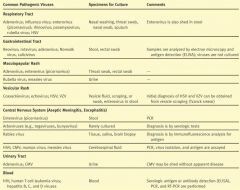
Urine
|
|
|
What types of viruses can cause vesicular rashes?
|
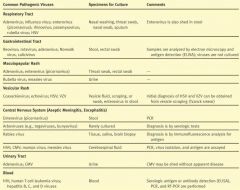
Coxsackievirus
Echovirus HSV VZV |
|
|
If you suspect a Coxsackievirus, echovirus, HSV, or VZV, what specimens should you take?
|
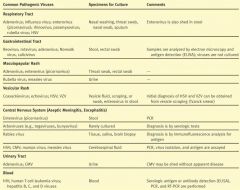
Vesicle scraping
Enterovirus in stool |
|
|
Which viruses can be obtained from a Tzanck Smear?
|
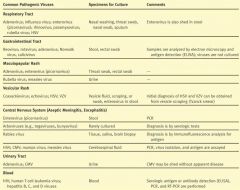
HSV and VZV
|
|
|
If you have aseptic meningitis or encephalitis, which viruses could be the culprit?
|

Picornavirus
Togavirus, bunyavirus Rabies virus HSV CMV mumps, measles |
|
|
What samples do you take for aseptic meningitis or encephalitis when picornavirus is suspect?
|
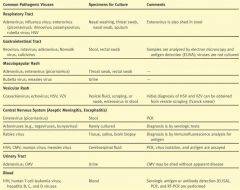
Stool
Perform PCR |
|
|
What samples do you take for aseptic meningitis or encephalitis when Rabies viruses are suspect?
|

Tissue, Saliva, Brain biopsy
Immunofluorescence used to detect |
|
|
What samples do you take for aseptic meningitis or encephalitis when HSV, CMV, mumps, or measles are suspect?
|
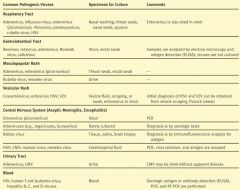
Cerebrospinal fluid
PCR virus isolation and antigen are assayed |
|
|
If you have a UTI, what viruses may be the culprit?
|
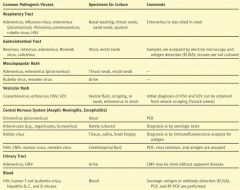
Adenovirus or CMV
|
|
|
If you suspect HIV or Hep B,C,D viruses, what should be used to test the blood sample?
|
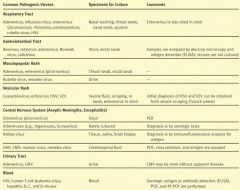
ELISA, PCR, and RT-PCR
|
|
|
Which Influenza type is responsible for regular outbreaks?
|
Influenza A
|
|
|
What are the glycoproteins on an influenza envelope?
|
Hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA)
|
|
|
What is a virus that has eight helical nucleocapsis segments with negative sense RNA?
|
Influenza Virus
|
|
|
Which glycoprotein of influenza virus has a spike protein that promotes fusion of the envelope to the cell membran, hemagglutinates RBCs, and elicits the protective, neutralizing antibody response?
|
HA Hemagglutinin
|
|
|
Which glycoprotein of influenza virus is a tetramer, facilitates release of virus, and undergoes antigenic changes, which give the viruses different designations N1, N2, etc.?
|
Neuraminidase NA
|
|
|
Which antiviral drugs target Neuraminidase receptors on influenza envelopes?
|
Zanamivir (Relenza) & Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
|
|
|
T/F
The M1, M2, & NP proteins are type specific and are therefore used to differentiate influenza A from B or C viruses |
True
|
|
|
T/F
The HA and NA of influenza A virus can undergo major (reassortment: shift) and minor (mutation: drift) antigenic changes to ensure the presence of immunologically naïve, susceptible people |
True
|
|
|
How are Strains of Influenza A virus classified?
|
1) Type (A, B, C)
2) Place of original isolation 3) Date of original isolation 4) Antigen (HA & NA) A/Bangkok/1/79 (H3N2) |
|
|
How are Strains of influenza B virus classified?
|
Same as A only No antigen
i.e. B/Singapore/3/64 |
|
|
What is the gradual accumulation of new epitopes on the H&N molecules of flu viruses called?
|
Antigenic Drift
|
|
|
What is a common mutation in the hemagglutinin gene?
|
Missense Mutations
|
|
|
What drugs inhibit one of the Matrix Proteins needed to get viral RNA into the cytosol of Influenza A viruses?
|
Amantadine and Rimantadine
|
|
|
Which drugs block the neuraminidase, which inhibits the release of fresh virions?
|
Zanamivir (Relenza) & Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
|
|
|
What tests can detect whether it is influenza A or B?
|
Rapid antigen assays
|
|
|
Which tests can detect whether it is influenza A or B AND distinguish different strains i.e. H5N1?
|
PT-PCR
|
|
|
Which test can detect viral antigen in exfoliated cells, respiratory secretions, or cell culture and are more sensitive assays?
|
Enzyme immunoassay or immunofluorescence
|
|
|
Which test uses specific antibody to detect and distinguish different influenza strains?
|
Immunofluorescence or hemagglutination inhibition
|
|
|
What tests can detect whether it is influenza A or B?
|
Rapid antigen assays
|

