![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
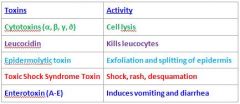
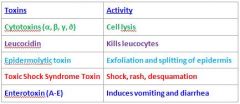
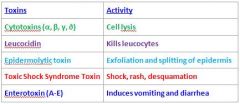
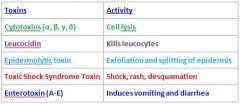
What shape are the S. Aureus Bacteriae?
|
Cocci
|
|
What does Aureus mean?
|
Gold
|
|
Where are S. aureus found?
|
Everywhere
(commonly come from needle sticks) |
|
What type of infection is S. aureus, typically?
|
Opportunistic infection because it is found everywhere
(takes advantage of weakened immune systems) |
|
|
What makes people feel sick when they have S. aureus infection?
|
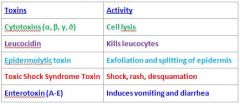
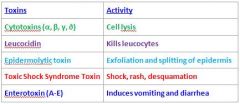
S. Aureus makes many toxins
|
|
|
What are the special enzymes that S. Aureus makes that can be used for diagnosis?
|
Coagulase- clots plasma (incubate bacteria with serum and if it clumps then it is coagulase positive)
Protein A- Antiphagocytic (protein A binds to Fc instead of Fab which prevents it from being recognized in macrophages) |
|
|
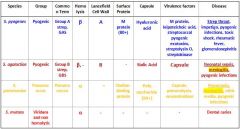
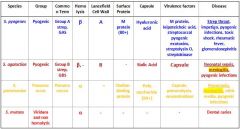
What are the different streptococcus species that we need to know?
|
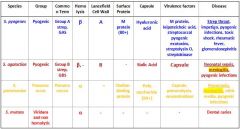
S. Pyogenes
S. Agalactiae S. Pneumoniae S. Mutans |
|
|
Which Streptococcal species cause meningitis?
|
S. Agalactiae
S. Pneumoniae |
|
|
Which Streptococcal species causes Strep throat, impetigo, pyogenic infections, toxic shock, rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis?
|
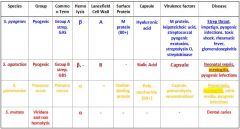
s. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal species causes neonatal sepsis, meningitis, & pyogenic infections?
|
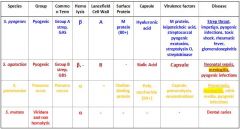
S. agalactiae
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal species causes meningitis, otitis media, and pyogenic infections?
|
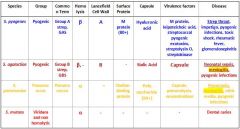
S. Pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal species display β Hemolysis?
|
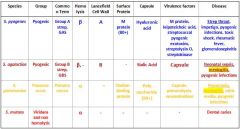
s. pyogenes
s. agalactiae |
|
|
Which streptococcal species display α hemolysis?
|
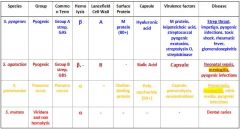
s. pneumoniae
s. mutans |
|
|
Which streptococcal bacteria has an A Lancefield Cell Wall?
|
s. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which streptococcal species has a B Lancefield Cell Wall?
|
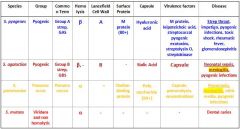
s. agalactiae
|
|
|
What bacteria is Group A strep?
|
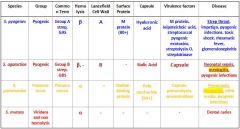
s. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which type of bacteria are Group B Strep?
|
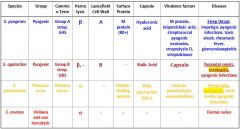
s. agalactiae
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal bacteria are pyogenic?
|
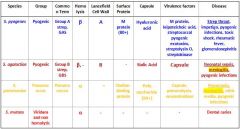
s. pyogenes
s. agalactiae s. pneumonia |
|
|
Which Streptococcal species has an M protein (80+)?
|
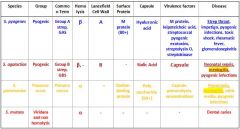
s. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal species has a Choline-binding protein?
|
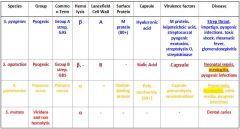
s. pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which streptococcal species has virulence factors that include M protein, leipoteichoic acid, streptococcal pyogenic exotoxins, streptolysin O, and streptokinase?
|
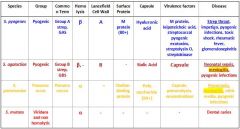
s. pyogenes
|
|
|
Which Streptococcal species has virulence factors that include its capsule, pneumolysin, and neuraminidase?
|
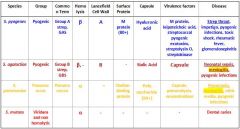
s. pneumoniae
|
|
|
Which type of bacteria are Group B Strep?
|
s. agalactiae
|
|
|
Hemolysis is a way to diagnose a bacterial infection by sticking the bacteria on a blood agar and seeing how wide the zone of lysis.
What do you see in α hemolysis? |
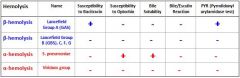
Narrow zone of partial hemolysis
Can see hemolysis, but it is not completely translucent |
|
|
Hemolysis is a way to diagnose a bacterial infection by sticking the bacteria on a blood agar and seeing how wide the zone of lysis.
What do you see in β hemolysis? |
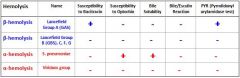
Wide clear translucent zone of complete hemolysis around the colony.
|
|
|
Which proteins play a factor in functional redundancy?
|
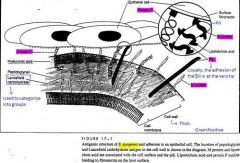
1. Protein F
2. M protein 3. Pili |
|
|
What makes functional redundancy so important?
|
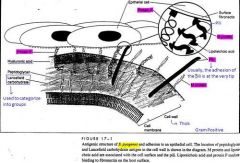
Attachment is so critical that the bacteria should have more than one way to attach.
|
|
|
Which bacteria are responsible for endodontic infections?
|
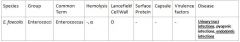
E. faecalis (Enterococci)
and odontolyticus |
|
|
What properties make S. mutans cariogenic?
|
See Chart
|
|
|
What properties make S. mutans cariogenic?
|

See Chart
|
|
|
What are the shape of Neisseria?
|
Dipplococci (kidney beans)
|
|
|
What are the species if Veilonella?
|
V parvula
V dispar V atypica |
|
|
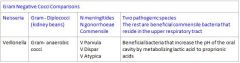
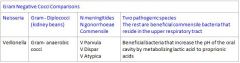
What are the beneficial gram negative cocci that we need to know?
|
Genus Neisseria many species that are Commensile in the upper respiratory tract
V. parvula, V. dispar, V. atypica ○ More predominant in saliva and tongue surface ○ "beneficial bacteria" Classified as this because it can increase the pH of the oral cavity It protects against caries by metabolizing lactic acid to acetic and propionic acids Lactic acid is more acidic than acetic and propionic acids There is a higher number of these bacteria in periodontally healthy sites than diseased sites ○ However, there is a higher number in HIV patients with necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis This bacteria is multifaceted |
|
|
Is the antigenic variation for N. gonococci based upon changing strains?
|
No it is based up changing proteins it expresses.
Pilin or Opa recombines with other bacteria |
|
|
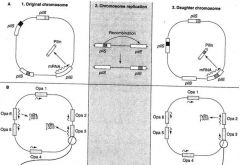
What occurs in antigenic variation for N. Gonococci that changes the Pilin gene?
|
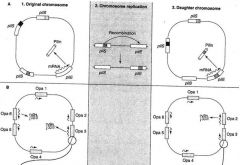
The chromosome contains multiple unlinked pilin genes, which are either expressions (pilE) or silent (pilS).
The expressing gene is transcribing a mature pilin protein subunit. During chromosome replication, one of the pilS genes recombines with one of the pilE genes, donating some of its DNA. The new daughter chromosome now produces an antigenic different pilin based on transcription of the donated sequences into protein. |
|
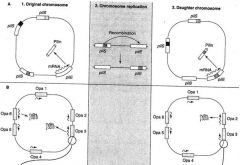
What happens for antigenic variation for N gonococci in the Opa genes?
|
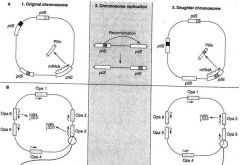
The chromosome contains multiple Opa genes.
Opa3 and Opa6 are "on" (producing protein), and the others are "off." During chromosome replication, replicative slippage in the leader peptide causes a five-base sequence (CTCTT) to b repeated variable numbers of times. Translation of the Opa will remain in-frame only if the number of added CTCTT nucleotides is evenly divisible by 3. |
|
|
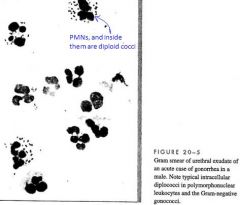
What are observable in PMNs infected with Gonorrhea?
|
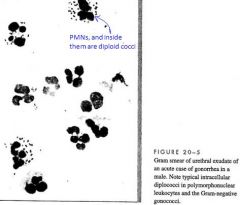
Diploid cocci
|
|
|
T/F
Patients with gonorrhea will not get it again after initial infection |
False
You cannot develop life-long antibodies against N Gonococci because of a method of antigenic variation unique to gonococci. |
|
|
Which Gram Positive Bacilli are spore forming?
|

Bacillus & Clostridium
|
|
|
Which Gram Positive bacteria are Facultative?
|

Corynebacterium (+aerobic)
Bacillus (+aerobic) Lactobacilli |
|
|
Which Gram Positive Bacilli are Microaerophilic?
|

Actinomyces (+anaerobes)
|
|
|
What are the different types of Mycobacteria?
|

M tuberculosis
M leprae |
|
|
What are the components of the RED complex?
|

□ Porphyromonas gingivalis
□ Tannerella forsythia (Bf) □ Treponema denticola |
|
|
What are the three species of Yersina and which one does not cause diarrhea?
|

Y pestis Bubonic plague not diarrhea
Y pseudotuberculosis Y enterocolitica |
|
|
What are the two different types of salmonellosis?
|
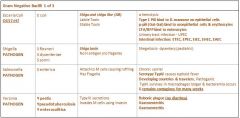
S. Enterica
S. Typhi |
|
|
What makes Salmonella Typhi worse?
|
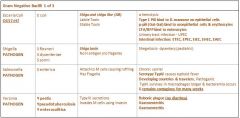
Invade & kill M cells and macrophages like S. enterica but persist in macrophage longer than E. enterica, so it can spread to other sites causing bacteremia.
You can pass this on through blood, stool, or urine for weeks. |
|
|
Where is typhoid fever most common?
|
Developing countries and travelers in industrialized countries.
|
|
|
Which Gram Negative Bacilli are pure pathogens?
|
Shigella
Salmonella Yersina |
|
|
Which Escheria Coli Pili is the common pili?
|
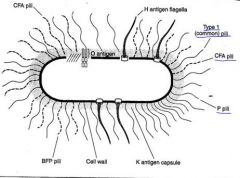
Type 1 Pili binds to D-mannose, which is common on epithelial cells
|
|
|
What are Escherichia coli's specialized pili?
|
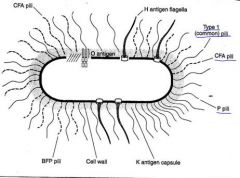
P pili binds to uroepithelial cells and erythrocytes
CFA/BFP binds to enterocytes |
|
|
What are the primary antigens used for serotyping?
|
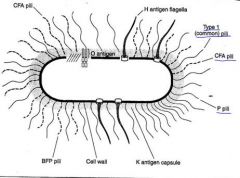
O = LPS; all have these
K = Kapsule; Many have these H = Peritrichous FlaHgella; Mobile bacteria (note:pili are NOT serotype factors) |
|
|
What is the Genera that is most virulent for humans for food-borne outbreaks?
|
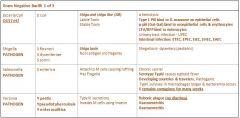
E Coli
O157:H7 |
|
|
How do UTI via UPEC E Coli occur?
|
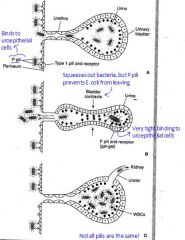
P pili binds to uroepithelial cells
Bladder squeezes out bacteria, but P pili prevents E. coli from leaving |
|
|
How does Enteropathic E Coli invade the cell?
|
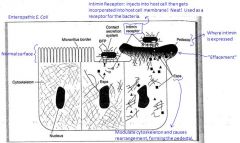
See picture
|
|
|
How does Shigella Spread?
|
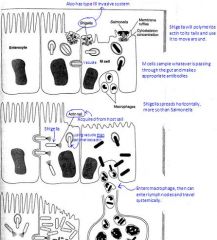
See picture
|
|
|
Which E coli group does O157:H7 fall into?
|
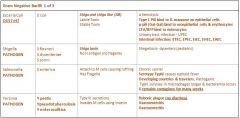
Hemorrhagic
|
|
|
What is the most virulent strain of Vibrio?
|
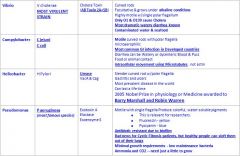
Vibrio Cholera
|
|
|
Which bacteria produces the most dramatic watery diarrhea known?
|
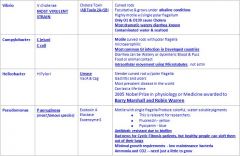
Vibrio Cholera
|
|
|
Which serotypes cause Cholera?
|
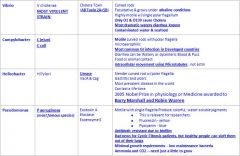
O1 & O139 cause cholera
|
|
|
What is unique about the Cholera Toxin?
|
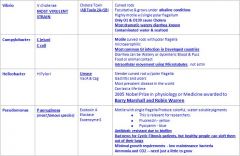
AB toxin 2A + 5B
|
|
|
How is Vibrio Cholera Spread?
|
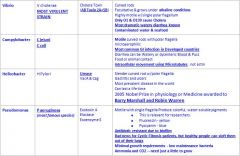
Contaminated water and seafood and it prefers alkaline environments (like the jejunum)
|
|
|
How does campylobacter get around?
|
It is motile with polar flagella
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of GI infection?
|
Campylobacter
|
|
|
T/F
Campylobacter uses actin to get around. |
False
It manipulates Microtubules |
|
|
What are the different species of campylobacter?
|
C jejuni
C coli |
|
|
Who won the nobel prize for discovering H. pylori?
|
Barry Marshall and Robin Warren
Swallowed it themselves |
|
|
How does H pylori survive in an acidic environment?
|
□ Urease
® Required for bacteria to survive, but does not cause damage; also produces CO2. ® Allows bacteria to live in stomach ® Converts urea to ammonia, which raises the pH and allows bacteria to thrive. |
|
|
What is the most famous species of Pseudomonas?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Where can Pseudomonas be found?
|
Almost anywhere because it just needs a little ammonia and CO2 to grow
|
|
|
T/F
Pseudomonas is easy to treat |
False
It makes a lot of exopolysaccharides which resist antibiotics |
|
|
Who does Pseudomonas infect?
|
Cystic fibrosis patients, because they can't get it out of lungs
|
|
|
What is the smallest bacteria?
|

Haemophilin
|
|
|
What is the most virulent strain of Haemophilin?
|

Hib
|
|
|
What is the vaccine for Haemophilin made of?
|

Purified PRP vaccine cannot be used on children under 2 because of the polysaccharide capsule
◊ New strategies developed using 3 PRP-conjugative vaccines using proteins derived from Corynebacterium diphtheriae and N. meningitides. |
|
|
Which bacteria leads to whooping cough?
|

Bordetella
|
|
|
How is the virulence regulated for Bordetella?
|
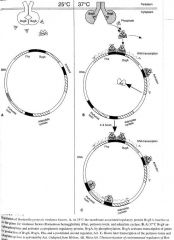
BvgAS two component system
|
|
|
What are the toxins for Bordetella Pertusis?
|

Pertusis AB toxin
Adenylate cyclase Tracheal cytotoxin |
|
|
What is the story behind Legionella?
|

See chart
|
|
|
What kind of disease is legionella?
|

Pneumonia from aquatic sources with headache, fever, chills, dry cough and chest pain
|
|
|
Where does legionella infect?
|

Alveolar macrophages
|
|
|
Is Legionella intracellular or extracellular disease?
|

Intracellular
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of cancer?
|

See Chart
|
|
|
What are the key regulators of the cell cycle?
|

Cyclins and Cyclin dependent Kinases
|
|
|
What are a family of nuclear proteins involved in the progression of cell cycles, no enzyme activity?
|

Cyclins
|
|
|
What is another term for commensile bacteria?
|
Autochthonous
Species characteristically in a particular habitat |
|
|
What are the Orange complex components?
|
Oh My eU Cant Play Pool For Shi
Middle eUbacterium Campylobacter Prevotella Peptostreptococcus Fusobacterium Streptococcus constellatus |
|
|
Which oral bacteria have black pigments?
|
Pg
Prevotella |
|
|
Which bacteria contribute to ANUG?
|
F. nucleatum
T. Denticola (spirochetes) |
|
|
Which bacteria contribute to LJP?
|
AA
|
|
|
Which bacteria contribute to perio abcess?
|
PG
F.nucleatum |
|
|
Which bacteria contribute to Rapidly Progressing Periodontitis?
|
AA
PG Spirochetes |
|
|
Which bacteria contribute to Refractory Periodontitis?
|
Tannerella Forsythia
|
|
|
Which oral bacteria is an early colonizer that has an amphipathic relationship with host?
|
Actinomyces
|
|
|
Which bacteria is an early colonizer that is an important determinant in plaque?
|
S. Sanguis
|

