![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
microphone |
device that changes acoustic energy into an electric current (can be altered and manipulated) |
|
|
transducer |
device that converts one form of energy into another form of energy |
|
|
frequency response |
difference between what frequencies a performance is actually transmitting to what the microphone is capturing |
|
|
flat response |
sensitive to all frequencies; reproduces sounds with little or no variation from the original sound |
|
|
polar pattern |
how sensitive a microphone is to sounds arriving at different angles about its central axis |
|
|
high pass filter |
allows frequencies above a designated point on the frequency spectrum to pass through unaffected and attenuates or decreases the amplitude of frequencies below that point; offer greater control over what is captured from a performance |
|
|
omnidirectional polar pattern |
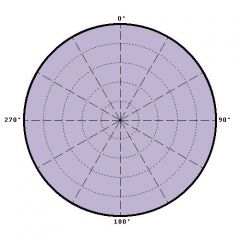
equally sensitive to sound sources from any direction; 360 degree pickup |
|
|
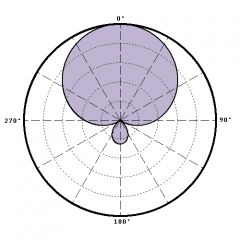
cardiod polar pattern |
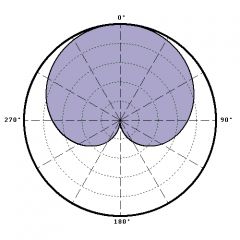
"shape of a heart"; more sensitive in the front and discriminates rear sound sources; 120 degree pickup |
|
|
super cardiod polar pattern |
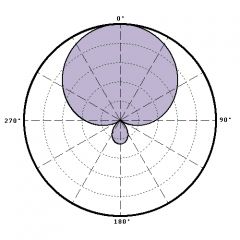
rejection of sound from the side is increased causing the front to be more sensitive |
|
|
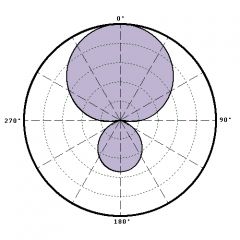
hyper cardiod polar pattern |
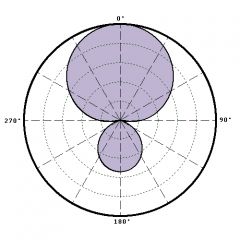
rejects side sound source more than super cardiod but picks up more sound from the rear; 100 degree pickup |
|
|
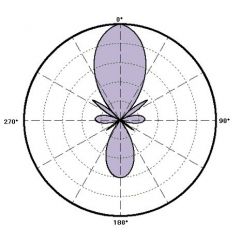
ultra cardiod polar pattern |
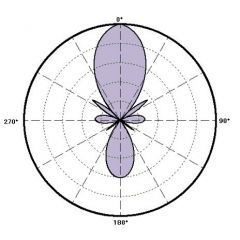
more sensitive to the front compared to the back and focuses on a smaller front area; "trades" some side rejection |
|
|
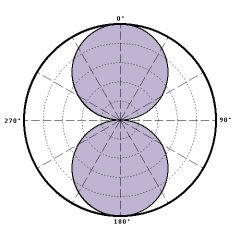
bidirectional or figure 8 polar pattern |
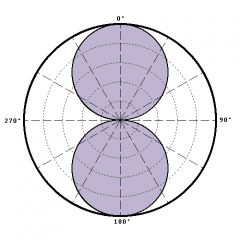
equally sensitive to front and rear sound sources; almost no sensitivity to the side sound source; front and back pickup |
|
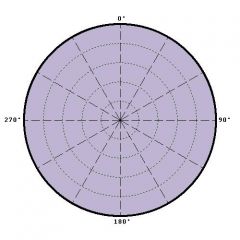
|
omnidirectional polar pattern |
|
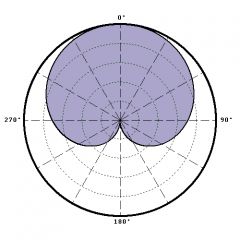
|
cardiod polar pattern |
|
|
super cardiod polar pattern |
|
|
hyper cardiod polar pattern |
|
|
ultra cardiod polar pattern |
|
|
bidirectional or figure 8 polar pattern |
|
|
signal-to-noise ratio |
measure of amount of noise to the amount of signal produced by an electric component |
|
|
impedence |
measure of resistance to the flow of electricity; measured in ohms |
|
|
loading down |
makes a microphone lose its level, distort, or sound thin |
|
|
sound pressure level (SPL) |
measure of the amplitude of a sound |
|
|
distortion |
alternation of the original shape (or other characteristic) of something (ie: object, image, sound, or wavelength) |
|
|
analog distortion |
when the voltage exceeds the amount of amplitude allowed by the electronic components of the piece of gear |
|
|
maximum SPL rating |
maximum amount of decibel level a microphone can accept before the output distorts |
|
|
microphone sensitivity |
amount of voltage produced when exposed to certain sound pressure levels |
|
|
condenser microphone |
use a capacitor; voltage is created by the diaphragm changing the distance between two plates |
|
|
ribbon microphone |
use a corrugated piece of metal suspended in a magnetic field; voltage is created through induction |
|
|
dynamic microphone |
use a diaphragm attached to a moving coil that surrounds a magnet; voltage is created through induction |
|
|
carbon microphone |
voltage is created through the use of loosely packed granules of coal-like material; among the first microphones created |
|
|
Who invented the first microphone? What year? |
Alexander Graham Bell in 1876 |
|
|
Who invented the carbon microphone? What year? |
David Edward Huges in 1878 |
|
|
Who invented the condenser microphone? What year? |
Edward Christopher Wente in 1916 |
|
|
Who invented the ribbon microphone? Between what years? |
Dr. Henry F. Olsen between the 1920s and 1930s |
|
|
Who invented the transverse current carbon microphone? During what years? |
Georg Neumann in the 1920s |
|
|
types of condenser microphones |
-Neumann U87 -AKG C414 -Neumann/Telefunken U47 -AKG/Telefunken Ela M 251 -Neumann KM 84 -Neumann M 49 |
|
|
types of dynamic microphones |
-Shure SM 57/58 -Sennheiser MD 421 -Shure SM7B -ElectroVoice RE20 -AKG D112 -Beyer Dynamic M 201 |
|
|
types of ribbon microphones |
-Royer R121 -Coles 4038 -RCA 77D -El Diablo |
|

|
Neumann U87 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
AKG C414 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
Neumann/Telefunken U47 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
AKG/Telefunken Ela M 251 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
Neumann KM 84 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
Neumann M 49 (condenser microphone) |
|

|
Shure SM57 (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
Shure SM58 (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
Shure SM7B (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
ElectroVoice RE20 (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
AKG D112 (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
Beyer Dynamic 201 (dynamic microphone) |
|

|
Royer R121 (ribbon microphone) |
|

|
Coles 4038 (ribbon microphone) |
|

|
RCA 77D (ribbon microphone) |
|

|
El Diablo (ribbon microphone) |
|
|
What was the first microphone called? |
A liquid transmitter |
|
|
Phantom power |
A voltage that powers some of the components in most condenser microphones; usually a button that is pressed up on a pre-amp or mixing console |

