![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
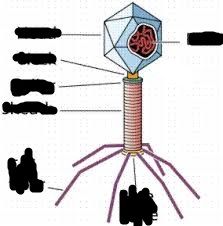
Name each part of the bacteriophage |
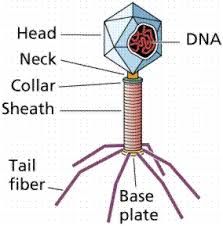
Head, Neck, collar, sheath, tail fiber, base plate, dna on the inside. picture does not show: capsid ( entire thing) site of injection ( bottom of base plate) |
|
|
What is a bacteriophage? |
a virus that will attach and reproduce in a bacterium |
|
|
What are the 4 stages of viral replication? |
1. attachment/ entrance 2. synthesis- of protein / nucleic acid units 3.brings the units together 4. release -of new virus particles |
|
|
What is the difference between the virulent phage and temperate phage? |
virulent: (violent) happens quickly temperate: slowly |
|
|
What is the difference of lysis and lysogenic? |
lysis:bursting open of the cell lysogenic: takes longer |
|
|
What is the genetic material? |
nucleic acid ( DNA/ RNA) |
|
|
Identify the name of the protein covering |
capsid |
|
|
what are the 5 kingdoms? |
Protista, monerans, plantae, animalia, fungi. |
|
|
What is KPCOFGS |
Kids Play Catch On Friday Good Stuff Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species |
|
|
Binomial Nomenclature |
a method of naming organisms by using 2 names, the genus and species name. |
|
|
Phylogeny |
history of the evolution of a species |
|
|
Dichotomous Key |
two-part keys used to identify things |
|
|
Taxa |
a group |
|
|
Taxonomy |
classification of organisms |
|
|
What are the 2 main reasons for taxonomy |
to identify things and groupings. |
|
|
what is the difference between genus and species |
Genus: How they are similar, capital letter Species: how they are individual, small letter |
|
|
What is a virus |
non cellular particle made up of proteins and genetic material - biological particles - Don't have living cell characteristics - Can only live with the help of a living cell. |
|
|
What are the 2 types of reproduction called? |
Lysis and lysogenic. |
|
|
Endemic |
diseases that are around all the time such as the common cold |
|
|
Epidemic |
when a disease starts to spread rapidly |
|
|
Pandemic |
a worldwide spread infectious disease |
|
|
Interferon |
small proteins mad when a virus succeeds in invading an animal cell |
|
|
oncogenic |
the causing development of a tumor |
|
|
vaccines |
solutions prepared from viral components or inactivated viruses |
|
|
what is the non-specific and specific body defense system |
Non-specific: skin, oils/sweat, mucous, cilia, stomach acid specific: fever, immune system/ antibodies, drug therapy |
|
|
What is the phylogeny of the virus |
- ancestors were organisms that lived as parasites - free-living forms that later became parasites -viruses arose from detached fragments of genetic material |
|
|
what is the most accepted phylogeny of the virus |
viruses arose from the detached fragments of the genetic material |
|
|
what is host specificity? |
viruses only enter specific hosts or host cells |
|
|
What happens in the lytic pathway? |
steps take place quickly, resulting in the host cell dying after its contents are released. The entire process from penetration to lysis is called the lytic cycle. |
|
|
What is the cause of lysis? |
the virulent phage |
|
|
What happens in the lysogenic pathway? |
The virus doesn't kill the host cell outright. It may take go a long time without any harm to the host. Bacteriophages that do not cause lysis are temperate phages. |
|
|
What is a prophage? |
genetic material of a bacteriophage |
|
|
What was Louis Pasteur responsible for? |
creating the vaccine for rabies |
|
|
What was Carolus Linnaeus responsible for? |
came up with the theory binomial nomenclature |
|
|
What was Edward Jenner responsible for? |
creating the vaccine for smallpox |
|
|
What was Jonas Salk responsible for? |
creating the vaccine for Polio |
|
|
What is rabies? |
the virus migrates from the blood into the nervous system where it destroys cells, causing convulsions |
|
|
What is small pox? |
invades the white cells of the body |
|
|
what is Polio? |
left people crippled for life |

