![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Can you vaccinate neonatal animals against E.coli?
|
No, don't mount immune animals
|
|
|
Treatment for E.coli
|
* fluid & electrolytes
* antibiotics should not be used indiscriminately b/c salmonella can take over if natural flora killed off *vaccines can be used to treat endotoxemia * antibiotics given IV to treat septicemia |
|
|
Are there good vaccines for Salmonella ?
|
No, cannot vaccinate animal that are carrier - also intracellular agent so difficult to detect
|
|
|
What zoonotic bacteria spread from cats, rats, (endemic to certain parts of usa wild animals have it and can ingest or flea bites)?
|
Yersinia pestis <- causes plague
|
|
|
What antibiotic effective for Yersinia?
|
tetracycline
|
|
|
T/F Shigella infects cattle, pigs, horses, etc.
|
False; Shigella
pathogen to humans/primates, can infect dogs but don’t show disease, does NOT infect cattle, pigs, horses, etc. |
|
|
T/F Penicillin is effective against Enterobacteriaceae
|
False
|
|
|
T/F Salmonella can cause enteritis and septicemia; septicemia in pregnant animals may lead to abortion
|
True; esp. associated pigs
|
|
|
T/F Salmonella, Clostridrium, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella are all in Enterobacteriaceae family.
T/F Enterobacteriaceae are gram positive cocci and facultative anarobes |
False; Clostridrium is NOT; others are
False; Enterobacteriaceae are gram negative rods and facultative anarobes, can survive in either environment |
|
|
How do you discriminate between E.coli and Salmonella?
|
* E.coli can ferment lactose on MaConkey agar
|
|
|
saprophytic (in decaying material) bacteria, found in mucous membranes, skin, opportunistic organism i.e. in wound infections
|
Pseudomonas
opportunistic, not usually cause of major outbreaks, causes sporodic disease, immunodef. more susceptible e.g. burn infection, otitis externa in dogs |
|
|
T/F Pseudomonas causes septicimeia, abortion, diarrhea in cattle?
|
False
|
|
|
What disease is Pseudomonas associated with in pigs?
What disease is Pseudomonas associated with in sheep? |
often carriers
Fleece rot |
|
|
What disease is Pseudomonas associated with in mares?
|
Genital tract infection, Ulcerative keratitis
|
|
|
Treatment for Pseudomonas ?
|
often drug RESISTANT, need to do sensitivity test
penicillin= NO; gentamicin <-YES. can also use amikacin; or polymyxin for topical use |
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause Hemorrhagic pneumonia in ___ frothy bloody discharge from nose
|
in mink
|
|
|
Burkholderia mallei causes ?
endemic to where? |
Burkholderia mallei causes 'Glanders'
exotic disease, endemic to Africa and mideast |
|
|
Diagnosis of Glanders?
|
Mallein test - interpalpebral test for DTH
- look for drooping of lower eyelid "mallein" is extract from Burkholderia mallei |
|
|
Treatment for Glanders?
|
* don't use antibiotic, NOT permitted
* became carrier, spread to other animals * cannot remove completely * cull infected animals? |
|
|
lumpy jaw which is caused by ?
|
- Actinobacillus bovis
|
|
|
Actinob. equuli causes ?
Explain pathogenesis: |
A. equuii : causes SLEEPY FOAL disease
- commensal of intestine, if immunosuppressed causes septicemia (animal become dull, sleepy) and infect kidney |
|
|
Actinobacillus suis causes :
|
Actinobacillus suis
* causes septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis in pigs * commensal of pig farms |
|
|
Actinobacillus suis antibiotic?
|
Treat with ampicillin or TMS
|
|
|
Past. multocida causes disease in?
Hint: PMS |
* associated w/dogs and cats in mouth
(not large animals) * enter via cut in mouth * rabbits (Hint: P. Multicida Snuffles) * birds |
|
|
Produces a leukotoxin, so vaccines are made with a leukotoxin Ag
|
Mannheimia haemolytica:
|
|
|
Mannheimia haemolytica do NOT infect ?
|

does not infect cats, dogs, pigs, etc.
only ruminants |
|
|
- Mannheimia haemolytica causes ____ in cattle
o ___ in sheep and goats |
SHIPPING FEVER in cattle
Mastitis (“BLUE BAG”) in sheep and goats ~ endotoxin cause bluish discoloration of mammary gland |
|
|
Are vaccines available in US for shipping fever in cattle?
If so, what do they protect against? |

Yes, protect cattle against leukotoxin of Manheimia haemolytica
|
|
|
Causes snuffels in rabbits?
|
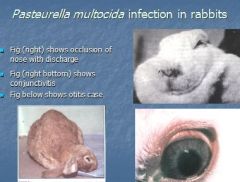
Past. multocida
|
|
|
Francisella tularensis causes what zoonotic diseases?
How transmitted? |
Tularemia
cats and dogs can get from rodents, ticks * Humans get it from tick bites and handling contaminated meat |
|
|
Tularemia caused by francisella tularensis in endemic to
|
USA
|
|
|
- Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia, used to be part of Haemophilus genus, causes ____ of swine
|
o causes CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA of swine
|
|
|
Do antibiotic completely remove Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia pathogen?
If the animal survives infection, they become a ____ |
o Antibiotics only reduce the symptoms, they do not get rid of the abscesses in the lungs and the organism survives in them and the pigs act as carriers
|
|
|
Associated GLASSER’S DISEASE in pigs
|
- Haemophilus parasuis -> GLASSER’S DISEASE
HP great desktops |
|
|
- Haemophilus parasuis causes
|
GLASSER'S disease
* septicemia in pigs * pneumonia in pigs * characterized by polyserositis in the pleuro and peritoneal cavity |
|
|
What pathogen transmitted venereally, males can carry the bacterium and transmit infection to females?
|
- Histophilus somni
- Taylorella equigenitalis |
|
|
What pathogens can causes abortion? (4)
|
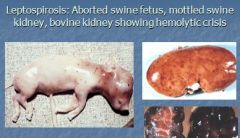
histophilus somni, salmonella, brucella, leptospira
e.g. salmonella typhimurium -> cattle and pigs - Taylorella equigenitalis rarely causes abortion |
|
|
Histophilus somni causes ?
|
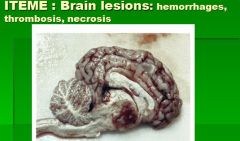
1. infection of genital tract
OR 2. - causes ITEME (infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis) - can multiply in brain - animals look dull and sleepy - can cause pneumonic infection - can also cause pericardial abscesses |
|
|
- Taylorella equigenitalis causes ?
Are serlogical tests available? |
Taylorella equigenitalis causes Contagious Equine Metritis (CEM), animal becomes sterile
- exotic disease, UK, ireland, etc. - eradicated in US NO sero.tests |
|
|
o What causes 1. KENNEL COUGH in dogs, 2. feline bronchopneumonia in cats,
3. causes ATROPHIC RHINITIS in pigs? |
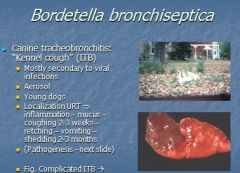
Bordetella bronchiseptica
|
|
|
- Moraxella bovis causes ?
|
Moraxella bovis: causes Infectious Bovine Kerato-Conjunctivitis (IBKC) or “Pink eye” in cattle
* has pilli and attaches to cornea and produced enzymes which damage cornea, cause opacity of cornea and blindness |
|
|
Moraxella bovis treatment?
antibiotics? vaccines? |
* penicillin locally
* tetracycline (oxytetracycline) parenteral o Pilus vaccine available o Treatable in early stages o Flies may transmit infection, use fly repellant tags o Keep animals away from sunlight |
|
|
- Intracellular bacterium
- DOES NOT KILL ANIMALS - Causes ABORTION - genital disease, predilection site is uterus and male genital tract |
Brucella (B. abortus)
|
|
|
Brucella causes
|
Brucella causes: endometritis, placentitis, semen abnormalities
|
|
|
Are there vaccines for treating brucella?
|
Live vaccine available, doesn’t work well at all; can infect humans (old, live vaccine)
|
|
|
Brucella intracellular bacterium, but can it survive in external environment for long time?
|
yes, for approx. 6 months
|
|
|
Is brucella a saprophyte?
|
No
|
|
|
Is brucella communicable to humans?
|
- All form of Brucella are communicable to humans EXCEPT B. bovis
(B.canis, B.suis, B.abortus, etc are zoonotic) |
|
|
Antibiotics for food producing animals with brucella?
|
Do not use antibiotics in Brucella infected food producing animals
|
|
|
- Gram neg curve bacteria (3)
|
Campylobacter, Lawsonia intercellaris, Helicobacter
|
|
|
Campy. jejuni causes ?
can it cause abortion? |
o Causes diarrhea in humans, dogs and cats
o Abortion rarely |
|
|
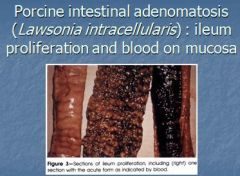
Lawsonia intercellaris causes? in ?
|
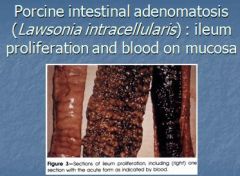
- Causes Porcine intestinal adenomastosis (PIA) in pigs
- Thickening of intestine, animal will have chronic diarrhea like “garden hose” |
|
|
Treatment for Lawsonia intercellaris?
|
- No vaccines
- Treat with tylosin (macrolide-class antibiotic) |
|
|
NAME spiral bacteria belonging to spirochete group, any spirals unlike camphylobacter (curvy)
- Has several serotypes - Predilection site is kidney!!!!!!!!!! Excreted in URINE – contaminates water sources and humans and animals can get infections by drinking contaminated water |
Leptospira
|
|
|
Carriers of leptospira?
|
rodents
|
|
|
Leptospira infectious to dogs and cats?
Zoonotic? |
No, cats can't get leptospira..can eat as many dead rats as they want
Yes, zoonotic |
|
|
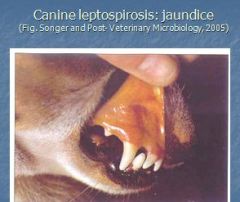
- L. icterrohaemorrhagiae is associated with dogs; what condition?
|
L. icterrohaemorrhagiae (dogs) -> jaundice
|
|
|
What STRAINS of leptospira associated with dogs? (2)
|
L. canicola
L. icterrohaemorrhagiae (can be fatal i think) |
|
|
Treatment for Leptospira?
Are vaccine available? Be specific why, why not |
Good vaccines available
- There are vaccines for dogs – outer sheath protein Ag - Tx: penicillin, streptomycin, tetracyclines, DOXYCYCLINE for dogs |
|
|
Brachyspira
- B. hyodysenteriae Causes? Treatment? Vaccine? |
* Causes swine dysentery
o Gram stain: fecal material, spiral bacteria seem o Culture on special BA (anaerobic) o No vaccines (intracellular?) o Tx: tylosin (spirocete = tylosin) o Disinfect area and keep animals off for 2 months |
|
|
Leptospira can cause meningitis in humans?
|
True
|
|
|
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae causes?
in ? aerobic? carriers? |
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae causes: swine dysentery
anaerobic, O2 tolerant Disease limited to intestine Carrier pigs (rats, mice temporary) |
|
|
Treatment for brachyspira hyodysenteriae ?
Hint: what's good antibiotic for curvy & spirocetes? |
* Antibiotics (e.g. Tylosin) in feed for prevention and treatment effective
* Sanitation/ disinfection concurrently Rest for 60 days (organism dies off) * Replacement pigs – from known source Quarantine and medication |
|
|
How to culture - B. hyodysenteriae?
|
Culture on special BA (anaerobic)
|
|
|
Swine dysentery: Clinical signs
|
Swine dysentery: Clinical signs, lesions (hemorrhagic colitis)
|
|
|
Borrelia: B. burgdorferi causes?
|
LYME DISEASE
|
|
|
Treatment for lyme disease?
|
Treatment/ control: doxycycline (tetracycline) or other antibiotics 4 weeks
Vaccine (outer sheath antigen – ospA), tick control |
|
|
What do all have in common?
Fusobacterium Mycoplasma Chlamydiae Ehrlichia Rickettsia |
Non spore-forming anaerobes
Fusobacterium Mycoplasma Chlamydiae Ehrlichia Rickettsia |
|
|
causes calf dyptheria
|
- Fusobacterium necrophorum
Two forms of calf diphtheria. Most common is acute oral (mouth) infection, seen in calves less than 3 mo. old. Second form is seen in older calves and affects the larynx, Both caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum, which also causes foul-in-the foot and liver abscesses in older cattle. |
|
|
- Causes contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP) in cattle
|
Mycoplasma mycoides
- No cell wall - anarobe, non spore forming |
|
|
Is contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP) in cattle fatal?
What causes it? |
Yes
Mycoplasma mycoides causes contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP) |
|
|
Can you culture Mycoplasma on Mac or BA?
Are vaccine available for Mycoplasma? Antibiotics? |
No, can't culture this way, they need a soft agar media with 20% serum
No, vaccine not available, and antibiotics may creat carrier state in CBPP; test and slaughter policy practiced -> with less contagious Mycoplasma diseases, tylosin a/o tetracycline are effective |
|
|
Can mycoplasma mycoides kill dogs in large numbers?
|
No
|
|
|
Is mycoplasma mycoides endemic to US or exotic disease?
|
exotic dz
|
|
|
Mycop. gallisepticum causes ?
|
M. gallisepticum
* causes chronic respiratory disease (CRD) in chickens |
|
|
Mycop. felis causes ?
|
conjunctivitis in cats
|
|
|
Chlamydiae, Ehrlichia, Anaplasma, Rickettsia, Neorickettsia, Coxiella, Bartonella: all treated with ??
|
Clamydiae, Ehrlichia, Anaplasma, Rickettsia, Neorickettsia, Coxiella, Bartonella: all treated with TETRACYCLINE
|
|
|
Clamydiae, Ehrlichia, Anaplasma, Rickettsia, Neorickettsia, Coxiella all treated with ?
|
: all intracellular bacteria; treated with tetracycline
|
|
|
- Causes: TRACK FEVER in dogs and hemorrhagic fever
|
Ehrlichia canis:
|
|
|
Ehrlichia does not affect ??
|
Ehrlichia does not affect cats
|
|
|
___ causes ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER
|
Rickettsia
|
|
|
Rickettsia (RMSF) is disease in ?
|
Rickettsia in dogs and humans; does not affect cats
|
|
|
Neorickettsia causes ___ in ____
|
Neorickettsia causes salmon poisoning in dogs, not cats
|
|
|
Coxiella burneti causes ____ in _____
How transmitted? |
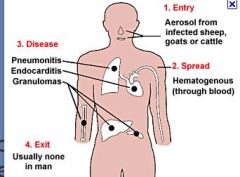
Coxiella burneti causes Q FEVER in ruminants and humans
- can infect placenta, abortion, fluid infective e.g. milk, urine, feces - zoonotic pathogen! |
|
|
vector for ehrlichea?
|
ticks
|
|
|
causes "cat scratch disease"
|
bartonella
|
|
|
cause ovine foot rot
|
- Fusobacterium necrophorum + Dichelobacter nodosus
|
|
|
T/F Potomac Horse Fever (Neorickettsia/Ehrlichia) can cause abortion ?
T/F Potomac Horse Fever (Neorickettsia/Ehrlichia) not fatal |
True
False, up to 30% cases are fatal |
|
|
Anaplasma and Neorickettsia are treated with ?
|
oxytetracycline
|
|
|
Can cause mastitis in cattle? (5)
|
Streptococcus (3)
Actinomyces pyogenes Enterobacteriaceae coli -> coliform Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
Can cause UTI in dogs? (name 5)
|
Enterobacteriaceae coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae Proteus mirabilis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Staphylococcus (3) |
|
|
Is mycoplasma fatal in dogs?
Is mycoplasma fatal in cattle? |
No, not usually
- M. mycoides fatal in cattle, but mild in dogs |
|
|
Causes pneumonia in cattle?
|
Enterobacteriaceae coli -> cattle
Klebsiella pneumoniae -> cattle Pasteurella multocida -> cattle Pseudomonas aeruginosa -> dogs and cats, sheep, cattle |
|
|
Can you use penicliin for mycoplasma infection?
Why? |
No, have no cell wall
|
|
|
Where might one find mycoplasma infection?
|

Respiratory illnesses in ruminants (CBPP) and pigs
Also conjuctivitis in cats MYCO MYC...Ck Bt Plw Pfr |
|
|
Aside from Mycoplasma, what else could cause conjunctivitis in eye of cat?
What antibiotic could you use to treat both? |
Chlamydia
|
|
|
Salmonella enterica causes disease in?
Salmonella dublin causes disease in? |
not species specific; all animals
Dublin? in cattle, sheep, horses, dogs |
|
|
Salmonella typhimurium causes disease in?
Salmonella typhi causes disease in? |
many animals, humans included
humans |
|
|
Salmonella cholerasuis causes disease in?
|
pigs
|
|
|
which salmonella serovar causes disease in chicks? in US?
|
Salmonella pullorum, called Pullorum disease; not common in US
Hint: both bird serovars end w/-rum |
|
Which salmonella serovar causes disease in adult birds outside US?
What name of disease? |
S. gallinarum, disease called Fowl typhoid; not common in US
|
|
|
Which pathogen causes typhoid in humans?
|
Salmonella typhi
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic Colitis is associated with what ?
|
Shiga toxin producing E.coli (STEC), a pathogenic strain
|
|
|
E.coli O157: K88 ; H2 (pig)
Pathogenic strains are classified by serotyping. What antigens are {O, K, H} associated with? |
O: cell wall
K: capsule and pilli antigen H: flagella |
|
|
Which of following is not a "coliform"?
Klebsiella E.coli Salmonella Streptococcus |
Coliform bacteria are Gram-negative non-spore forming rods which can ferment lactose.
Therefore, Salmonella (NLF) and Strep (gr+) cannot be included |
|
|
Can coliforms cause mastitis in cattle?
|
yes
|
|
|
Atrophic Rhinitis
|
Pasteurella multocida -> pigs
|

