![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tiny satellite colony around Staphaureus |
Haemophilus Infleunza |
|
|
Haemophilus Species |
H. Infleunzae H. Parainfleunzae H. Ducreyi |
|
|
Haemophilus (Specimen Requirements) |
1-General principles 2-Susceptible to drying and extreme temperatures -> Immediate plating 3-Special Measurements for H. Ducreyi recover from genital ulcers |
|
|
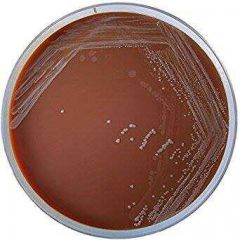
Haemophilus (General Characteristics) |
Gram - Coccobacilli Oxidase Variable Catalase + Non-pigmented Slightly yellowish Ultrastructural features similar to other pathogenic organisms All members are aerobic or facultative anaerobic Fastidious organisms Cannot grow on MacConkey |
|
|
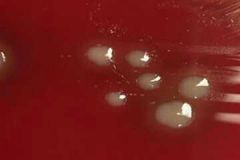
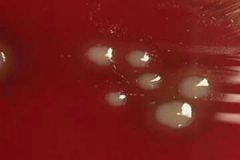
X and V Growth Requirement Test |
Principle 1- X and V factor disks are paper disks impregnated with X (Hemin) and V (NAD: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) growth factors 2. Ddifferentiate Haemophilus species based on their requirements for these growth factors Procedure 1- Inoculate Muller Hinton agar with the bacterial suspension using a sterile swab to obtain confluent growth 2- Aseptically apply one X factor disk, one V factor disk, and one XV factor disk and slightly press down to ensure full contact with the medium 3- Incubate for 18-24 hrs at 35-37C in 3-5% CO2 4- Examin for growth around the disks Results: 1- Growth around X and XV disk factors --> factor X is required by the organism 2- Growth around V and XV disk factors --> factor V is required by the organism 3- Growth around XV factor only --> factorsnX and V are required by the organism to grow Precautions: 1- Do not use blood and chocolate agar 2- Blood has X factor (Hemin) and Chocolate has X and V factors (Hemin and NAD: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) 3- Give false positive results Bacteria: Haemophilus |
|
|
Haemophilus (Anitmicrobial Susceptibility Testing) |
According to CLSI: 1- Use HTM ( Haemophilus Test Medium) instead of Muller Hinton Agar 2- Has the necessary nutrients and growth factors required for these fastidious organisms' confleunt growth |
|
Identify
|
Haemophilus Species 1- Non-pigmented 2- Slightly Yellowish in color |
|
|
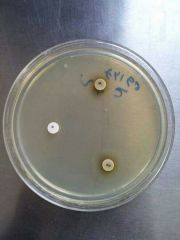
Horse blood- bacitricin Agar |
1- Solid Medium 2- Quantitative procedures 3- Selective isolation 4- Haemophilus Species (H. Infleunzae) 5- Respiratory clinical specimen |
|
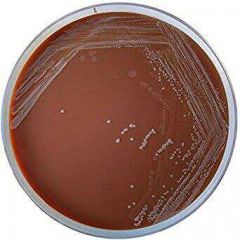
Identify |
Horse-blood-bacitricin Agar 1- Solid Medium2- Quantitative procedures3- Selective isolation4- Haemophilus Species (H. Infleunzae)5- Respiratory clinical specimen |
|
|
Beta-Lactamase Detection Test |

Principle: 1- Determines the ability of some bacteria to produce beta lactamase enzyme that hydrolyze the beta lactam-ring component destroying the antimicrobial activity of some beta-lactam drugs. 2- Chromogenic Cephalosporins (beta-lactam antimicrobial agent) changes the color from yellow to pink) when their beta-lactam ring has been hydrolyzed by the beta lactamase enzyme produced by the tested organism. Procedure: 1- Place a beta-lactam disk on a clean glass slide. 2- Hydrate it by a dropper and distilled water 3- Rub the colony to be tested on the hydrated disk by a wooden stick 4- Examin Change in color in the inoculated area within 5s-10min Results 1- Deep Pink Color --> + 2- Yellow Color (no change in color) --> - Bacteria: 1-Haemophilus Infleunzea +
|
|

Identify:
|
Beta lactamase test Principle:1- Determines the ability of some bacteria to produce beta lactamase enzyme that hydrolyze the beta lactam-ring component destroying the antimicrobial activity of some beta-lactam drugs.2- Chromogenic Cephalosporins (beta-lactam antimicrobial agent) changes the color from yellow to pink) when their beta-lactam ring has been hydrolyzed by the beta lactamase enzyme produced by the tested organism.Procedure:1- Place a beta-lactam disk on a clean glass slide.2- Hydrate it by a dropper and distilled water3- Rub the colony to be tested on the hydrated disk by a wooden stick4- Examin Change in color in the inoculated area within 5s-10minResults1- Deep Pink Color --> +2- Yellow Color (no change in color) --> -Bacteria:1-Haemophilus Infleunzea + |
|
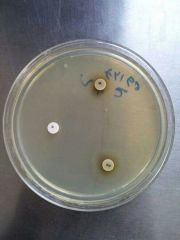
Identify (test) |
X and V Growth Requirements Tests Principle1- X and V factor disks are paper disks impregnated with X (Hemin) and V (NAD: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) growth factors2. Ddifferentiate Haemophilus species based on their requirements for these growth factorsProcedure1- Inoculate Muller Hinton agar with the bacterial suspension using a sterile swab to obtain confluent growth2- Aseptically apply one X factor disk, one V factor disk, and one XV factor disk and slightly press down to ensure full contact with the medium3- Incubate for 18-24 hrs at 35-37C in 3-5% CO24- Examin for growth around the disksResults:1- Growth around X and XV disk factors --> factor X is required by the organism2- Growth around V and XV disk factors --> factor V is required by the organism3- Growth around XV factor only --> factorsnX and V are required by the organism to growPrecautions:1- Do not use blood and chocolate agar2- Blood has X factor (Hemin) and Chocolate has X and V factors (Hemin and NAD: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)3- Give false positive results Bacteria:Haemophilus |
|
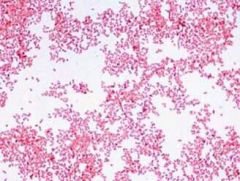
Identify |
Pleomorphic Gram - Coccobacilli Haemophilus |
|
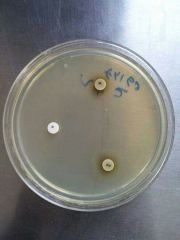
Identify |
1- X factor is required for growth --> H. Ducreyi |
|
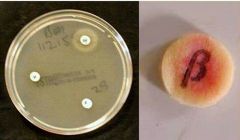
Identify |
H. Infleunzae 1- Requires both X and V factors 2- Beta lactamase positive |
|
|
H. Infleunza |
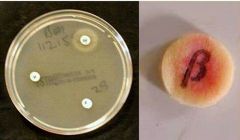
1- Gram negative coccobacillin (on chocolate agar) 2- Factor X/ Factor V/ Factor XV : -/-/+ 3- Beta Lactamase Positive |
|
|
Tests 1- Gram negative coccobacillin (on chocolate agar) 2- Factor X/ Factor V/ Factor XV : -/-/+ 3- Beta Lactamase Positive |
H. Infleunzea |
|
|
H. Ducreyi |
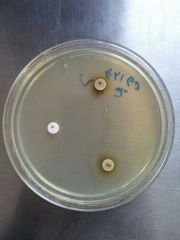
1- Gram negative coccobacillin (on chocolate agar) 2- Factor X/ Factor V/ Factor XV : +/-/+ |
|
|
Tests 1- Gram negative coccobacillin (on chocolate agar) 2- Factor X/ Factor V/ Factor XV : +/-/+ |
H. Ducreyi |
|
|
Tests 1- Gram negative coccobacillin (on chocolate agar) 2- Factor X/ Factor V/ Factor XV : -/+/+ |
H. Parainfleunzea |
|
|
Haemophilus Detection |

1-Direct Detection by light microscopy (pleomorphic gram - coccobacilli) 2-Commercial available latex agglutination kits for the detection of H. Influenzea type b capsular polysaccharide |
|
|
Muller-Hinton-based Chocolate Agar |
1- Enriched Medium 2- Isolation and Cultivation 3- Fastidious Organisms 4- Particularly, H. Ducreyi 5- Supplemented with 1% Isovitalix 6- Supplemented with 3ug/ml Vancomycin for thr inhibitiom of gram + organisms coloniIng the genital tract |
|
|
Heart-Infusion-based Agar |
1- Enriched Medium 2- Isolation and Cultivation 3- Fastidious Organisms 4- Particularly, H. Ducreyi 5- Supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum 6- Supplemented with 3ug/ml Vancomycin for thr inhibition of gram + organisms colonizing the genital tract |
|
|
Burkholderia (General Characteristics) |
1- Previoudly a part of pseudomonas (Genus) 2- Gram - 3- Rod-shaped Bacteria (Bacilli) 4- Oxidase Positive 5- Non-Lactose Fermenter 6- Obligate Aerobic 7- Motile by means of single or multiple polar flagella (except B. Mallei) 8-"Grows on MacConkey |
|
|
Burkholderia (Species) |
Human pathogen: 1- B. Cepacia (pulmonary infection in patients with cystic fibrosis CF) 2- B. Pseudomalliae Others 3- B. Malliae |
|
|
Burkholderia (Media) |
Broth 1- Thioglycolate 2- Broth-blood culture systems Agar 1- Blood Agar 2- Chocolate Agar 3- MacConkey Agar 4- OFPBL: Oxidative-fermentative-polymyxin B-bacitricin- lactose agar 5- PC: Pseudomonas Cepacia agar 7- Ashdown's Agar |
|
|
OFPBL: Oxidative-fermentative-polymyxin b-bacitricin-lactose Agar |
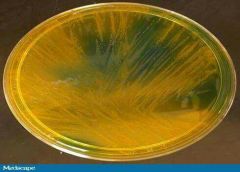
1- Selective 2- Solid Medium 3- Qualitative Procedures 4- Detection and isolation 5- B. Cepecia 6- From clinical speciemem (Respiratory Secretions of CF patients) 6- Colonies: Yellow with yellow halos |
|
|
Pseudomonas Cepacia (CP) Agar |

1- Selective 2- Differential 3- Detection and isolation 4- B. Cepacia 5- Fromclinical specimen and mixed cultures of CF patients Contains: 6- Bile salts and crystal violet which inhibit gram + bacteria 7- Polymyxin B and Ticarcillin which inhibut gram - bacteria 8- B. Cepacia utilizes pyruvate present in the medium --> alkaline products changing the medium color from bright pink to red (phenol red is the indicator) |
|
|
Ashdown's Medium Agar |
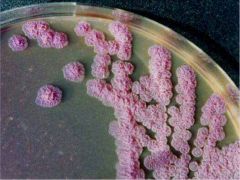
1- Selective 2- Differential 3- Isolation and detection 4- B. Pseudomalliae Contains 5- Crystal violets and gentamicin to inhibit the growth of the other bacteria 6- B. Pseudomalliae take up the neutral red ( in medium) to produce flat wrinkled purple colonies |
|
|
Vibrio (General Characteristics) |
1- Gram - 2- Rod-shaped (Bacilli) 3- Oxidase + 4- Non-lactose fermenter 5- Glucose fermenter 6- Beta Hemolytic 7- Grow on MacConkey |
|
|
Vibrio (Specimen Requirements) |
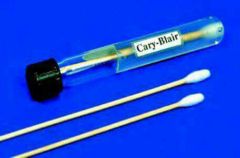
1- General principles 2- Stools samples suspected to contain Vibrio specieaahould be colleted in Cary-blair medium |
|
|
Vibrio (Media) |
Broth: Thioglycolate Broth-blood culture system Alkaline peptone water broth Agar: 1- Blood (Beta Hemolytic) 2- Chocolate 3- MacConkey (NLF) 4- TCBS: Thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar |
|
|
Alkaline Peptone Water Broth |

1-Enrichment 2- Vibrio species 3- From food, water, and clinical specimen 4- Bacterial sample inoculated, incubated for 5-8 hrs at 35-37C 5- Subcultured in TCBS agar |
|
|
TCBS: Thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar |
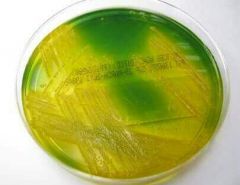
1- Selective Agar 2- Isolation and cultivation 3- Vibrio Species 4- Alkaline pH of the medium enhances the growth of V. Cholerae and inhibits that of others 5- Sucrose (for metabolism) is fermented by the V. Cholerae --> acid end product 6- Colonies yellow and large 7- Bromothymol blue and thymol as indicators |
|
|
Vibrio Cholerae (Direct Detection) |
1- Microscopy: Gram negative bacilli 2- Serotyping of toxigenic strains of V. Cholerae (01 and 0139) using specific antisera. Negative for both strains is reported as non-01 3- ELISA (Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) and commercial available latex agglutination kits for the rapid detection of the toxin |
|
|
Aeromonas Pleisomonas (shigelloides) Chromobacterium (violaceum) (General Characteristics) |
1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase + 4- NLF 5- Glucose Fermenters 7-Grow on MacConkey 6- Aeromonas/ Chromobacterium beta hemolytic Pleisomonas non-beta hemolytic |
|
|
Aeromonas Pleisomonas (shigelloides) Chromobacterium (violaceum) (Media) |
Broth: 1- Thiogylcolate 2- Broth-blood culture systems Agar: 1- Blood Agar 2- Chocolate Agar 3- Maconkey Agar 4- TSA II: Tryptic Soy Agar with 5% SRBC and ampicillin |
|
|
TSA II: Tryptic Soy Agar with 5% SRBC and ampicillin |
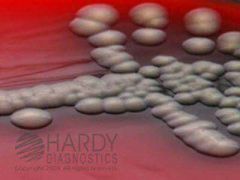
1- Selective 2- Isolation and cultivation 3- Aeromonas spp 4- Ampicillin inhibits Enterobacteriaceae and some gram positive bacteria 5- Colony: Smooth, Convex, Grayish, Beta-hemolytic |
|
|
String Test |

1- Differentiate V. Cholerae (+) from Aeromonas spp (-) since both are isolated feom diarrheal stools/ have same biochemical properties on culture media/ oxidase + 2- Differentiate V. Cholerae (+) from othe Cholerae species 3- Isolated colony (18-24hr) from suspected bacterium is emulsified with Na Deoxycholate (known as bile salts) it lyses the cell releases the DNA. 4- Suspension loses its turbidity and becomes viscous 5- Mucoid string is formed when an inoculating loop is drawn slowly away from the suspension |
|
|
Ekinella w atba3oha |
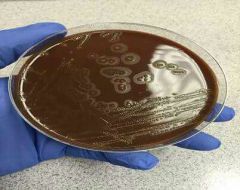
1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase + 4- FA 5- Non-motile 6- Fastidious 7- Do not grow on MacConkey 8- Grow on blood and chocolate 9- Pit the agar |
|
|
Ekinella Spp |
Ekinella Corrodens 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase + 4- Nonmotile 5- FA 6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey 8- Takes its name from its ability to corrode (pit) the agar 9- Exude Chlorine bleach odor 10- non-hemolytic 11- Slight greening may occur Round th colony |
|
|
Pasteurella Multocida |
Pasteurella Multocida 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey 8- Pit the agar 9- Non-hemolytic 11- Translucent 10- Exude must/ mushroom order |
|
|
Actinobacillus (Aggregatibacter) Actinomycetemcomitans |
Actinobacillus (Aggregabacter) Actinomycetemcomitans 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey 8- Non-hemolytic 9- Translucent 10- pinpointed after 24 hr 11- Slight Tinge after 48 hr |
|
|
Kingella Denitrifcans |
Kingella Kingae 1-Small 2- Translucent 3- Non-hemolytic After 24 hr 4- Grow on Thayer-Martin Agar 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey8- Pit the agar |
|
|
Kingella Kingae |
Kingella Kingae 1- Translucent 2- Or slightly opaque 3 - Beta Hemolytic 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey8- Pit the agar |
|
|
Cardiobacterium Hominis |
Cardiobacterium Hominis 1- Circular 2- Smooth 3- Opaque 4- Slight alpha hemolytic After 48 hr 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey8- Pit the agar |
|
|
Capnocytophaga Spp |
Capnocytophaga Spp 1- yellow 2- Pink 3- nonhemolytic 1- Gram - 2- Bacilli 3- Oxidase +4- Nonmotile5- FA6- Grow on blood and chocolate 7- Does not grow on MacConkey 8- Pit the agar After 48 hr |

