![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. The culture of an organism is usually referred to as what? b. Which simple tests does initial identification rely on? (2) c. What does further identification rely on? (3) |
a. Gold Standard b. - Microscopy - Growth Characteristics c. - Biochemical tests - Antigen detection - Toxin demonstration |
|
|
a. When is indirect detection used? b. Name 3 methods of indirect detection |
a. Used on organisms that cant grow b. - Immunofluorescence - PCR (DNA amplification) - Serological diagnosis |
|
|
a. What is 'Serological Diagnosis' b. What does IgM stand for? c. What is IgM? |
a. Identification of antibodies in the Serum b. Immunoglobin M c. - Antibody - Made by B-cells - 1st antibody to appear in response to an antigen |
|
|
During Microscopy, microorganisms are STAINED. a. Name 4 different stains and state which organisms they are used for b. Name the most commonly used stain, what its used for and its effect |
a. 1. Gram stain = Bacteria (gram neg/pos) 2. Cotton Blue = Fungi 3. Darkfield Microscopy = Spirochetes 4. Ziehl-Nielsen = Myobacteria b. - Gram stain - differentiates between gram positive and negative bacteria - Gram+ve = Purple - Gram-ve = Pink |
|
|
State 5 common Morphologies which can be revealed via microscopy
|
1. Cocci 2. Rod 3. Clusters 4. Pairs 5. Chains |
|

|
a. Positive b. Negative c. Lipotechoic Acid d. Techoic Acid e. Lipopolysaccharides f. Peptidoglycan |
|
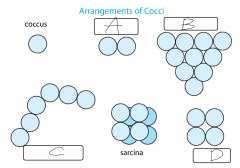
|
a. Diplococci b. Staphylococci c. Streptococci d. Tetrad |
|
|
a. What are Cocci shaped colonies arranged in clusters called? b. Give two examples of bacterial species which - are gram positive and - are arranged as described in part a |
a. Staphylococci b. - S. aureus - S. epidermidis |
|
|
a. Give 3 symptoms of S. aureus infection b. Describe these 3 symptoms c. How do people tend to become infected with S. aureus |
a. - Bacteraemia - Endocarditis - Necroitising Pneumonia b. - Bacteraemia = presence of bacteria in blood - Endocarditis = Inflammation of Endocardium - Necroitising = cells dying due to disease/injury/lack of blood supply - Pneumonia = Lung infection... inflammation of alveoli c. Via Nosocomial outbreaks |
|
|
S. epidermidis: - is a bacteria which lives on __(a)__ and has a __(b)__ relationship - is an __(c)__ pathogen - infections tend to occur in people who are __(d) - is a __(e)__ device infection |
a. the skin b. commensal c. opportunistic d. immunocompromised e. prosthetic |
|
|
a. What is a Virulence Factor? b. Name 3 enzyme Virulence Factors produced by S. aureus c. Name 3 toxin Virulence Factors produced by S. aureus d. Name 2 others |
a. a harmful quality possessed by a microorganism that can cause disease b. - Coagulase - Catalase - Nuclease c. - Toxic Shock Syndrome - Cytotoxins - Exfoliative toxins d. - Slime Capsule - Cell Wall |
|
|
Give 3 ways in which S. aureus can be detected in a laboratory
|
- Coagulase production - Catalase production - DNAase production |
|
|
a. What are cocci shaped colonies arranged in chains called? b. What are the 2 types of groups of bacterial species which are - arranged as referred to in part a and - are gram positive |
a. Streptococci b. - Streptococci Alpha-Haemolytic - Streptococci Beta-Haemolytic |

