![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DISCLAIMER: All information taken from printed handouts issued at late December 23 for new MSA Set.
The print outs used are on the reverse of this flash card.
|
BA 013 - BA Team Leaders BA 001 - Purpose of BA Procedures BA 011 - Physiological effects of wearing BA BA 005 - Safe movement: Doors stairs and landmarking BA 004 - Wearers guidance BA 006 - Search and Rescue Procedures |
|
|
The BA team Leader is responsible for the BA Team whilst in the risk area. What things must they consider when making decisions? |
- The IC/ Sector commandars brief
- Their knowledge & experience
- Any information received from outside risk area
- Visual and other 'cues' inside the risk area (noise/temperature)- Evidence gathered from situation, task and event
- Information from equipment, such as Control Module & TIC- Information from other BA team members |
|
|
What are the duties of a BA team leader? |
- Ensure the BA team is fully briefed
- Ensure any relevant information is passed to the ECO, IC, sector Commandar or other BA teams
- Ensure appropriate firefighting equipment is provided and tested before entering risk area.
- Lead the team to complete allocated tasks and return to ECP
- Promote and maintain regular communications within BA team
- Co-ordinate pressure and telemetry signal checks with ECP
- test communication equipment with the ECO/ BA communications operative. Check radio channel and lock it if possible
- Monitor working conditions, may impact working duration
- Exchange information on pressure readings with ECO if telemetry is lost
- Regularly pass on info on conditions/layout/hazards and BA team status to ECO
- Ensure that when BA teams meet in the risk area, team leaders exchange all relevant information
- Ensure that BA wearers committed as a BA team always remain together.
- Decide whether to continue with operations if comms with ECP fail, recognising that a BA emergency team may be committed
- Prompt BA team members to task rotate
- Ensure that if it is felt necessary to deviate from brief that this is communicated to the IC/sector commander prior to any change in tactics
- Prompt all BA team to operate 'incident state' or 'withdraw' function on control module
- Provide feedback to the officer responsible for the ECP upon exit of the risk area |
|
|
The BA team leader must withdraw the BA team and inform ECO if any of the following occur |
- Any BA team member has uncontrolled loss of air.
- A BA set low pressure warning actuates.
- Any BA team member seems unwell or confused. - Any BA team members control module display becomes faulty or unreadable.
- A BA set DSU Actuates within the team (ECO shou,c also be alerted to this by the ECB)
- Any BA team member indicates they may have been exposed to an irrespective atmosphere due to a dislodged or defective face mask.
- A sustained and/or unexplained breakdown of both radio and telemetry communication
- And BA team member reaches a pre-determined pressure reading set by briefing officer
- An emergency evacuation signal sounds and receipt is confirmed by ECO
- loss of firefighting media
- Conditions at the risk area have deteriorated to the extent that BA team members are exposed to an unacceptable level of risk. |
|
|
What are the 2 circumstances in which Single BA deployment is allowed? |
- In open air - In line of sight from the ECO |
|
|
Considerations of risks when wearing BA |
- Entry to the risk area is defined by the position of entry control. all staff passing entry control must wear RPE
- Firefighters are only to be committed to the risk area wearing BA on the instructions of the IC once the required level of BA entry control is in place
- Multiple BA teams of 2 working together is good practice opposed to large BA teams.
- Where a fire or risk is still present BA teams must be committed with extinguishing media
- The IC should ensure sufficient BA teams are deployed to ensure firefighting BA teams do not have to separate for Hose management whilst inside structures
- No search and rescue team should operate inside a structure that contains smoke filled compartments, that have the potential for any form of Rapid fire progression, without the protection of suitable fire extinguishing media (either carried with them or by another BA team)
- Hose management teams must operate behind the protection afforded by the firefighting team they are supporting. The firefighting team being supported must take all reasonable measures to ensure the conditions the Hose management team are operating in pose no risk of any form of rapid-fire progression.
- BA wearers (both SDBA and EDBA) are only to be used for a 'second wear' in exceptional circumstances (ie. To save salable life)
- During damping down and cutting away operations where fire compartments remain hot/warm the minimum RPE level is breathing apparatus. Unseen fire gases will still be present so therefore particulate filters will not provide the correct level of protection. |
|
|
What are the duties of a BA wearer en-route to incident? |
Nominated BA wearers must not get 'rigged' in BA en-route to incidents |
|
|
Duties of a BA wearer at incident? |
- Don and start in safe air
- Carry out buddy checks
- Ensure the set has a reading of at least 240 bar when going through entry control
- Report to the ECP
- Calculate TAP
- Confirm radio channel
- Establish call sign (BA alpha team 1) - Don BA set and hand BA tally to ECO before entering
- Ensure a BA telemetry signal - Undertake an 'A' or 'B' test (when taking over a set or preparing for a second wear)
- Recieve a brief from the IC or Sector commander (must include: The situation, hazards, where and how to enter, objectives, any. limitations on air, and questions the team has)
|
|
|
Duties of a BA wearer following an incident - testing |
- A BA wearer can only carry out one incident ground 'A' test on their BA set - The BA set is not to be used after the second wear unless a 'B' test has been carried out - If a BA set that has already been worn is then allocated to another BA wearer a 'B' test must be completed. - BA sets that have become heavily contaminated must be bagged on scene and 'B' tested before being worn again - The ECO should be informed if the wearer has completed a fireground 'A' or 'B' test, already worn at incident or feels unfit to wear. - Carry out all incident ground testing away from risk area so that any DSU sound will not be heard by wearers in the risk area - On return to station ensure that the appropriate testing and cleaning is carried out on BA set and ancillary equipment and appropriate logbook and records completed |
|
|
3 post wear health and welfare points |
- On completion of a BA wear, ensure self and other team members are not suffering the effects of heat stress and on the instructions of a relevant officer relax PPE, allow to cool down, hydrate as soon as possible, rest and recuperate.
- BA wearers must report any injury, safety or near-miss events to the IC
- As soon as possible after wearing BA clean and wash hands to reduce the risk of cross contamination from the risk area |
|
|
What 5 effects can working hot conditions can on the body? |
- Fatigue - Confusion - Deterioration in performance and decision making - Reduction in manipulative skills - Adverse effects to vision |
|
|
What 3 ways may BA wearers be subjected to heat? |
- Environmental (heat generated by the environment ie. The fire) - Metabolic heat (heat generated by the BA wearer through normal functions) - Psychological stress (stress or panic, may also increase metabolic heat generation) |
|
|
What is the optimal/ideal core body temperature? |
37 degrees Celsius |
|
|
What will lead to a hyperthermic reaction? |
An increase of 2 degrees core body heat |
|
|
What will lead to a hypothermic reaction? |
A decrease of 2 degrees core body heat |
|
|
What body temperature could be a fatal (emergency action/assistance required) |
An increase of 5 degrees core body temperature |
|
|
What are the 6 main effects on the body's core temperature? |
- Metabolic rate - Environment - Clothing - Age - Fitness - Gender |
|
|
What are the 2 sub categories of Heat exhaustion? |
- Water depletion (intense thirst, rapid pulse, headache, dark urine) - Salt depletion (muscle cramps, abdominal cramps, dizziness, nausea, vomiting) |
|
|
What's the treatment for Heat Exhaustion? |
- Removal from source of heat - Relax dress in shaded area - Drink 1 litre of fluid containing electrolytes - Avoid caffeine and alcohol (due to diuretic properties) - Radial cooling (both arms or full body cold water immersion post incident) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Heat Syncope? |
- Lay down with legs elevated above head - Relax dress in shaded area - Drink water in small sips - No caffeine or alcohol - Radial cooling (both arms or full body cold water immersion post incident) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Heat stroke? |
- Removal from source of heat - Loosen clothing, relax in shaded area - Moisten lips with water - Spray water & use of fans - Place wet sheet over whole body - Call ambulance |
|
|
What is Thermal Loading? |
The build up of metabolic heat in addition to environment heat trapped by PPE unable to leave the body. |
|
|
What things can be put in place at an incident to prevent/control thermal loading/core body heat rising? |
- Shaded holding and recovery area away from the immediate risk area - BA wearers in the holding and recovery area should relax their PPE unless they're an emergency BA team - Drinking water available at the holding and recovery area - Recognise the stresses of the tasks that BA wearers are required to complete and relieve them appropriately - BA wearers should only be committed for second wears in exceptional circumstances (ie. To save saveable life) - The rest and recovery periods should only be shortened in exceptional circumstances (ie. To save saveable life) and no other BA wearers are available |
|
|
What is the guidance following an ambient wear? |
30 min rest and 500ml of cool water |
|
|
What is the guidance following a hot wear? |
60 mins of rest and 1000ml of cool water |
|
|
What 4 things should a IC or SC being informed of BA team entanglement do? |
- Ensure that the officer responsible for the ECP briefs and commits the BA emergency team - Consider declaring a 'firefighter emergancy' - Consider isolation of electrical supplies - Commence accident investigation |
|
|
What are the staircase materials and characteristics? |
- Stone staircase involved in fire should be avoided as they can collapse without warning - Metal staircase conducts heat and electricity - Timber staircases are flammable - Reinforced concrete is relatively safe but extreme temperatures may cause spalling and eventual loss of strength. |
|
|
What signs can indicate conditions on the otherside of a door? |
- If the door has a vision panel it can be used to assess conditions inside the compartment - The door surface may be hot - The paint blistered or PVC deformed - Smoke may be issuing from under the door or around the frame - There may be hazard warning signs indicating what may be on the otherside |
|
|
How could a BA team landmark before entering the building? |
- The type and size of building or structure - The position of the building in relation to its surroundings - Position of the appliances outside the building - LFB equipment committed into the building |
|
|
List some of the hazards that a BA team could encounter at an incident |
- Atmosphere (Atmosphere could be oxygen deficient, toxic, flammable ect) - Temperature (hot or cold) - Physiological strain (raised core temperature leading to poor decision making and exhaustion) - Psychological strain (conditions at incident leading to emotional response) - Reduced visibility (smoke) - Electricity - Cables and structural failure - Environmental (weather, terrain, height, unsafe structures, confined spaces) - Hazardous materials - Manual handling (PPE and SDBA set adds significant weight load for the wearer) |
|
|
What information can be gained under fire & rescue service legislation? |
- Industrial on-site plans - Risk-based geographical information - Locations that require additional control measures (guidelines, EDBA or telemetry repeaters) - RVP points - Areas with limited penetration of radio signals - Resources needed to implement control measures |
|
|
What does ' BA ' mean? |
Breathing Apparatus |
|
|
What is ' C1 '? |
C1 BA radio interface |
|
|
What does ' Comms ' mean? |
Communications |
|
|
What does ' Comms-Ops ' mean? |
Communication operative |
|
|
What does ' CPC ' mean? |
Chemical protective clothing |
|
|
What does ' CU ' mean? |
Command Unit |
|
|
What does ' DSU ' mean? |
Distress signal unit (automatic or manually operated) |
|
|
What does ' DPFM ' mean? |
Dual purpose facemask |
|
|
What does ' EDBA ' mean? |
Extended duration breathing apparatus |
|
|
What does ' ECB ' mean? |
Entry control board |
|
|
What does ' ECO ' mean? |
Entry control operative |
|
|
What does ' ECP ' mean? |
Entry control point |
|
|
What does ' ECPS ' mean? |
Entry control point supervisor |
|
|
What does ' EMU ' mean? |
Electronic monitoring unit |
|
|
What does ' EP ' mean? |
Entry point |
|
|
What does ' ESA ' mean? |
Einheit stecken anschlussfilter (meaning Standard plug-in connection) |
|
|
What does ' GDM ' mean? |
Gas detection monitor |
|
|
What does ' GTS ' mean? |
Gas tight suit |
|
|
What does ' HMEPO ' mean? |
Hazardous materials and environmental protection officer |
|
|
What does ' HSE ' mean? |
Health and Safety Executive |
|
|
What does ' HUB ' mean? |
Telemetry HUB |
|
|
What does ' IC ' mean? |
Incident commander |
|
|
What does ' IS ' mean? |
Intrinsically safe |
|
|
What does ' LED ' mean? |
Light emitting diode |
|
|
What does ' LPW ' mean? |
Low pressure warning (can be electronic or pneumatic in operation) |
|
|
What does ' LPM ' mean? |
Litres per minute |
|
|
What does ' LTS ' mean? |
Liquid tight suit |
|
|
What does ' OIC ' mean? |
Officer in charge |
|
|
What does ' OSG ' mean? |
Operations Support Group (new department name for PEG and BDC) |
|
|
What does ' OSU ' mean? |
Operational support unit |
|
|
What does ' POMS ' mean? |
Purchase order management system |
|
|
What does ' RA ' mean? |
Risk assessment |
|
|
What does ' RPE ' mean? |
Respitory protective equipment |
|
|
What does ' RPELO ' mean? |
Respiratory protective equipment logistics officer |
|
|
What does ' SA ' mean? |
Scientific advisor |
|
|
What does ' SIA ' mean? |
Senior accident investigator |
|
|
What does ' SDBA ' mean? |
Standard duration breathing apparatus |
|
|
What does ' TAP ' mean? |
Turn-around point |
|
|
What does ' TAT ' mean? |
Turn-around time |
|
|
What does ' TNR ' mean? |
Test not recorded |
|
|
What does ' TOW ' mean? |
Time of warning (audible and visual warnings to indicate end of working duration) |
|
|
What does ' TTW ' mean? |
Time to warning (end of working duration and the start Iof safety margin) |
|
|
What does ' USAR ' mean? |
Urban search and rescue |
|
|
Can a firefighter in development be a BA team leader? |
No |
|
|
What information would an IC gather on route and upon arrival at an incident? |
- Number of people involved - Approximate ages, mobility and dependencies - Last known location and activity - Information from fire survival calls (calls to control from people trapped in building) - Location in relation to the fire |
|
|
What 2 thing could an IC do to build a picture of the layout of high rises? |
- In some building lobbies there are sketched layouts of the premises - Send a firefighter to a safe floor to report back the general layout of the floors |
|
|
What is the minimum rank to be a "Search co-ordinator" and what must they wear? |
Sub officer and a surcoat with the insert "Search co-ordinator" |
|
|
What is the role of a search co-ordinator? |
Gather information, assist the IC and recording information on the FIB board |
|
|
What search techniques should be used by BA Teams? |
- At beginning of search spread out wide to cover as much area as possible whilst maintaining contact with each other and the wall - Use the 1.25m of personally line to the maximum - Max of 4 to be connected to ensure no one is more than 6m from team leader in contact with the wall - Team should ensure they search under, in and on all articles of furniture. All spaces large enough to conceal a small casualty should be opened and searched. - The search must be thorough. People trapped by fire or smoke can hide under beds, in cupboards and under clothes. - Furniture that is moved should be put back in its original position. This aids fire investigation, prevents it being searched again and could be another teams landmark. - When turning a corner in a room it is good practice for the whole team to realign themselves by placing their back on the wall before moving off in a new direction. - When opening any door the area behind the door should be swept before moving on. - A pile of boxes, Ladder or chair at top of stairs could indicate someone has made their way to the loft or roof and area should be checked. - All BA teams must give regular progress updates to ECO. - The use of controlled ventilation can be very effective to improve conditions for both teams searching aswell as those being rescued, but this most only be carried out on the orders of IC. - As they progress into an incident, BA teams should landmark the route taken so that they can withdraw with safety and confidence. By doing this they will also pass useful information to the ECO and other teams. |
|
|
What 6 things should a IC take into account when deciding on a search method? |
- Any pre-planning - The number and location of persons involved - The type of structure to be searched - The scale and complexity of the incident - The hazards and risks presented - The other tasks to be achieved (Firefighting, structural safety, shoring etc) |
|
|
What 4 places could a search commence from? |
- The point of entry - The point of greatest danger for casualties within and area - Close to the likely seat of fire - Some other designated point within the structure |
|
|
What 2 types of search procedures are there? |
- Directional - Compartmental |
|
|
What is the fundamental principle of a compartment search procedure? |
For the BA team to attempt to fully search each compartment they enter before moving on to the next compartment |
|
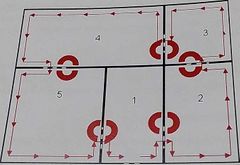
What search procedure is this? |
Directional |
|
|
What 5 considerations should there be when landmarking a casualty? |
- A noticeable landmark such as stairs - Always on brief wall - In a place of safety away from hazards such as heavy smoke - In a simple location for entering team to locate - As close to the exit as feasibly possible |
|
|
What are the steps involved in rescuing a heavy casualty? |
- A radio message sent to entry control stating you've located a very heavy casualty and require an additional BA team with a spare BA set - A plastic salvage sheet should also be requested to use as a sliding rescue sheet - The casualty should be rolled onto their side onto the recovery position (in addition to maintaining an open airway this position places the face close to the floor where the air may be cooler and less contaminated) - With the arrival of the additional BA team the spare BA set facemask should be placed on the casualty and the set started up. - Salvage sheet should be set up next to the casualty and the casualty rolled onto it. - If the BA team still cannot move the casualt out then they should be attended to until the fire is out |
|
|
What is the difference between stage I and stage II BA entry control? |
- More than 1 ECP is required - More than 6 wearers are deployed to the risk area at 1 time - The incident and structures involved are complex and and or the increased deployment of BA, plus the increased risks associated with BA operations, demand a greater degree of control and supervision - BA operations are likely to be Protracted - Guidelines are required - The risks presented to BA teams demand a higher level of BA emergency provision, involving the need for BA emergency teams - EDBA is required - BA telemetry repeater(s) - Confirmed basement fire (where size and layout indicate stage II is appropriate) - BA emergency team(s) have been committed - When chemical protective clothing wearers are out of the line of sight of ECP - When other agencies are being committed in BA |
|
|
What contents are in the BA ECB pouch? |
- A and B guidelines - 14 Aide Memoires - Evacuation Whistle - Entry Control Surcoat (no longer kept in the pouch but needed when setting up ECP) |
|
|
What are the duties and limitations of a ECO? |
An ECO's responsibility is for the control and management of the ECP. An ECO is not responsible for supervising the tasks allocated to BA teams, that responsibility rests with the IC or SC The ECO must not be involved or allocated any other tasks. |
|
|
When nominated by a Officer in Charge an ECO is responsible for the examination and testing of the following: |
- ECB and its telemetry functionality is fully tested, - ECO surcoat - Chinagraph pencils (Black for SDBA or respiratory tally and white for EDBA tally) - Evacuation whistle - Main guideline tallies A+B and branch line tallies 1-4 (FRU only) - BA aides memoire set of 14 - BA guidelines - IEC pack (resuscitator) - ECB tripod and bracket - Thermal imaging camera - Telemetry repeaters (FRU and PL only) - Ensure that the EASE bag and cylinder is available (PL and FRU only) - Ensure the ECB, HUB and its telemetry functionality is fully tested |
|
|
What 4 laminated sheets are available to the entry control point: |
- Incident information - Casualty information - High-rise information - Incident plan (formatted for drawing layout and floor plans |
|
|
What should happen if the ECB fails? |
- The ECO should request a second ECB to use (they must ot leave the ECB themselves) - The ECO must maintain close contact with the BA wearers via radio communications - The time the ECB fai,ed must be reported by the ECO to the IC and they must annotate the ECB accordingly - On acquiring the 2nd ECB the BA tallies can be ransferred, at which point the new ECB will update with the time of warning. All written information must be transfered onto the replacement ECB and the defective ECB retained at the ECP for reference - This second ECB must be operating with the BA tallies inserted and telemetry signal, established within 5 mins of the first ECB failing. If no second ECB is available within 5 mins, or that also fails the IC must consider withdrawing the BA teams - If a prolonged loss of telemetry signal is experienced or the ECO has any concerns for the safety of the BA wearers, inform the person responsible for the ECP and consider initiating emergency procedures |
|
|
If a BA team is required to re-enter the risk area to perform a specific task, they may re-enter providing what? |
- The BA team have remained under the control and supervision of the ECP - There are no doubts about the fitness and wellbeing of any BA wearer for the task to be undertaken - All BA team members must have a cylinder content of at least 210 bar - The task will be of a short duration and the IC or SC considers the BA wearers have sufficient air to complete it and return to ECP before the low pressure warning actuates |
|
|
Other than is exceptional circumstances EDBA wearers should not be used for 're-entry' tasks. True or false? |
True |
|
|
In exceptional circumstances I.e. to save saveable life the IC of SC can recommit BA wearers for a second wear at the same incident if no fresh BA wearers are available. True or false? |
True |
|
|
The ECO must inform the person responsible for the ECP and commit a BA emergency team when: |
A BA team or wearer has not returned to the ECP by their time of low pressure warning and cannot be contacted to confirm their safety and wellbeing - A DSU is heard to have been actuated or is indicated to have been actuated on the ECB - Where audible or visual indications suggest a BA team or wearer appear to be in distress or imminent danger - A prolonged and unexplained breakdown in communications has occurred - A BA team or wearer has requested assistance |
|
|
The emergency team should consist of BA wearers who have not been previously committed. True or false? |
True |
|
|
An emergency BA team must be: |
- Led by a minimum of a leading firefighter - At least as large as the largest BA team or teams working together on the same task - Rigged to the same level of protection as BA teams already committed - Equipped with BA radio communications for the team leader, the same radio channel as BA teams already committed to enable the emergency team - Leader to monitor and communicate with committed BA teams - One 'EASE bag' carried by every two/four BA wearers - BA emergency team armbands |
|
|
An emergency crew on standby will need to provide or be provided: |
- An additional ECB and HUB set up and annotated 'BA emergency team/BAET' - One 'EASE bag' carried by every two/four BA wearers in the BA emergancy teams - A charged 45mm second jet (where resources allow this should be from an alternative pump and water supply) - Consider other items of specialist equipment such as, breaking in gear and stretcher |
|
|
How many wearers can 1 ECB HUB support? |
Up to 18 BA wearers |
|
|
The more BA ECB repeaters deployed the less BA wearers can be connected at one time. True or false? |
True |
|
|
What are the maximum wearers able per amount of repeaters deployed? |
1 repeater - 18 BA wearers 2 repeaters - 14 BA wearers 3 repeaters - 10 BA wearers 4 repeaters - 6 BA wearers |
|
|
What are the 3 possible locations for ECB repeaters? |
- The bottom of the stairs - At the entrance to, or at a sharp corner in a corridor or tunnel - At a landmark where telemetry signal was lost by retracing steps to regain connection and then deploying the repeater |
|
|
What 5 emergancy Procedures are available to a BA team? |
- To sound control module distress signal unit (DSU) - To go into entrapped procedure - To mutually exchange air with another BA wearer - To call for assistance by radio - Partial set removal in extreme circumstances |
|
|
A DSU must be operated immediately by a BA team member if they: |
- Become lost or disorientated - Become confused or distressed - Become trapped or injured and in difficulty - Have problems with their BA set |
|
|
Upon hearing an ADSU/DSU the BA team leaders of all teams are to direct their BA teams to investigate the source of the sound. Assisting BA wearers in distress out ranks everything but other factors should be considered, such as: |
- having sufficient air to be able to assist - OIC may instruct you to continue with your own brief - Maintaining safe egress - Firefighting teams who are firefighting may need to continue their role in order to allow teams to carry out their own tasks - Whether the BA team is already carrying out a rescue - BA team hearing an ADSU/DSU should advise the ECO and keep them informed of their actions |
|
|
When making the decision to withdraw after actuation of ADSU/DSU BA team leaders should consider: |
- How close they are to the exit - How close they are to the fire - Whether staying where they are puts them in further risk - Whether attempting to withdraw puts them in further risk - Can they see or hear other BA teams who may be able to assist - Impact of fitness or condition of BA team members on their ability to withdraw |
|
|
If any BA wearer has an accidental actuation of their DSU the BA team must take the following actions: |
- Inform the ECO to confirm accidental - Withdraw from risk area and report to ECP |
|
|
What actions must a ECO take after learning of an accidental DSU activation? |
- Inform other BA teams committed - Update information to OIC or ECPS - Instruct the BA team to stay under air when they report to ECP - Cancel the DSU with the wearers control module key - Establish if all BA team members have sufficient air to continue operations - Establish the wellbeing of the BA team - Allow BA team to re-commit and continue operations |
|
|
When a BA team become aware that they cannot withdraw from the scene of operations they should take the following actions: |
- Inform the ECO - Operate one DSU - Relax as much as possible - Maintain physical contact with other team members - Keep speech and movement to a minimum - Do not use additional flow button - Do not adjust the cylinder valve - keep all personal lamps switched on |
|
|
Partial BA set removal is a technique available to BA wearers for self-rescue in extreme circumstances where: |
- Egress is through a restricted opening and no other safe means of degrees is available - Adopting entrapped Procedures presents an intolerable risk to the safety of the BA team - The technique is carried out systematically under supervision and with assistance - The BA team leader should consider the physiological and psychological effects of the environment - Frequent pressure readings must be undertaken |
|
|
What must ECO's being informed of a BA team cable entanglement do? |
- Commit emergancy team - Inform IC |
|
|
What must IC's or SC being informed of BA team entanglement must: |
- Consider declaring a "firefighting emergancy" - Consider isolation of electrical supply - Commence accident investigation |
|
|
What are the main features of the MSA M1 SDBA? |
- Positive pressure - first breath operated
- Ergonomic lightweight - Backplate and harness, adjustable to suit wearer
- Telemetry system - With connected firefighter cloud remote monto ring
- Control module - With both digital and analogue pressure gauges, buddyblights and integrated telemetry
- Rescue hose - With quick release couplings
- Configurable as either SDBA or EDBA - Clean connect couplings - Which automatically flush when making in-line connections - Integrated anti entanglement device for SDBA - Rescue handle - (kevlar with a maximum load of 240kg) - Alphaclick 2 quick release cylinder connection - Dual purpose face mask - (DPFM) that allows for either the connection of a LGDV positive pressure, or a filter cartridge (FC) negative pressure |
|
|
What is STOP CAB? |
S elf contained T wo stage O pen-circuit P ositive pressure C ompressed A ir B reathing apparatus |
|
|
What is the MSA M1 SDBA full set weight? |
13kg |
|
|
What is the MSA M1 SDBA Working duration? |
26 mins |
|
|
What are the MSA M1 SDBA Backplate characteristics? |
D urable E rgonomic F lame retardant H ighly resistant to chemicals A nti static L ight weight M olded carbon composite material |
|
|
When does the pneumatic whistle go off? |
Between 72-62 bar - 10 mins to zero bar |
|
|
When will the pressure relief valve activate? |
Overpressure from the HP hose (11 bar/400lpm discharge) |
|
|
What is the life span of the cylinders? |
15 years |
|
|
When are the cylinders tested and to what bar? |
450 bar every 5 years |
|
|
What is the capacity of the cylinder in liters and how many liters of compressed air is stored? |
6.8 liters cylinder with 1836 liters of air |
|
|
What is a cylinder charged to? |
300 bar |

