![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
188 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the two ways of measuring the rate of respiration? |
1) measuring and how much oxygen is used up- The faster it is consumed, The faster the respiration rate. 2) rate at which carbon dioxide made. |
What do we breathe in and out? |
|
|
What is the formula for the respIratory quotient? |
RQ= Carbon dioxide produced -------------------------------------- Oxygen used |
|
|
|
What Is the metabolic rate? |
The sum of all the reactions that are occurring in the body |
The sum of something |
|
|
What Does it mean if the metabolic rate is high? |
More oxygen is needed as aerobic respiration is faster |
Something more is needed |
|
|
Why can changes in temperature and pH change the respiration rate? |
Because they affect enzymes and respiration is controlled by enzymes |
They effect something |
|
|
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration? |
Glucose —> lactic acid (+energy) |
|
|
|
What is anaerobic respiration? |
The muscles not receiving enough oxygen |
The muscles... |
|
|
What is anaerobic respirations two main disadvantages? |
-The lactic acid that is made by Anaerobic respiration built up in the muscles causing pain and fatigue -anaerobic respiration releases much less energy per glucose molecule than aerobic respiration |
-something builds up somewhere - realised much less... |
|
|
What is the oxygen debt? |
The incomplete breakdown of glucose resulting in the build of lactic acid |
Something not being completed |
|
|
During recovery of anaerobic respiration- why do the heart and breathing rate stay High? |
-rapid blood flow can carry lactic acid away to the liver -extra oxygen can be supplied enabling the liver to break down the lactic acid |
Two points. Rapid something can carry something Extra something can be supplied |
|
|
Where does respiration release energy from? |
Respiration releases energy from food |
|
|
|
Which molecule is the energy from respiration trapped in ? |
ATP |
Three letters |
|
|
What can ATP be used for? |
Provide the energy for many different processes in living organisms |
To provide something |
|
|
What does aerobic respiration use? |
Oxygen |
We breath it in |
|
|
What is the symbol equation for aerobic respiration? |
C6H1206+6O2—>6CO2+6H2O |
A lot of 6's |
|
|
What do enzymes do? What are they sometimes called? |
They speed up the rate of reaction. Biological catalysts |
Speed up... |
|
|
What do enzymes speed up chemical reactions occurring in? |
.respiration .photosynthesis .protein synthesis |
Three points two are similar |
|
|
What molecule fits into the active site of the enzyme? |
Substrate |
|
|
|
What is the key term used when only one enzyme and substrate fit together? |
Specificity |
|
|
|
When do enzymes work best? And what is this called? |
At a particular temp or pH It's called the optimum |
A particular... |
|
|
What happens to an enzymes at low temperatures? |
Molecules move slower so are less likely to collide |
Molecules... |
|
|
What happens at high or low pH and at high temps? |
Denaturing may occur |
Changing shape |
|
|
How can we calculate how temperature alters the rate of reaction ? |
Q10- rate at higher temp ----------------------------- Rate at lower temp |
Equation |
|
|
What are proteins made of? |
Long chains of amino acids |
Long.... |
|
|
Proteins have four different functions - what are 4 examples? |
-structural proteins used to build cells and tissues -hormones which carry messages to control a reaction -carrier proteins which carries oxygen -and enzymes |
-structural proteins -hormones -carrier proteins - |
|
|
Each protein has its own no. And order of amino acids-what does this mean ? |
This makes each type of protein molecules a different shape snd gives it a different function |
Gives it two different things |
|
|
Who were the two people that discovered the structure of DNA? |
Watson and crink |
|
|
|
What were the two pieces of data Watson and crink used? |
-photos taken using X-Ray's which showed DNA had two chains wound into a helix -data showing bases occurred in pairs |
|
|
|
When did Watson and crink discover the structure of DNA? And when were they given a Nobel prize? |
1953 1962 |
|
|
|
What are proteins made of? |
Long chains of amino acids |
Long.... |
|
|
What are ribosomes the site of? |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
|
What are the size of ribosomes? |
Too small to be seen with a light microscope |
...to be seen with... |
|
|
When might mutations occur? |
Randomly but usually through chemicals or radiation |
Three ways |
|
|
When they occur mutations: - - - |
-may lead to the production of different proteins -often harmful but may have no effect -may give the individual an advantage |
-produces ... -can be... But... -may give the individual... |
|
|
Although each cell in the body has the same gene it does not mean that all the same proteins are made, why? What does this allow? |
Genes are switched off in different cells. This allows different cells to have different functions. |
Light switch |
|
|
What do genes mutations do? Why? |
They alter or prevent the production of the protein that is normally made, because they change the base code of the DNA, and so the order of amino acids in the protein |
Alter or prevent ... Because the change the base... |
|
|
Proteins have four different functions - what are 4 examples? |
-structural proteins used to build cells and tissues -hormones which carry messages to control a reaction -carrier proteins which carries oxygen -and enzymes |
-structural proteins -hormones -carrier proteins - |
|
|
Each protein has its own no. And order of amino acids-what does this mean ? |
This makes each type of protein molecules a different shape snd gives it a different function |
Gives it two different things |
|
|
Who were the two people that discovered the structure of DNA? |
Watson and crink |
|
|
|
What were the two pieces of data Watson and crink used? |
-photos taken using X-Ray's which showed DNA had two chains wound into a helix -data showing bases occurred in pairs |
|
|
|
When did Watson and crink discover the structure of DNA? And when were they given a Nobel prize? |
1953 1962 |
|
|
|
Where are the mitochondria and ribosomes found? |
In the cytoplasm |
In the... |
|
|
What does the number of mitochondria depend on? |
How active the cell is |
|
|
|
What occurs in mitochondria? |
Respiration |
|
|
|
Why do the liver and muscles need more mitochondria? |
The liver carries out many functions and the muscles need to contract |
Liver carries out ... |
|
|
What are two advantages to becoming multicellular? |
.It allows an organism to become larger and more complex . It also allows different cells to take on different jobs |
|
|
|
What is cell differentiation? |
Allowing cells to take on different jobs |
Allowing cells to do something |
|
|
What are three things organisms need to become multicellular? |
. Allow communication between all the cells in the body . Supply all the cells with enough nutrients . Control exchanges with the environment such as heat and gases |
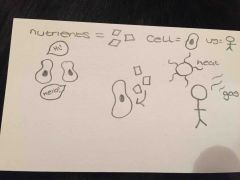
|
|
|
The nucleus contains genes, each gene…1). 2). |
1) is a section of a chromosome made of DNA 2) codes for a particular protein |
|
|
|
Each gene contains a different sequence of bases-what are the bases and the base pairs? |
A-T C-G |
|
|
|
Where are proteins made? |
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
DNA cannot… So… |
It cannot leave the nucleus so a copy Of the gene needs to be made that can leave the nucleus and carry the code to the cytoplasm |
It cannot leave somewhere so… |
|
|
What do the DNA base codes control? And what do they code? |
They control which protein is made. Because the base sequence in the DNA codes for the amino acid sequence in the protein |
|
|
|
The code for proteins is carried from the DNA to the…?by a molecule called…? |
Ribosomes mRNA |
|
|
|
Many of the proteins that are made are…, Which control…. |
Enzymes which control the activity of the cell |
|
|
|
What are two advantages to becoming multicellular? |
.It allows an organism to become larger and more complex . It also allows different cells to take on different jobs |
|
|
|
What is mitosis? |
A process that produces new cells for growth |
Produces new cells for something |
|
|
What are three things organisms need to become multicellular? |
. Allow communication between all the cells in the body . Supply all the cells with enough nutrients . Control exchanges with the environment such as heat and gases |
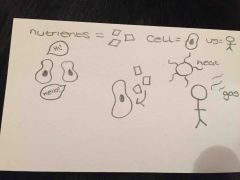
|
|
|
Why does DNA replication take place with mitosis? |
So that each cell produced still has two copies of each chromosome |
Each cell produced still needs to have two of something |
|
|
Body cells in mammals have two copies of each chromosome, what is this called? |
They are called diploid cells |
A weird name beginning with D |
|
|
What is the rhyme to remember mitosis and meiosis? |
Mitosis in my toes, meiosis in my ovs |
Miss Campbell made it up |
|
|
What is cell differentiation? |
Allowing cells to take on different jobs |
Allowing cells to do something |
|
|
What are three things organisms need to become multicellular? |
. Allow communication between all the cells in the body . Supply all the cells with enough nutrients . Control exchanges with the environment such as heat and gases |
|
|
|
The nucleus contains genes, each gene…1). 2). |
1) is a section of a chromosome made of DNA 2) codes for a particular protein |
|
|
|
Each gene contains a different sequence of bases-what are the bases and the base pairs? |
A-T C-G |
|
|
|
Where are proteins made? |
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
DNA cannot… So… |
It cannot leave the nucleus so a copy Of the gene needs to be made that can leave the nucleus and carry the code to the cytoplasm |
It cannot leave somewhere so… |
|
|
What do the DNA base codes control? And what do they code? |
They control which protein is made. Because the base sequence in the DNA codes for the amino acid sequence in the protein |
|
|
|
What is the process of mitosis? |
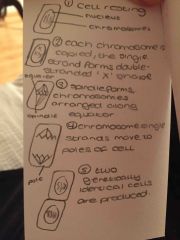
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Many of the proteins that are made are…, Which control…. |
Enzymes which control the activity of the cell |
|
|
|
What is meiosis? |
It's the type of cell division that produces gametes |
It produces something (sex cells) |
|
|
Why are gametes haploid cells? What are Gametes? |
Because they contain only one chromosome from each pair They are sex cells |
Only contain one of something |
|
|
What produces genetic variation in meiosis? |
Zygote gets one copy of the gene from one parent another copy from the other parent |
The parents |
|
|
How is the structure of the sperm cells adapted to its function? |
-it has many Mitochondria to provide energy to swim to the egg -an Acrosome that releases enzymes to Digest the egg membrane |
-needs to swim -need something else |
|
|
What are the two divisions in meiosis? |
-in the first division one chromosome from each pair moves opposite poles of the cell -in the second division the copies of each chromosome come apart and move to opposite poles of the cell |
Think about chromosomes and poles of cells |
|
|
Describe meiosis |
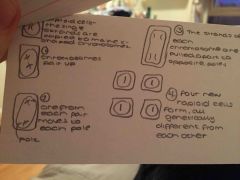
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
It's the type of cell division that produces gametes |
It produces something (sex cells) |
|
|
What are the three different types of blood vessels and what are their jobs? |
-arteries transport blood away from the heart to the tissue -Baines transport the blood back to the heart from the tissues -capillaries link arteries to veins and allow materials to pass between the blood and the tissues |
-A -V -C |
|
|
What are the jobs of arteries veins and capillaries? |
-arteries have a thick muscular and elastic a wall to resist the high pressure -veins have large lumen and valves to try and keep the blood moving back to the heart because the pressure is low -capillaries have permeable walls so substances can be transferred between the blood and the tissues |
-thick… to… -large… To… Because… -permeable… So… |
|
|
Why are gametes haploid cells? What are Gametes? |
Because they contain only one chromosome from each pair They are sex cells |
Only contain one of something |
|
|
What produces genetic variation in meiosis? |
Zygote gets one copy of the gene from one parent another copy from the other parent |
The parents |
|
|
Describe mitosis |
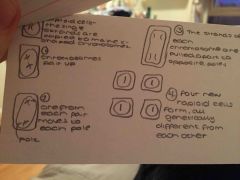
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What are the two divisions in meiosis? |
-in the first division one chromosome from each pair moves opposite poles of the cell -in the second division the copies of each chromosome come apart and move to opposite poles of the cell |
Think about chromosomes and poles of cells |
|
|
Describe mitosis |
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What does plasma (liquid in blood) carry around the body? |
-dissolved food substances, such as glucose -carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs -hormones from the clans where they are made, to their target cells -plasma proteins such as antibodies -waste substances such as urea |
Five things |
|
|
What are the ways of red blood cells are adapted to their function of carrying oxygen? |
-they are small so they can pass through small blood vessels -there shaped like biconcave discs, so large surface area to exchange oxygen cooker -they contain haemoglobin to combine with oxygen (it makes them red) -they don't have a nucleus so there is more haemoglobin |
|
|
|
What does the Biconcave shape of red blood cells mean? |
It provides a larger surface area to volume ratio to exchange oxygen more quickly |
|
|
|
Haemoglobin reacts with oxygen to get oxyhemoglobin- how is this reaction reversible? |
When the oxyhemoglobin reaches the tissues, the oxygen is released |
When it reaches the tissues... |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
It's the type of cell division that produces gametes |
It produces something (sex cells) |
|
|
What are the three different types of blood vessels and what are their jobs? |
-arteries transport blood away from the heart to the tissue -Baines transport the blood back to the heart from the tissues -capillaries link arteries to veins and allow materials to pass between the blood and the tissues |
-A -V -C |
|
|
What are the jobs of arteries veins and capillaries? |
-arteries have a thick muscular and elastic a wall to resist the high pressure -veins have large lumen and valves to try and keep the blood moving back to the heart because the pressure is low -capillaries have permeable walls so substances can be transferred between the blood and the tissues |
-thick… to… -large… To… Because… -permeable… So… |
|
|
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker muscle wall in the heart? |
Because It has to pump blood all around the body rather than just to the lungs |
|
|
|
What is a double circulatory system? |
The blood is pumped to the lungs and returns to the heart to pump to the body. This means the blood is at a higher pressure and flows to the tissues at faster rate |
The blood is pumped… This means... |
|
|
Why are gametes haploid cells? What are Gametes? |
Because they contain only one chromosome from each pair They are sex cells |
Only contain one of something |
|
|
What produces genetic variation in meiosis? |
Zygote gets one copy of the gene from one parent another copy from the other parent |
The parents |
|
|
How is the structure of the sperm cells adapted to its function? |
-it has many Mitochondria to provide energy to swim to the egg -an Acrosome that releases enzymes to Digest the egg membrane |
-needs to swim -need something else |
|
|
What are the two divisions in meiosis? |
-in the first division one chromosome from each pair moves opposite poles of the cell -in the second division the copies of each chromosome come apart and move to opposite poles of the cell |
Think about chromosomes and poles of cells |
|
|
Describe mitosis |
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What does plasma (liquid in blood) carry around the body? |
-dissolved food substances, such as glucose -carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs -hormones from the clans where they are made, to their target cells -plasma proteins such as antibodies -waste substances such as urea |
Five things |
|
|
What are the ways of red blood cells are adapted to their function of carrying oxygen? |
-they are small so they can pass through small blood vessels -there shaped like biconcave discs, so large surface area to exchange oxygen cooker -they contain haemoglobin to combine with oxygen (it makes them red) -they don't have a nucleus so there is more haemoglobin |
|
|
|
What does the Biconcave shape of red blood cells mean? |
It provides a larger surface area to volume ratio to exchange oxygen more quickly |
|
|
|
Haemoglobin reacts with oxygen to get oxyhemoglobin- how is this reaction reversible? |
When the oxyhemoglobin reaches the tissues, the oxygen is released |
When it reaches the tissues... |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
It's the type of cell division that produces gametes |
It produces something (sex cells) |
|
|
What are the three different types of blood vessels and what are their jobs? |
-arteries transport blood away from the heart to the tissue -Baines transport the blood back to the heart from the tissues -capillaries link arteries to veins and allow materials to pass between the blood and the tissues |
-A -V -C |
|
|
What are the jobs of arteries veins and capillaries? |
-arteries have a thick muscular and elastic a wall to resist the high pressure -veins have large lumen and valves to try and keep the blood moving back to the heart because the pressure is low -capillaries have permeable walls so substances can be transferred between the blood and the tissues |
-thick… to… -large… To… Because… -permeable… So… |
|
|
Go through how the heart works and use all of the key terms |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker muscle wall in the heart? |
Because It has to pump blood all around the body rather than just to the lungs |
|
|
|
Describe mitosis |
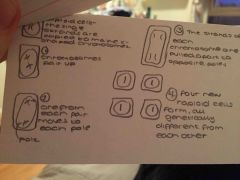
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Why are gametes haploid cells? What are Gametes? |
Because they contain only one chromosome from each pair They are sex cells |
Only contain one of something |
|
|
What produces genetic variation in meiosis? |
Zygote gets one copy of the gene from one parent another copy from the other parent |
The parents |
|
|
How is the structure of the sperm cells adapted to its function? |
-it has many Mitochondria to provide energy to swim to the egg -an Acrosome that releases enzymes to Digest the egg membrane |
-needs to swim -need something else |
|
|
What are the two divisions in meiosis? |
-in the first division one chromosome from each pair moves opposite poles of the cell -in the second division the copies of each chromosome come apart and move to opposite poles of the cell |
Think about chromosomes and poles of cells |
|
|
Describe mitosis |
Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What does plasma (liquid in blood) carry around the body? |
-dissolved food substances, such as glucose -carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs -hormones from the clans where they are made, to their target cells -plasma proteins such as antibodies -waste substances such as urea |
Five things |
|
|
Go through how the heart works and use all of the key terms |
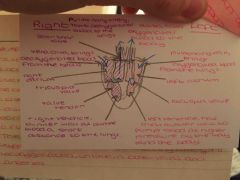
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What does the Biconcave shape of red blood cells mean? |
It provides a larger surface area to volume ratio to exchange oxygen more quickly |
|
|
|
Haemoglobin reacts with oxygen to get oxyhemoglobin- how is this reaction reversible? |
When the oxyhemoglobin reaches the tissues, the oxygen is released |
When it reaches the tissues... |
|
|
When are the two main phases of rapid growth? |
One is just after birth and the others adolescence |
|
|
|
What is the best measure of growth? |
Dry mass is the best measure of growth |
|
|
|
Why might different parts of an organism grow at different rates? |
Because different parts of the organism may be needed at different times during the life of the organism |
|
|
|
Why is measuring dry mass hard? |
Because you have to kill the organism and have to drive off the water |
|
|
|
Stem cells stay undifferentiated, what does this mean? |
This means they can develop into different types of cells |
Can develop into something |
|
|
Where can stem cells be obtained? |
They can be obtained from embryos |
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of stem cells |
Pros-
They could potentially be used to treat some medical conditions
Cons-
Some people think it's wrong because the embryos are destroyed |
|
|
|
What are the Fourways plants and animals grow differently? |
-Animals tend to grow a certain size but many plants can carry on growing. -plant cell division only happens in areas called meristems, found at the tips of roots and shoots. -The main way that plants gain height is by cells enlarging rather than dividing -many plant cells keep the ability to differentiate, but most animal cells lose this at an early age |
-about growing -about cell division -about gaining height -about ability to differentiate |
|
|
When are the two main phases of rapid growth? |
One is just after birth and the others adolescence |
|
|
|
What is the best measure of growth? |
Dry mass is the best measure of growth |
|
|
|
Why might different parts of an organism grow at different rates? |
Because different parts of the organism may be needed at different times during the life of the organism |
|
|
|
Why is measuring dry mass hard? |
Because you have to kill the organism and have to drive off the water |
|
|
|
Stem cells stay undifferentiated, what does this mean? |
This means they can develop into different types of cells |
Can develop into something |
|
|
Where can stem cells be obtained? |
They can be obtained from embryos |
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of stem cells |
Pros-
They could potentially be used to treat some medical conditions
Cons-
Some people think it's wrong because the embryos are destroyed |
|
|
|
What are the Fourways plants and animals grow differently? |
-Animals tend to grow a certain size but many plants can carry on growing. -plant cell division only happens in areas called meristems, found at the tips of roots and shoots. -The main way that plants gain height is by cells enlarging rather than dividing -many plant cells keep the ability to differentiate, but most animal cells lose this at an early age |
-about growing -about cell division -about gaining height -about ability to differentiate |
|
|
What may selective breeding programs cause? |
They may lead to inbreeding, where too closely related individuals mate, and this can cause health problems within the species |
Think about the relationships between the animals |
|
|
What can inbreeding (reducing variety Alleles) lead to? |
-An increased risk of harmful recessive characteristic is showing up in offspring
-A reduction in variation, so that populations cannot adapt to change so easily |
-and increased risk of something
-A reduction in something |
|
|
What is one advantage and disadvantage of genetic engineering? |
Advantage-is that organisms with desired features can be produced quickly
Disadvantage-there is a risk that the inserted genes may have unexpected side-effects |
|
|
|
What are three examples of genetic engineering? |
-Rice that contains beta-carotene has been made using the genes that control beta-carotene production from carrots and inserting them. Humans can then convert the carotene from rice into vitamin day
-Genetically engineered bacteria have been made that produces human insulin
-crop plants have been made that are resistant to herbicides frost damage or disease |
|
|
|
What are two ethical issues with genetic engineering? |
-Some people worry about possible long-term side-effects (may disturb natural ecosystems)
-Others think it is morally wrong |
|
|
|
What are two ethical issues with genetic engineering? |
-Some people worry about possible long-term side-effects (may disturb natural ecosystems)
-Others think it is morally wrong |
|
|
|
What are the four steps of genetic engineering? |
-Desired characteristics are selected
-The genes responsible are identified and removed (isolation)
-The genes are inserted into an organism
-Organisms reproduce (Replication) |
|
|
|
What are two ethical issues with genetic engineering? |
-Some people worry about possible long-term side-effects (may disturb natural ecosystems)
-Others think it is morally wrong |
|
|
|
What are the four steps of genetic engineering? |
-Desired characteristics are selected
-The genes responsible are identified and removed (isolation)
-The genes are inserted into an organism
-Organisms reproduce (Replication) |
|
|
|
What is genetherapy? |
It is the process of using genetic engineering to change a persons jeans and cure certain disorders |
|
|
|
What are two ethical issues with genetic engineering? |
-Some people worry about possible long-term side-effects (may disturb natural ecosystems)
-Others think it is morally wrong |
|
|
|
What are the four steps of genetic engineering? |
-Desired characteristics are selected
-The genes responsible are identified and removed (isolation)
-The genes are inserted into an organism
-Organisms reproduce (Replication) |
|
|
|
What is genetherapy? |
It is the process of using genetic engineering to change a persons jeans and cure certain disorders |
|
|
|
What does gene therapy involve? |
It could involve body cells or gametes |
|
|
|
What are two ethical issues with genetic engineering? |
-Some people worry about possible long-term side-effects (may disturb natural ecosystems)
-Others think it is morally wrong |
|
|
|
What are the four steps of genetic engineering? |
-Desired characteristics are selected
-The genes responsible are identified and removed (isolation)
-The genes are inserted into an organism
-Organisms reproduce (Replication) |
|
|
|
What is genetherapy? |
It is the process of using genetic engineering to change a persons jeans and cure certain disorders |
|
|
|
What does gene therapy involve? |
It could involve body cells or gametes |
|
|
|
Why is changing the jeans in gamma much more controversial? |
Because it is sometimes difficult to decide which jeans parents should be allowed to change this could lead to design the babies |
|
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
How was Dolly the sheep made? |

Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
How was Dolly the sheep made? |

Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Why might animals be cloned? |
-Mass-produce animals with desired characteristics
-produce animals that have been genetically engineered to produce human products
-Produce human embryos to supply stem cells for therapy |
|
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
How was Dolly the sheep made? |

Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Why might animals be cloned? |
-Mass-produce animals with desired characteristics
-produce animals that have been genetically engineered to produce human products
-Produce human embryos to supply stem cells for therapy |
|
|
|
What is an ethical dilemma with cloning? |
Some people think that it is wrong to clone people as they will not be true individuals |
|
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
How was Dolly the sheep made? |

Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Why might animals be cloned? |
-Mass-produce animals with desired characteristics
-produce animals that have been genetically engineered to produce human products
-Produce human embryos to supply stem cells for therapy |
|
|
|
What is an ethical dilemma with cloning? |
Some people think that it is wrong to clone people as they will not be true individuals |
|
|
|
What is a risk of cloning? |
Genetically modified animals could be cloned to supply replacement organs humans. People are worried this means diseases could spread from animals to humans |
|
|
|
What was the process which made Dolly the sheep? |
Nuclear transfer |
|
|
|
How was Dolly the sheep made? |

Back (Definition) |
Think back to the diagram |
|
|
Why might animals be cloned? |
-Mass-produce animals with desired characteristics
-produce animals that have been genetically engineered to produce human products
-Produce human embryos to supply stem cells for therapy |
|
|
|
What is an ethical dilemma with cloning? |
Some people think that it is wrong to clone people as they will not be true individuals |
|
|
|
What is a risk of cloning? |
Genetically modified animals could be cloned to supply replacement organs humans. People are worried this means diseases could spread from animals to humans |
|
|
|
Why would recreating endangered or extinct animals be bad? |
Because they would all be related and will be one sex |
|
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning plants? |
Advantages: growers can be sure of characteristics of plan since all plants will be genetically identical. it is also possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seeds.
Disadvantages: if the plants become susceptible to diseases or to change in the environmental conditions, then all the plants will be affected. There is a lack of variation |
-Grow as can be sure of something and it is possible to do something that may be difficult otherwise
-If plants become susceptible to something it can cause problems and there is also a lack of something |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning plants? |
Advantages: growers can be sure of characteristics of plan since all plants will be genetically identical. it is also possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seeds.
Disadvantages: if the plants become susceptible to diseases or to change in the environmental conditions, then all the plants will be affected. There is a lack of variation |
-Grow as can be sure of something and it is possible to do something that may be difficult otherwise
-If plants become susceptible to something it can cause problems and there is also a lack of something |
|
|
Describe the process of tissue culture |
-The plant is selected as certain characteristics
-A large number of small pieces of tissue are cut from the plants
-Small pieces of tissue are grown in a test tube or dishes containing a growth medium
-Septic technique is used at All stages to stop any microbes infecting the plant |
|
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning plants? |
Advantages: growers can be sure of characteristics of plan since all plants will be genetically identical. it is also possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seeds.
Disadvantages: if the plants become susceptible to diseases or to change in the environmental conditions, then all the plants will be affected. There is a lack of variation |
-Grow as can be sure of something and it is possible to do something that may be difficult otherwise
-If plants become susceptible to something it can cause problems and there is also a lack of something |
|
|
Describe the process of tissue culture |
-The plant is selected as certain characteristics
-A large number of small pieces of tissue are cut from the plants
-Small pieces of tissue are grown in a test tube or dishes containing a growth medium
-Septic technique is used at All stages to stop any microbes infecting the plant |
|
|
|
Why is cloning plants easier than going animals? |
Because many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate but animals loses ability |
Plants have the ability to still do something when animals don't |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning plants? |
Advantages: growers can be sure of characteristics of plan since all plants will be genetically identical. it is also possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seeds.
Disadvantages: if the plants become susceptible to diseases or to change in the environmental conditions, then all the plants will be affected. There is a lack of variation |
-Grow as can be sure of something and it is possible to do something that may be difficult otherwise
-If plants become susceptible to something it can cause problems and there is also a lack of something |
|
|
Describe the process of tissue culture |
-The plant is selected as certain characteristics
-A large number of small pieces of tissue are cut from the plants
-Small pieces of tissue are grown in a test tube or dishes containing a growth medium
-Septic technique is used at All stages to stop any microbes infecting the plant |
|
|
|
Why is cloning plants easier than going animals? |
Because many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate but animals loses ability |
Plants have the ability to still do something when animals don't |
|
|
Why do bacterial cells differ from plant animal cells? |
Because they lack a true nucleus, Mitochondria and chloroplasts |
Because they lack three things in the cell |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning plants? |
Advantages: growers can be sure of characteristics of plan since all plants will be genetically identical. it is also possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seeds.
Disadvantages: if the plants become susceptible to diseases or to change in the environmental conditions, then all the plants will be affected. There is a lack of variation |
-Grow as can be sure of something and it is possible to do something that may be difficult otherwise
-If plants become susceptible to something it can cause problems and there is also a lack of something |
|
|
Describe the process of tissue culture |
-The plant is selected as certain characteristics
-A large number of small pieces of tissue are cut from the plants
-Small pieces of tissue are grown in a test tube or dishes containing a growth medium
-Septic technique is used at All stages to stop any microbes infecting the plant |
|
|
|
Why is cloning plants easier than going animals? |
Because many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate but animals loses ability |
Plants have the ability to still do something when animals don't |
|
|
Why do bacterial cells differ from plant animal cells? |
Because they lack a true nucleus, Mitochondria and chloroplasts |
Because they lack three things in the cell |
|
|
Where is DNA found in the bacterial cell and as what? |
DNA is found in the cytoplasm as a single circular strand or chromosome |
|

