![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is affected by enzymes? |
Rate/kinetics of reaction NOT thermodynamics (i.e. Keq) |
|
|
Name five ways that enzymes affect a reaction |
1. stabilization of transition state 2. proximity effects 3. microenvironmental effects 4. acid base catalysis 5. covalent catalysis |
|
|
How do catalysts reduce the free energy of activation of the reaction? |
Stabilizing the transition state |
|
|
Keq |
how much substrate and product are present at equillibrium (steady state, will not change)
Keq=product/substrate |
|
|
Free energy equation |
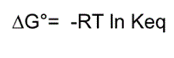
|
|
|
Variables in free energy equation |
R=1.98 x 10^-3 Kcal/mol K
1 Kcal=4.2 kJoules T=temp in Kelvins G=kilocalories/mol |
|
|
What does Keq mean? |
Keq=10^-4: means 10,000 substrate to 1 product, NOT favorable reaction, free energy is positive
Keq=10^4: means 10,000 product to 1 substrate, favorable reaction, free energy is negative
Keq=1: free energy is zero
*can couple unfavorable reactions with favorable to make work |
|
|
Free energy term |
Describes amount of energy absorbed or released in reaction |
|
|
What must be true in a thermodynamically favorable reaction? |
Substrate must be less stable than the product, i.e. bond energies within substrate are weaker than product
Example: CO2 is stable, glucose bonds are less stable, glucose to CO2 is from less stable to more stable
Bond energy differences=major force of a reaction and towards entropy |
|
|
Rate constant (kr) |
Determined by the free energy of activation (which is reduced by catalysts)
Amount of substrate concentration also influences
Catalysts need to bind to substrate and via bond energy make it more unstable; it will lower Ea |
|
|
What is true about reversible reactions? |
Usually have to add ATP to make it work This occurs even though final state more stable than initial state
Example: oxidation and resynthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate |
|
|
What happens as you lower activation energy? |
Rae increases, larger turnover number (kCat) |
|
|
Numbering classes of enzymes |
First number=one of six major classes
Second and third=subclass and sub-subclasses
Fourth number=accession number, showing order in which enzyme was accepted into nomenclature |
|
|
Six major classes enzymes |
Oxidoreductases Transferases Hydrolases Lyases Isomerases Ligases |
|
|
Oxidoreductases |
Oxidation-Reduction reaction
Ex. Lactate dehydrogenase |
|
|
Transferases |
Group transfer
Ex. hexokinase |
|
|
Hydrolyases |
Hydrolysis reactions (water coming in and out)
Ex. chymotrypsin |
|
|
Lyases |
Addition and removal of groups from double bonds
Ex. fumarase |
|
|
Isomerases |
Isomerization (intramolecular group transfer) --changing groups within same molecule (i.e. ketose to aldetose)
Example: Triose phosphate isomerase |
|
|
Ligases |
Ligation of two substrates at expense of ATP
Example: Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase |
|
|
How do we avoid the problem of water in reactions? |
Put in organic solvents so we can get A and B together in the right orientations so they can create C
This is what an enzyme does...tries to get water out of system (desolvation) and create right orientation for catalysis, as well as putting strain in the bonds |
|
|
Proximity effects |
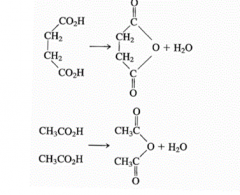
Enzyme helps put substrates together so they can react
Example: succinic acid to succinyl anhydride vs acetic acid to acetic anhydride
When water taken out of system and succinic acid esterified together, can work better |
|
|
Transition state |
When enzyme binds to a compound and makes it into a condition where it will be easy to move to the next step
Usually tetrahedral All has to do with bond energies |
|
|
What do drugs do? |
Mimic transition state
Example: HIV protease inhibitors becomes tetrahedral so protease can't work anymore because it binds to enzyme, bond energy stabilized
Another example--Serrin gas |
|
|
What are ways to increase the pKa of an enzyme? |
Put in organic solvent/hydrophobic environment; H2O not there, nothing to pull the proton off
This is how you make a conjugate base |
|
|
What are ways to lower the pKa of an enzyme |
Use charges or polar amino acids in process |

