![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does an animal cell contain? |
A nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria |
|
|
What is the nucleus? |
Contains DNA that controls what the cell does |
|
|
What is the cytoplasm? |
Gel like substance - where most chemical reactions happen |
|
|
what is the cell membrane? |
holds the cell wall together, decides what goes in to out |
|
|
Mitochondria is.... |
where the reactions for respiration take place. Respiration releases energy - making the cells work |
|
|
Animal and plant cell have 4 things in common, name them.. |
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitrochondria |
|
|
Plant cell has 3 extras these are.. |
rigid cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplasts |
|
|
The rigid cell wall... |
made of cellulose, gives support of cell. |
|
|
large vacuole.. |
contains cell sap, a weak solution of water and sugar |
|
|
chloroplasts.. |
where photosynthesis occurs, contains chlorophyll |
|
|
Bacteria cells have no.. |
nucleus |
|
|
Bacteria cells are a lot smaller than plant or animal cell, and contain 4 features .. |
1) Chromosomal DNA 2) Plasmids 3) Flagellum 4) Cell wall |
|
|
Chromosomal DNA.. |
one long circular chromosome, controls: cell's activities and replication - floats free in cytoplasm |
|
|
Plasmids.. |
small loops of extra DNA, contain genes for things like drug-resistance, can be passed between bacteria |
|
|
Flagellum.. |
long, hair-like structure = rotates, makes bacterium move |
|
|
Cell wall.. |
supports the cell |
|
|
What are cells studied using... |
TELESCOPES. They let us see what we can't with the human eye. Like the internal structure, even tinier things like the plasmids |
|
|
What does DNA carry.. |
instructions for characteristics from your parents to you. |
|
|
A DNA molecule has how many strands.. |
two strands, coiled together in the shape of a double helix |
|
|
What are the stands held together by.. |
four different bases.. adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) |
|
|
name the base pairings.. |
A-T (think Tony and Angelina) C-G (think cats and gatto) |
|
|
What are the base pairs joined together by.. |
weak hydrogen bonds |
|
|
What is a gene? |
a section of the DNA, the sequence of bases in a gene codes for a specific protein. |
|
|
How do cells make proteins.. |
by stringing amino acids together in a particular order |
|
|
What are proteins make out of.. |
organelles ribosomes |
|
|
What is done using mRNA.. |
allowing the cell to get information from the DNA to the ribosome in the cell cytoplasm |
|
|
What is mRNA.. |
a molecule, like DNA only shorter and single stranded like a messenger between the DNA between the DNA in nucleus |
|
|
Explain the process.. |
the two DNA strands UNZIP - DNA used as a temple for mRNA - base pairings ensure it's complementary ( matches the other side) = TRANSCRIPTION mRNA molecules move out of the nucleus and joins risosome amino acids that match the mRNA are brought to the R by molecules called tRNA job of Ribosome is to stick amino acids together - to make a polypeptide - protein = TRANSLATION |
|
|
What are mutation? |
a change to an organisms DNA sequence -effect sequence could effect: the sequence of amino acids in the protein which could effect the shape of the protein and so its function |
|
|
Why could a mutation be harmful.. |
cause a genetic disorder - e.g. cystic fibrosis |
|
|
Why could a mutation be beneficial... |
could produce a new characteristic that is beneficial - eg. mutations in genes making them resistant to antibiotics |
|
|
What are enzymes.. |
catalysts produced by living things acts as a biological catalyst are all proteins can work inside or outside the body |
|
|
Give 3 example in which enzymes help.. |
1) DNA replication - help copy a cells DNA before it divides 2)Protein synthesis - enzymes hold amino acids in place to form bonds 3) Digestion - various enzymes are secreted into the gut |
|
|
Enzymes have special shapes so they can catalyse reactions.. |
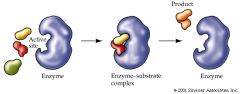
usually involves being spilt apart or joined
together |
|
|
What is the active sight.. |
where the substrate joins on to |
|
|
For the enzyme to work.. |
the substrate has to fit snuggly into the active sight. 'Lock and Key' mechanism |
|
|
Enzyme controlled reaction, the variables.. |
temperature, pH, substrate concentration (varying the concentrations of the starch solutions.) |
|
|
What is the Human Genome Project.. |
thousands of scientists worked together to find every single human gene. Good: predict and prevent diseases - develop better medicines, improve forensic science Bad: increased stress, discrimination by employers = more likely to discriminate agasint people who are genetically likely to get a disease. |
|
|
oWhat is genetic engineering.. |
use enzymes to cut and paste into useful genes, producing GM, genetically modified genes |
|
|
Genetic engineering can benefit humans? |
reducing vitamin A deficiency, growing golden rice = which contains two genes from other organisms producing human insulin gene can be inserted into bacteria to produce human insulin increasing crop yield, genes modified to make them resistant to herbicides |
|
|
Why is genetic engineering a controversial topic? |
will effect wildlife- affecting number of weeds and flowers = reducing farmland biodiversity not everyone is convinced they are safe |
|
|
what is a diploid cell? |
a human body cells are diploid, meaning they have two versions of each chromosome |
|
|
What is mitosis? |
makes new cells for growth and repair. when a cell divides, it makes to cells identical to the original cell - with a nucleus containing the same number |
|
|
when is mitosis used? |
when human and animals and plants want to grow to replace cells that have been damaged |
|
|
What does mitosis result in.. |
two identical cells, if the cell gets signal that it needs to divide = DNA is copied - forms X shape one arm - exact duplicate of the other chromosomes then line up - get pulled apart by cell fibres - opposite ends - two membranes - become two nuclei of the two new cells cytoplasm divides = two new diploid cells = genetically identical |
|
|
asexual reproduction also uses mitosis.. |
no genetic variation - strawberry plants form runners |
|
|
What are gametes? |
are sex cells, called ova (ovum) in females and sperm in males |
|
|
Are gametes haploid or diploid? |
HAPLOID. they have one copy of each chromosome = why two gametes combine at fertilisation = resulting in zygotes diploid - as they have 2 copies of each chromosomes. |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
involves two cell divisions - when a cell divides to produce 4 haploid nuclei - chromosomes are not identical |
|
|
The process of meiosis.. |
duplicates its DNA - one arm of each chromosome - exact copy of the other arm the chromosome pairs line up in the centre - pulled apart - some of mothers and some of the fathers = new cell - mix means = variation in off-spring line up again - pulled apart - 4 haploid gametes |
|
|
cloning mammals.. |
type of asexual reproduction |
|
|
process of cloning.. |
unfertilised egg - remove its nucleus, taken from an adult body cell diploid nucleus - containing full number of chromosomes = inserted into a 'empty' egg cell electric shock - stimulates it - makes it divide implanted into an adult female |
|
|
Cloning uses.. |
help with the shortage of organs for transplants - gm pigs being bred with suitable organisms for humans study of clones lead to - greater understanding preserve endangered species |
|
|
issues surrounding cloning.. |
reduced gene pool = fewer different alleles in the population - new disease - all wiped out cloned mammals might'd live as long = cloned from an older animal often fails, born with genetic defeats, immune systems are weaker |
|
|
what can embryonic stem cells do.. |
can into any type of cell. The cells in the embryo are all the same - these are the embryonic stem cells. |
|
|
What are stem cells able to do.. |
stem cells are able to divide to produce either more stem cells or different types of specialised cell = this process the embryo starts to develop a recognisably human body - with organs + systems |
|
|
stem cells may be able to cure many diseases.. |
bone marrow transplant - producing new blood cells experimented with extracting stem cells from very early human embryos + growing them |
|
|
against embryonic stem cell research.. |
human embryos shouldn't be used fro experiments - one potential human life |

