![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PARKINSONS drugs: |

|
|
|
PARKINSONS drugs: what optimises the effect of L-DOPA? |
Entacapone (a COMT inhibitor) |
|
|
What are the adverse effects of L-DOPA? |
Nausea, vomiting Postural hypotension Psychosis Impulse-control disorders Excessive day-time sleepiness
MOTOR: on-off effect wearing off effect dyskinesia and dystonia |
|
|
PARKINSONS drugs: what drugs are given at an early stage? |
Beign MOA-B inhibitor. |
|
|
PARKINSONS drugs: what drugs are given for mild-moderate disability without cognitive impairment? |
Dopamine agonist |
|
|
PARKINSONS drugs: what drugs are given for moderate to severe impairment? |
Levodopa with a COMTI |
|
|
PARKINSONS drugs: What are non-drug treatment options? |
Human embyronic mesencephalic graft
Stimulation: of the sub thalamic nucleus Pallidotomy |
|
|
HUNTInGTON's drugs |
Palliative and symptomatic: Antidopaminergic (= aytpical antipsychotic drugs) = tetrabenazine, haloperidol, olanzapine
Antidepressant drugs = imipramine amityptiline. |
|
|
DBS: what are the potential uses? |
Implant into STN in Parkinson's disease Tourette Syndrome Major Depressive disorder Obsessive compulsive disorder. |
|
|
Outline the mechanism of DBS: |
Application of mild, adjustable and reversible electrical current to target sites. Stimulation causes pattern changes across populations of neurones resulting in modulation. Suppress abnormal oscillations in basal ganglia networks.
Stimulation results in the activation of outputs. this results in a change in neuronal activity. |
|
|
STROKE treatment: |
1. Thrombolysis if infarct: tpA 2. Transfer to stroke unit 3. Antiplatelet therapy = 300mg aspirin and then 75mg clopidogrel 4. Address risk factors 5. Treat complications 6. MDT rehabilitation 7. Advice and education |
|
|
MS Treatment: What are the top 3 drugs? |
Natalizumab Alemtuzumab Fingolimod |
|
|
What are other MS drugs? |
IFN Beta/GA Teriflucomide DMF
Phase 3 trials: ocrelizumab, daclizumab, laquuinimod. Phase 2 trials: simponimod, firategrast, ofatumumab. |
|
|
What is the aim in MS treatment? |
NEDA = no evidence of disease activity = no relapses, no sustained disability progression, no MRI activity.
|
|
|
Name 3 orally-adminisited MS drugs: |
Teriflunomide Fingolimod DMF |
|
|
How are Natalizumab and Alemtuumab administered? |
IV |
|
|
PAIN: centrally acting analgesics: What are the key forms? |
1. Opiates: morphine, codeine, heroin = are all agonists for mu opioid receptors that bind endogenous enkepahlin found on lamina 1 cells and C fibre afferents. Block the excitatory action of the C fibres on lamina 1 cells.
2. Clondine, an Alpha 2 adrenoceptor agonist - has effects similar to GABA-ergic interneurons. (presynaptically inhibit the primary afferent and postsynaptic inhibition of the projection neurone- inhibitory) |
|
|
PAIN: how does acupuncture work? |
Thought to activate A delta fibres and in doing so descending inhibitory control of nociception.
Analgesia can also be produced by stimulation of non-noxious afferents. Stimulate lamina 2 cells. Basis of TENS. |
|
|
Depression/Anxiety: what are the aspect to CBT? |
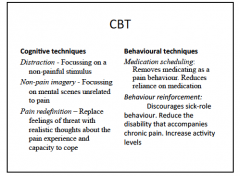
|
|
|
PAIN: describe the mechanism of action of morphine: |
Activates K+ conductance out of the cell and decreases calcium conductance into the cell.
OVERALL - decreases the excitability and decreases the release of neurotransmitters. |
|
|
PAIN: name 3 opioids: |
Morphine Codeine Tramadol |
|
|
PAIN: what are some of the negative S/Es of opioids? |
CNS: analgesia, resp depression, drowsiness, euphoria or dysphoria, miosis, nausea and vomitting.
CVS: hypotension
GI system: delayed gastric emptying and decreased biliary and pancreatic secretions
Urinary urgency Itching
|
|
|
PAIN: what is the metabolite of morphine that can aciculate if renal function is impaired? |
M6G metabolite. |
|
|
PAIN: outline the opioid ladder: |

|
|
|
PAIN: non-opioids: what is the mechanism of action of Paracetamol? |
It reduces the active oxidised form of COX-2 and modulate the endogenous cannabinoid system. Analgesic, antipyretic but little anti-inflammatory effect. |
|
|
PAIN: non-opioids: what is the mechanism of action of NSAIDs? |
They inhibit COX enzymes:
Aspirin: COX1 and COX2 inhibitors: analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflam. (prevent prostaglandin formation)
Ibuprofen, diclofenac and ketoprofen: also inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition. Plus additional mechanisms…analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. |
|
|
PAIN: name a selective COX-2 inhibitor: |
Refecoxib. |
|
|
PAIN: what are the indications and side effects of NSAIDs? |
Indicated for: rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, dysmenorrhea, gout and muscle spasm.
SEs: nausea, GI bleeds. |
|
|
PAIN: non-opioids: name and explain the MOA of anticonvulsant drugs: |
1. Carbamazepine: acts on sodium channels. 2. Sodium valproate: acts on sodium channels. 3. Pregabalin: acts on the alpha 2 delta sub unity of calcium channels. |
|
|
What are the indications for antidepressants and what is the MOA? |
Neuropathic pain, cancer, depression, Huntington's disease.
TCADs inhibit the reuptake of amines and also block sodium and calcium channels. |
|
|
PAIN: What medication are used for migraines? |
Triptans Ergoatamine derivatives
|
|
|
PAIN: State the key receptors involved in complex types of pain: |

|
|
|
PAIN: what are the 1st, 2nd and 3rd line drugs for neuropathic pain? |
1st line - SNARIs = duloxetine and venlafaxine TCAs Pregabalin, gabapentin (calcium channel ligands)
2nd line - Tramadol Capsaicin patches (vanilloid receptors) Lidocaine
3rd line- Strong opioids Botulinum toxin A |
|
|
PAIN: name 3 local anaesthetics and their MOA. What is the main risk? |
Lignoicaine, bupivacaine, prilocaine
MOA: blockage od sodium channels.
Risks: systemic toxicity, hypotension, resp depression and bradycardia. |
|
|
PAIN: what is the modes of administration and MOA of general anaesthetics + their major risk: |
Inhaled or IV MOA: activation of inhibitory receptors or inhibition of excitatory receptors
RISK = induce CV depression |
|
|
PAIN: Name 4 Inhaled and 4 IV general anaesthetics: |
Inhaled: Halothane Enflurane Isofulrane Nitrous oxide
IV Propofol Thiopental Etomidate Ketamine |
|
|
PAIN: how is trigeminal neuralgia treated? |
Carbamazepine Baclofen Phenytoin Valproate Clonazepam
|
|
|
EPILEPSY: anti epileptic drugs: what are the main classes? |
Sodium channels Benzodiazepines Barbiturates Calcium channels Neurotransmitter uptake Neurotransmitter release Neurotransmitter synthesis Neurotransmitter receptors |
|
|
EPILEPSY: anti-epileptic drugs: |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: explain the meaning of zero order or saturation kinetics of Phenytoin: |
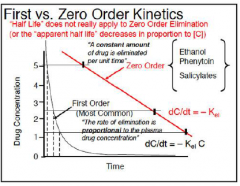
|
|
|
EPILEPSY: what drugs act on sodium channels? |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: what drugs act on calcium channels? |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: what drugs are GABA A receptor positive allosteric modulators? |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: what drugs act on: NT release? NT uptake? NT synthesis? |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: what do Vigabatrin and Tiagabine inhibit? |

Relevant because epilsepy may be accompanied by a loss of cortical chandelier GABA-ergic cells. |
|
|
EPILEPSY: what drugs should be given for each type of epilepsy? |

|
|
|
EPILEPSY: how should status epileptics be managed? |
It is a medical emergency. Treat with Diazepam IV.
May be potential for vagal nerve stimulate and DBS in the future. |
|
|
ADDICTION: what are the broad classes of treatments? |

|
|
|
MS: name some key anti-spastic drugs that are currently used in MS |
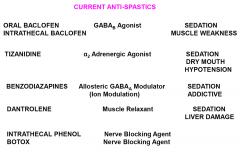
|
|
|
CANNABINOIDS: what is Rimonabant? |
CB1 Antagonist Anti-obesity drug
|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: classify drugs of abuse into CLass A, B and C: |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what are the key receptors for drugs of abuse? |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what is ecstasy? |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what are the MDMA targets? |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what are the symptoms of acute MDMA toxicity? |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what are the risks of smoking cannabis? |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: name a CB1 receptor agonist that is used therapeutically: |

|
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: how can nicotine addiction be managed? |
Nicotine replacement therapy- nicotine agonists Bupropion - monomamine- especially dopamine reuptake inhibitors. |
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: how can opiate addiction be managed? |
Methadone = opioid agonist
Buprenorphine - mu receptor, partial agonist, kappa antagonists
Clonidine and lofexidine - alpha 2 adrenreceptor agonists
Naltrexone: relapse prevention. |
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: what is Varenicline? |
Varenicline: is a α4β2 partial agonist
Adverse effects: nausea, psychiatric disturbances (FDA black box warning) |
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: how can cocaine/crack addiction be managed? |
Detoxification and anti-cocaine vaccine |
|
|
DRUG DEPENDANCE: how can alcohol addiction be managed? |
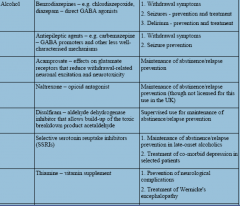
|
|
|
DEPRESSION: TCADS: |

|
|
|
DEPRESSION: SSRIS |

|
|
|
DEPRESSION: MAOIS |

|
|
|
DEPRESSION: Explain the delay of action of TCADs: |
•Tricyclic drugs inhibit reuptake of amines •The immediate increase in synaptic concentration of amines may lead to activation of somatic neuronal autoreceptors (e.g. 5-HT1A type) •The activated autoreceptors decrease firing of the neurones •During the first weeks of treatment the autoreceptors desensitize •The neurones will return subsequently to the normal firing rate •The inhibition of reuptake continues and the level of amines continues to be high |
|
|
DEPPRESION: what is escitalopram? |
It is a new S-isomer of citalopram |
|
|
DEPRESSION: Reversible MAOIs: |

|
|
|
DEPRESSION: what/where does Venlafaxine and Reboxetine act? |

|
|
|
DEPRESSION: What is Agomelatine? |
Recent drug with new mechanism of action: agonist at melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors and antagonist at 5-HT2c receptors (may act as a noradrenaline/dopamine disinhibitor) Onset of effect in the first week of treatment; improves sleep quality; less sexual dysfunction than SSRIs; anxiolytic effects; no discontinuation syndrome
|
|
|
BIPOLAR: how can Bipolar be managed? |
Lithium: used as maintenance treatment in bipolar disorder, acute mania and drug-resistant depression Narrow therapeutic margin (0.6-1mM)
Renal and thyroid function checked before treatment (and then at regular intervals during maintenance treatment) Adverse effects: thirst, nausea, fine tremor, polyuria, weight gain, oedema, acne |
|
|
MOOD STABILISERS: state two mood stabilising drugs that are also used in epilepsy and for neuropathic pain: |

|
|
|
MOOD DISORDERS: what are the non-pharmacological approaches? |

|
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: what are the typical antipsychoitcs used? |
Typical antipsychotics (neuroleptics) chlorpromazine, thioridazine, fluphenazine, haloperidol, flupenthixol |
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: what are the atypical antipsychoitcs used? |
Atypical antipsychotics (neuroleptics) risperidone, olanzapine, clozapine, quetiapine
•Atypical neuroleptics may improve cognition (MODERATE EFFECTS) •All atypicals also have significant antagonist activity at 5-HT2 receptors •Clozapine blocks D4 receptors with high affinity
|
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: what are adverse effects of using antipsychoitcs used? |
Extrapyramidal effects (acute dystonias, parkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia) Rise in prolactin (galactorrhoea, amenorrhoea) Weight gain (atypicals) Dyslipidemia (atypicals) Type 2 diabetes (atypicals) General - allergic and toxic reactions, Anticholinergic effects (clozapine, haloperidol) Postural hypotension |
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: name a rare antipsychotic drug complication:
|
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome • hyperpyrexia • rigidity • confusion • autonomic instability |
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: what is an irreversible complication of antipsychotics? |
Tardive Dyskinesia. |
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: what is Clozapine? |
It is the drug of choice in drug resistance.
but risk of aggranulocytosis. |
|
|
SCHIZOPHRENIA: name two drugs that can be given as depot injections: |
Fluphenazine, Haloperidol. |
|
|
ANXIETY: what are the main classes of anxiolytics? |
•Benzodiazepines (clonazepam, alprazolam…) = positive allosteric modulators of the GABA A receptor complex. •5-HT1A agonists (buspirone, ipsapirone) partial agonism •β-antagonists (propranolol…) •SSRIs (fluoxetine, escitalopram, paroxetine…) •Barbiturates (obsolete)
|
|
|
ANXIETY: how do benzodiazepine and barbiturates effect the GABA A channel? |
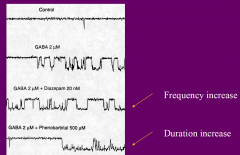
|
|
|
ANXIETY: how can benzodiazepine overdose be managed? |
With Flumaxenil. |
|
|
ANXIETY: what are the treatments for Generalised Anxiety disorder? |
buspirone •venlafaxine, duloxetine (SNRI) •fluoxetine, escitalopram (SSRI) •risperidone, quetiapine, olanzapine (APD)
|
|
|
ANXIETY: HYPNOTICS: what are the unwanted effects of benzodiazepines used as hypnotics? |
Unwanted effects of benzodiazepines used as hypnotics •Change in sleep patterns (suppress deep sleep and REM sleep) •Daytime sedation •Rebound insomnia •Tolerance •Dependence (withdrawal syndrome characterised by anxiety, nausea, muscle cramps, seizures) |
|
|
ANXIETY: what are the complications of benzodiazepines in the elderly? |
Psychomotor impairment Risk of falls Daytime drowsiness Intoxication Amnesia Depression Respiratory problems Abuse and dependence |
|
|
DEMENTIA: what are the 2 classes of drugs used as treatment? |

|
|
|
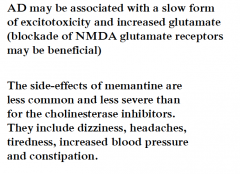
DEMENTIA: what is the MOA and side effects of using MEMANTINE? |
|
|
|
DEMENTIA: what symptomatic medication may be used? |

|
|
|
DEMENTIA: what are some potential disease modifying therapies? |

|

