![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Growth Cone |
respond to different chemicals sent by target cells like chemoattractants and chemorepellants
10-20 um in length, longer than cell body usually -depending on its makeup can be inhibited or attracted to certain cues |
|
|
Epilepsy, autism, schizophrenia are primarily caused by defects in |
neural migration during weeks 12-20 |
|
|
Attractive and repulsive cues to the growth cone |
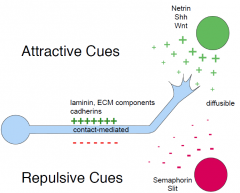
|
|
|
Netrin induces |
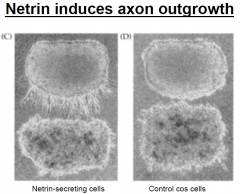
outgrowth. It is an attractant to the growth cone |
|
|
Semaphorins are |

repellents for the growth cone |
|
|
axonal guidance occurs ____. Why? |
Early; to simplify things. If you build up earlier, it's easier to modify later. |
|
|
Netrin is produced in |
the floorplate and ventricular plate to draw neurons down |
|
|
TF Netrin is always an attractant |
False, Netrin can function as a repellent thanks to molecular versatility Unc5 receptors allow neurons to be repelle by netrin instead of attracted. The same situation occurs for other attractants/repellents with different receptor/ligand combinations |
|
|
How do a limited number of molecular cuessolve the wiring problem?
|
1. Simplicity:
• start early • use intermediate targets 2. Versatility: • use multiple and redundant cues • positive and negative • permissive and instructive • use cues that are multi-functional 3. Plasticity: • allow errors early, refine later • learn as you go (modulation of responses) |
|
|
Corpus callosum is formed by |
week 20 |
|
|
How does neuronal wiring occur in stages? |
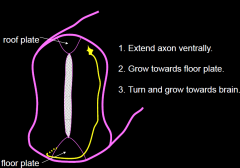
1) Extend axon ventrally 2) Grow towards floor plate 3) turn and grow towards brain Netrin is secreted ventrally and causes growth in the direction, Shh induces turning |
|
|
Commissural neuron outgrowth |
Attractive protein cues cause them to extend from dorsal, cross over the midline into ventral and extend there.
|
|
|
Axons grow towards the floor platebecause |
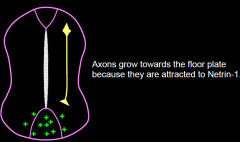
they are attracted to Netrin-1.
|
|
|
Trochlear Motor Axonsgrow
|
away from the floorplate (remember the trochlear nerve is the odd cranial nerve that doesn't come around ventral |
|
|
Netrin inhibits outgrowthof the (which cranial nerve)? |
Trochlear (4) |
|
|
after neurons cross the midline, netrin causes them to do what? |
Nothing, after neurons cross the midline, they stop responding to netrin They are now repelled by slit |
|
|
Unc5 related receptors |
allow neurons to be repelled from netrin instead of attracted |
|
|
Roof plate produces |
BMP; repels axons |
|
|
Congenital Mirror Movement Disorder is a result
|
hands move at the same time because there is no commnunication between hemispheres
|
|
|
Plasticity is necessary for axons to |
leave the midline |
|
|
At what point do axons gain the ability to respond to other cues?
|
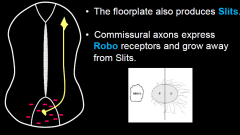
When they reach the floorplate. Commissural axons begin to express Robo and grow away from Slits that are expressed in the floorplate (at the midline). |
|
|
Explain how a commissural neuron grows in 3 steps |
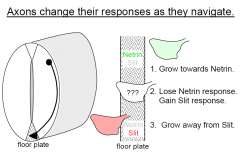
|
|
|
How do axons use several mechanismsto change their responses to cues |
1. Receptor interactions modulate signaling
2. Changes in the intrinsic state of the cell 3. Local protein synthesis or stabilization |
|
|
When the Robo3 receptor is present, axons
|
ignore slits |
|
|
When Robo3 is absent or mutated, axons
|
no longer enter the floorplate
|
|
|
Horizontal Gaze Palsy with Progressive Scoliosis (HGPPS)
|
Loss of horizontal saccades and/or pursuit in both eyes in lateral gaze. Corticospinal and somatosensory tracks are uncrossed Rig1/ROBO3 is mutated in HGPPS |
|
|
Slit2 _____ Netrin response
|
silences |
|
|
Changes in the intrinsic state of the cell can be manifested how?
|
cAMP levels affect how cells respond to ligands
|
|
|
BDNF:
|
normally attracts xenopus spinal cord neurons |
|
|
EphA2 is translated
|
only after crossing themidline.
Controlled by specificsequences in the3’ UTR of EphA2 |
|
|
How does axon guidance signalinglead to directed outgrowth?
|
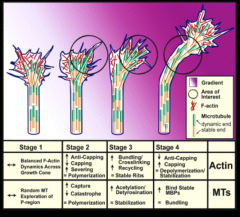
|
|
|
Directed movement of the growth coneinvolves regulated changes in the cytoskeleton. What are they?
|
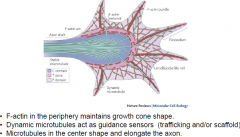
|
|
|
what regulates the cytoskeleton?
|
Small GTPases • Rho, Rac, Cdc42• well characterized regulatorsof the actin cytoskeleton• Regulated by binding GDP/GTP • GEFs (Guanine Exchange Factors): activate (~70 in mammals) |
|
|
Chemoaffinity hypothesis |
Proposed by Roger Sperry that neurons or their axons and dendrites are drawn toward a signaling chemical that indicates the correct pathway. |
|
|
The Stripe Assay
|
temporal axons of retina only want to grow on anterior tectum tissue but nasal axons grow regardless of anterior or posterior tectum tissue; happens because posterior tectum secretes repulsive signal (ephrin) and temporal axons are the only one to have receptor for signal
|
|
|
Ephrin receptors are |
tyrosine kinases |
|
|
ephrin ligands are |
membrane bound repellents |
|
|
ephrin |
Cell surface tethered guidance cues. They react with Eph receptors in juxtacrine signaling (interact with other proteins on other cell surfaces). Ephrine in sclerotome extra-cellular matrix repels the migrating neural crest cells that have Eph receptors on their surface.
|
|
|
Ephrins and their receptors generate |
generate topographic maps |
|
|
How does ephrin signaling cause temporal retinal neurons to know where they're going? |
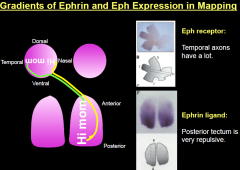
|
|
|
EphA and EphB signaling in the retinal pathway |
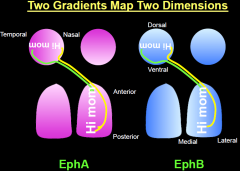
|
|
|
How is a smooth map generatedusing Ephrins and Eph receptors?
|
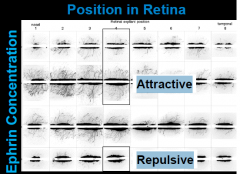
• Ephrins can be both attractive and repulsive.
• Ephrin activity is exquisitely concentration sensitive. |
|
|
increases in cGMP/cAMP levels cause? Decreases? |
Increase: usually attraction decreases: usually repulsion |
|
|
EphA and B specify what? |
the lateral-medial axis |
|
|
What is fasiculation? What does it involve? |
the formation of a bundle of axons. Involves adhesion molecules -May have secondary effects on guidance and topography - May also be used to follow pioneer axons |
|
|
TF Sema3A attracts axons and dendrites |
False, Sema3A repels axons, but DOES attract dendrites |
|
|
Dendritic tiling |
Dendrites must avoid themselves and other axons, so they repel through Dscam (Down Syndrome cell adhesion molecule) |
|
|
What kind of receptor is Dscam? |
a netrin receptor |
|
|
Dscam mediates |
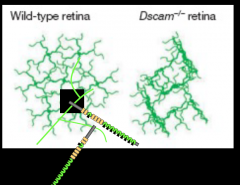
self repulsion |
|
|
Give an overview o f how axons are guided to the right location |
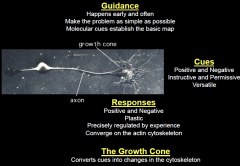
|
|
|
How does autism relate to axon guidance?
|
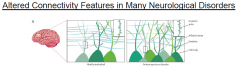
Too many connections, too many spines. Improper growth. |
|
|
synkinesis
|
movement disorders |
|
|
agenesis |
corpus callosum growing in the wrong way (not uniform) |

