![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
To understand that different stages use different setsof cues and, therefore, that growth cones must be reprogrammed at choice points |
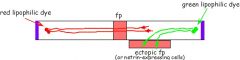
1.After crossing midline/ floorplate commissural axons lose responsiveness to netrins Ectopic FP: axons exposed before reaching midline turn axons exposed after midline don't
2.Also become sensitive to repellants (responsive to inhibitory molecules) -semaphorins, -Slits
Sensitivities switch. |
|
|
What do Slit, Robo and Comm expression do to axons? |
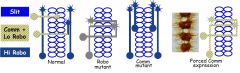
Drosophila Robo encodes R for Slit (inhibitory protein)
Robo protein is expressed at high levels on axons that don't cross midline
C. axons initially express low levels, high levels after cross
Robo mutants: no protein. axons go back and forth across midline
Comm: expressed only in neurons that cross midline, switched off after they cross
Comm mutants (no protein): high levels of Robo protein in cells that would normally cross midline - now don't cross
Forced Comm expression: Robo protein lost everywhere. Low Robo phenotype
So Comm inhibits Robo
|
|
|
How do growth cone sensitivities get reprogrammed? |
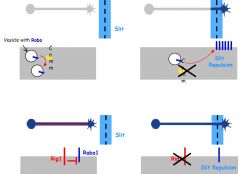
Robo is prevented from functioning Invertebrates Camm encodes 'trafficking' proteins that prevent Robo reaching cell surface. Growth cone can't receive Slit inhibitory signal before crossing.
Vertebrates Robo homologs (no Camm homologs): Robo1 expressed before and after crossing Rig1 (Robo3) only expressed in precrossing fibres Rig1 blocks Robo1 signalling until midline crossed. Loss of Rig1 results in failure to cross FP |
|
|
Tolook at how axons get on and off axon scaffolds – The role of fasciculation |
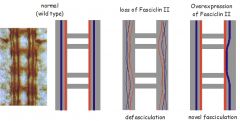
Homophilic binding (like binds like) by cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) eg Fasciclin II |
|
|
Tolook at how axons get on and off axon scaffolds – Getting off in the target area |
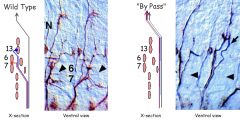
Fas II adhesion controls defasiculation overexpression of Fas II leads to 'by pass' phenotype motor axons fail to defasiculate and miss their targets |
|
|
Tolook at how targets are selected |
2 main types: 1.Discrete targets 2.Topographic maps |
|
|
To look at how targets are selected Discrete targets |
Axons looking for specific labels on their targets (ablation studies) Netrin expressed in specific muscles (diffusible chemoattractant) Loss - like ablating muscle axons wander and don't make synapses Ectopic- axons innervate wrong muscles Fasciclin 3 expressed in specific muscles and the axons that innervate them (homophilic adhesion molecule) Ectopic- innervates new targets |
|
|
To look at how targets are selected Topographic maps |
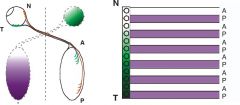
Neighbouring neurons send axons to neighbouring sites in target to maintain topology. Sperry The 'stripe assay' shows cells from P tectum make a non-permissive factor that repels T retinal axons Evidence: activity abolished by heat treatment of P but not A membranes P membranes cause T growth cones to collapse in vitro
Inhibitory factors = Ephrin A2 and A3. expressed in grdt in tectum Eph R (Eph A3) expressed in counter grdt in retina |

