![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are parts of upper limbs |
-humerus -radius -ulna -carpals -metacarpals -phalanges |
|
|
what structures make up anterior wall of axilla? |
-pectoralis major -pectoralis minor -clavicle |
|
|
what structures make up posterior wall of axilla? |
-scapula (subscapularis) -teres major (inferiorly) -latissimus dorsi (inferiorly) |
|
|
what structures make up medial wall of axilla? |
-thorax -serratus anterior
|
|
|
what structures make up lateral wall of axilla? |
intertubular sulcus (groove) of humerus |
|
|
what are contents inside axillary sheath? |
-axillary artery -axillary vein -brachial plexus |
|
|
what are 4 major branches of subclavian artery? |
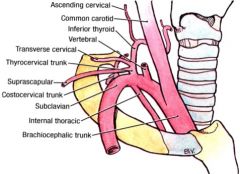
-vertebral artery -internal thoracic artery -thyrocervical trunk -costocervical trunk |
|
|
what are 3 branches of thyrocervical trunk |
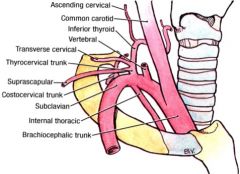
-inferior thyroid artery -transverse cervical artery -suprascapular artery |
|
|
2 terminal ends of costocervical trunk |
-root of neck -first 2 intercostal spaces |
|
|
where does subsclavian artery become axillary artery? |
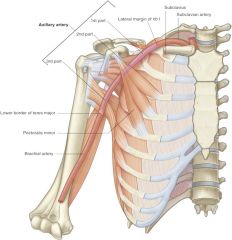
1st rib |
|
|
where does axillary artery become brachial artery? |
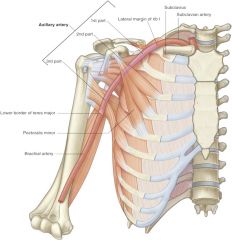
inferior border of teres major |
|
|
parts of axillary artery are divided based upon spatial relationship with what muscle? |
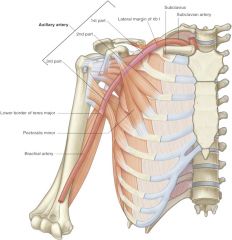
pectoralis minor |
|
|
what are 6 branches of axillary artery? |
-superior thoracic artery -thoracoacromial trunk -lateral thoracic artery -subscapular artery -anterior humeral circumflex artery -posterior humeral circumflex artery |
|
|
what are 4 branches of thoracoacromial trunk and where do they supply? |
-acromial (acromion process) -deltoid (deltoid) -pectoral (pectoralis muscles) -clavicular (articulation between clavicle and sternum) |
|
|
what are 2 branches of subscapular artery and where do they supply?** |
-circumflex scapular artery (posterior aspect of scapula) -thoracodorsal artery (latissimus dorsi) |
|
|
what is the location of anterior and posterior humeral circumflex arteries? |
surgical neck of humerus |
|
|
what are 3 major veins in and around axilla? |
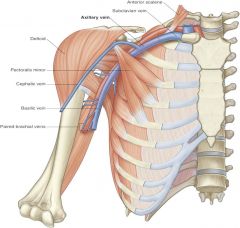
-brachial vein -basilic vein -cephalic vein |
|
|
which vein do brachial, basilic and cephalic vein drain into? |
axillary vein |
|
|
which vein does axillary vein drain into? |
subclavian vein |
|
|
subclavian vein along with internal jugular vein merge to from which vein? |
brachiocephalic vein |
|
|
For the most part, but not always, the major veins are located deep OR superficial to their corresponding artery? |
superficial |
|
|
pathway of brachial vein drainage into axillary vein |
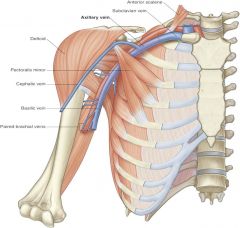
brachial vein --> basilic vein --> axillary vein |
|
|
pathway of cephalic vein drainage into axillary vein |
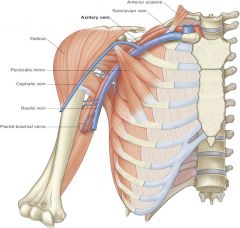
cephalic vein --> axillary vein |
|
|
bone of arm (brachium) |
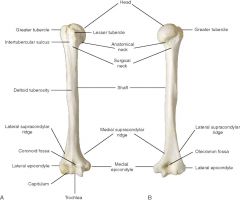
humerus |
|
|
bones of forearm (antebrachium) |
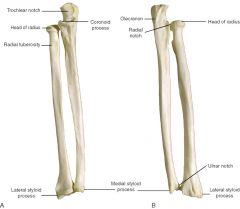
-radius -ulna |
|
|
bones of hand |
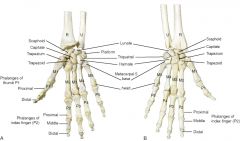
-carpals -metacarpals -phalanges |
|
|
joint at shoulder |
glenohumeral joint |
|
|
joint at elbow |
humeroulnar joint |
|
|
joint at wrist |
radiocarpal joint |
|
|
4 joints in hand |
-midcarpal joint -carpometacarpal joint -metacarpo-phalangeal joint -interphangeal joint |
|
|
what nerve and artery sit in the radial groove (sulcus) of humerus? |
-radial nerve -profunda brachii artery
|
|
|
where can you find the radial notch and ulnar notch? |
radial notch is on the ulna (proximal) ulna notch is on the radius (distal) |
|
|
how many carpal bones in wrist? |
8 |
|
|
how many bones are in hand total? |
27 |
|
|
what are 8 carpal bones? |
-Scaphoid -Lunate -Triquetral -Pisiform -Trapezium -Trapezoid -Capitate -Hammate
Mnemonic: Some Lovers Try Position That They Cannot Handle |
|
|
pectoralis major -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
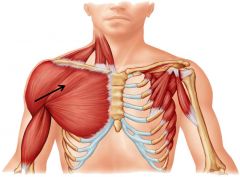
ORIGIN: -clavicle, anterior sternum, upper 6 costal cartilage, and aponeurosis of external oblique INSERTION: -lateral aspect of intertubercular groove (bicipital groove) of humerus ACTIONS: -flex shoulder -adduction of humerus -medial rotation of humerus -also involves in forced respiration INNERVATION: -lateral and medial pectoral nerves |
|
|
Deficiency of pectoralis major |
Poland syndrome |
|
|
what are 3 muscles in anterior compartment of arm? |
-biceps brachii -brachialis -coracobrachialis |
|
|
What nerve innervate muscles in the anterior compartment of arm? |
musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
Muscles in the anterior compartment of arm general action |
flexion |
|
|
biceps brachii -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
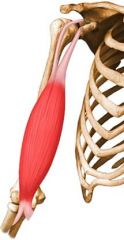
ORIGIN: -short head: coracoid process -long head: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula INSERTION: -radius (radial tuberosity) ACTION: -flex forearm (humero-ulnar joint, strong) -supinator (radio-ulnar joint, strong) -flex arm (weak) -shoulder adduction (short head) INNERVATION: -musculocutaneous nerve |
|
|
coracobrachialis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
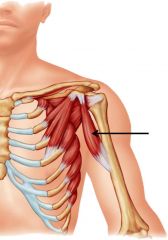
ORIGIN: -coracoid process INSERTION: -humeral midshaft (medial) ACTION: -flex arm -adduct arm INNERVATION: -musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
brachialis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
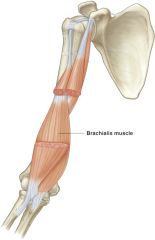
ORIGIN: -anterior distal portion of humerus INSERTION: -ulnar coronoid process ACTION: -flex forearm (major) INNERVATION: -musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
location of musculocutaneous nerve in relation to coracobrachialis and brachialis |
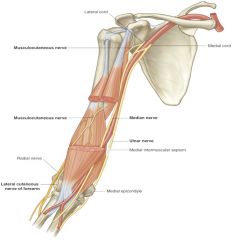
musculocutaneous nerve pierces through coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles. It also runs between brachialis and biceps brachii muscles. |
|
|
what are 3 muscles of posterior compartment of arm? |
-triceps brachii -anconeus -brachioradialis |
|
|
what nerve innervates muscles in the posterior compartment of arm? |
radial nerve |
|
|
muscles in the posterior compartment of arm general action |
extension |
|
|
triceps brachii -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
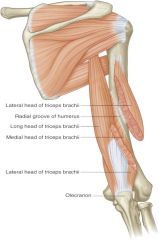
ORIGIN: -long head: infraglenoid tubercle (scapula) -lateral head: posterolateral surface (humerus) -medial or deep head: posterior surface below radial groove (humerus) INSERTION: -single tendon on olecranon (ulna) ACTION: -forearm extension at elbow -shoulder extension (long head only) -shoulder adduction (long head only) |
|
|
anconeus muscle -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
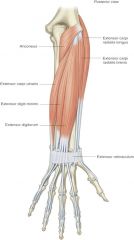
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle (humerus) INSERTION: -olecranon process (ulna) ACTION: -forearm extension at elbow -pronation INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
brachioradialis muscle -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
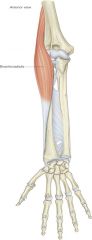
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle (humerus) INSERTION: -styloid process (radius) INNERVATION: -radial nerve ACTION: -flex forearm**
**exception to posterior compartment rule** |
|
|
which muscle in the posterior compartment of arm that will flex instead of general rule of extension? |
brachioradialis |
|
|
relationship of radial nerve and profunda brachii artery with triceps brachii |
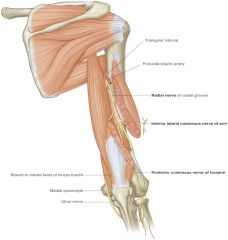
deep to lateral head of triceps brachii |
|
|
Major branches of brachial artery |
-profunda brachii artery -superior ulnar collateral -inferior ulnar collateral -humeral nutrient |
|
|
location of brachial artery in relation to axilla and humerus |
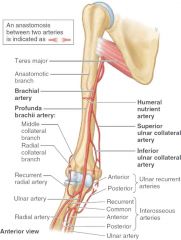
enters axilla medially and at humeral midshaft, the artery moves anterioly |
|
|
radial artery is a branch of which artery? and where does it branch off of? |
-brachial artery -radial neck |
|
|
location of radial artery in relation to brachioradialis muscle |
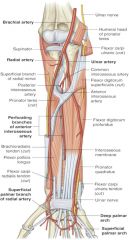
radial artery is deep to brachioradialis muscle (proximal half of forearm) |
|
|
location of radial artery in relation to radial nerve |
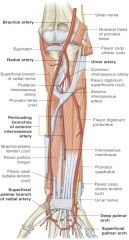
radial artery is medial to radial nerve (middle third of forearm) |
|
|
location of radial artery in relation to brachioradialis tendon |
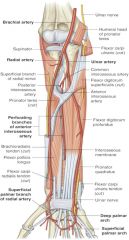
radial artery is medial to brachioradialis tendon (covered only by deep fascia, superficial fascia and skin in distal forearm) |
|
|
ulnar artery is a branch of which artery? where does it branch off of? |
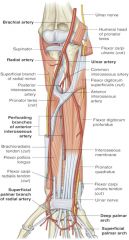
-brachial artery -radial neck |
|
|
ulnar artery is found in what aspect of forearm? |
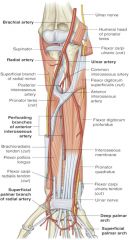
medial |
|
|
location of ulnar artery in relation to pronator teres muscle |
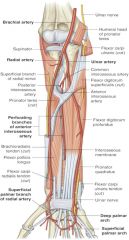
ulnar artery is deep to pronator teres |
|
|
location of ulnar artery in relation to flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus |
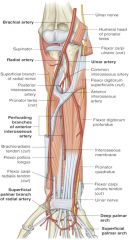
ulnar artery passes through fascial plane between those two muscles |
|
|
in distal forearm, what is location of ulnar artery in relation to ulnar nerve? |
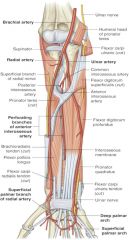
ulnar artery is lateral to ulnar nerve |
|
|
what are superficial veins of upper limbs? |
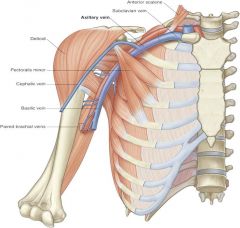
-cephalic vein -basilic vein |
|
|
pathway of superficial lymphatic system of upper limb |
lymphatic plexus of hand --> basilic/cephalic vein --> axillary lymph nodes |
|
|
pathway of deep lymphatic system of upper limb |
radial, ulnar, brachial, axillary veins --> axillary lymph nodes |
|
|
what are superior, medial and lateral borders of cubital fossa? |
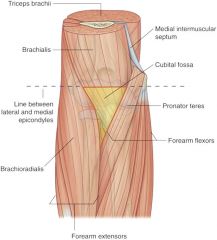
superior: epicondyle line medial: pronator teres lateral: brachioradialis |
|
|
relationship between cephalic vein and basilic vein in term of their location |
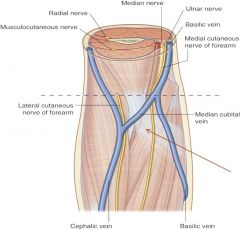
lateral: cephalic vein medial: basilic vein |
|
|
what are 3 ligaments of humero-ulnar and radio-ulnar joints? |
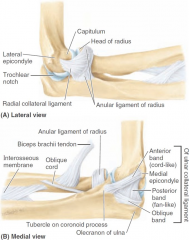
-radial collateral ligament -ulnar collateral ligament -anular ligament of radius |
|
|
location of radial collateral ligament |
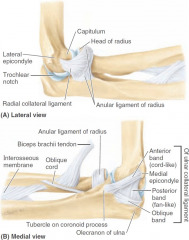
lateral epicondyle to anular ligament of radius (proximal radio-ulnar joint) |
|
|
location of ulnar collateral ligament |
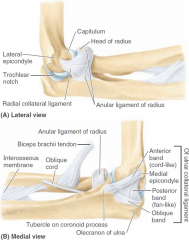
medial epicondyle to coronoid process/olecranon of ulna |
|
|
what are 3 bands of ulnar collateral ligament? |
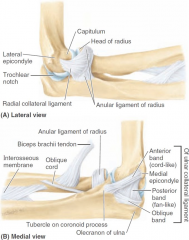
-anterior band -posterior band -oblique band |
|
|
which ligament holds radius and ulna together? |
anular ligament of radius |
|
|
when arm is flexed, which band of ulnar collateral ligament will stretch? |
posterior band |
|
|
when arm is extended, which band of ulnar collateral ligament will stretch? |
anterior band |
|
|
3 types of elbow injuries |
-subclinical subluxation (radius is partially pulled downward and away from ligament) -subluxation (radius is completely pulled downward and away from ligament) -dislocation (radius is completely moved laterally away from ligament) |
|
|
what are borders of forearm compartments? |
-antebrachial fascia -interosseous membrane -fibrous intermuscular septum |
|
|
muscles in posterior compartment of forearm are innervated by which nerve? |
radial nerve |
|
|
muscles in anterior compartment of forearm are innervated by which nerve? |
median nerve |
|
|
which 2 muscles in the anterior compartment are innervate by ulnar nerve instead of median nerve? |
-1/2 of flexor digitorum profundus -flexor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
what are superficial muscles of anterior forearm? |
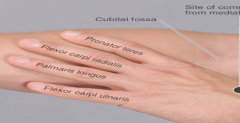
-pronator teres -flexor carpi radialis -palmaris longus -flexor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
superficial muscles of anterior forearm share a common origin, which is? |
medial epicondyle of humerus |
|
|
pronator teres -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
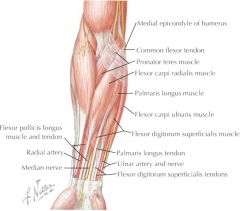
ORIGIN: -medial epicondyle of humerus via common flexor tendon -medial side of coronoid process of ulna INSERTION: -radius ACTION: -pronates at elbow joint INNERVATION: -median nerve
|
|
|
flexor carpi radialis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
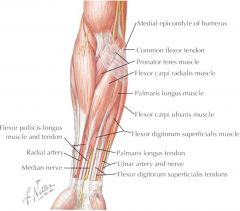
ORIGIN: -medial epicondyle of humerus via common flexor tendon INSERTION: -2nd metacarpal ACTION: -flex wrist -abduct wrist INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
palmaris longus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
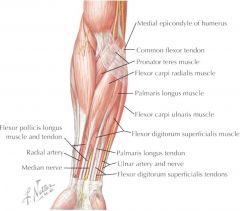
ORIGIN: -medial condyle of humerus via common flexor tendon INSERTION: -palmar aponeurosis of hand ACTION: -flex wrist INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
flexor carpi ulnaris -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
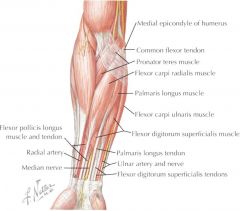
ORIGIN: -medial epicondyle of humerus via common flexor tendon -olecranon of ulna INSERTION: -pisiform carpal bone ACTION: -flex wrist -adduct wrist INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
what is special about palmaris longus? |
14% of people don't have it on one side of their body |
|
|
what is an intermediate muscle of anterior forearm? |
-flexor digitorum superficialis |
|
|
flexor digitorum superficialis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
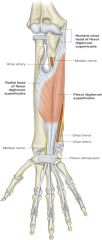
ORIGIN: -medial epicondyle of humerus via common flexor tendon -upper 1/2 of radius INSERTION: -palmar aspects of middle phalanges II-V ACTION: -flex proximal interphalangeal joints INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
what are 3 deep muscles of anterior forearm? |
-flexor pollicis longus -flexor digitorum profundus -pronator quadratus |
|
|
flexor pollicis longus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
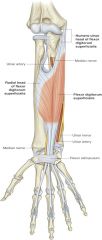
ORIGIN: -proximal aspect of radius and interosseous membrane INSERTION: -distal phalanx of thumb ACTION: -flex interphalangeal joint INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
flexor digitorum profundus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
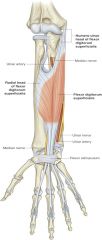
ORIGIN: -anterior aspect of ulna and interosseous membrane INSERTION: -distal phalanx of II-V ACTION: -flex distal interphalangeal joints INNERVATION: -ulnar nerve** -median nerve
|
|
|
pronator quadratus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
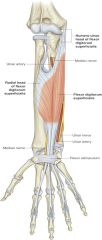
ORIGIN: -anterior distal surface ulnar diaphysis INSERTION: -anterior distal aspect of radius ACTION: -forearm pronation INNERVATION: -median nerve |
|
|
what are 2 arteries of anterior forearm |
-ulnar artery -radial artery |
|
|
ulnar artery location in the anterior forearm |
-deep to superficial/intermediate layers to reach medial forearm -passes superficial to flexor retinaculum in ulnar canal at wrist and enters hand |
|
|
radial artery location in anterior forearm |
-inferolaterally under brachioradialis muscle -lateral to flexor carpi radialis tendons in distal forearm -winds around lateral aspect of radius and crosses floor of anatomical snuff box -pierces first dorsal interosseous muscle |
|
|
what are muscles of posterior forearm? |
-brachioradialis -anconeus -extensor carpi radialis longus -extensor carpi radialis brevis -extensor carpi ulnaris -extensor digitorum (communis) -extensor digiti minimi -extensor indicis -supinator -abductor pollicis longus -extensor pollicis longus -extensor pollicis brevis |
|
|
which nerve innervate muscles of posterior forearm? |
radial nerve |
|
|
extensor carpi radialis longus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
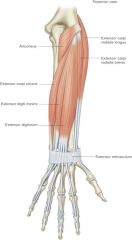
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus INSERTION: -2nd metacarpal ACTION: -extend wrist -abduct wrist INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
extensor carpi radialis brevis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
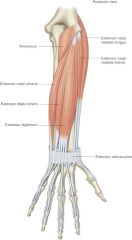
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus INSERTION: -2nd and 3rd metacarpal ACTION: -extend wrist INNERVATION: -radial nerve -abduct wrist |
|
|
extensor carpi ulnaris -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
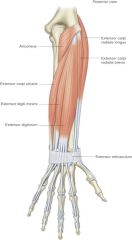
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus -ulna INSERTION: -5th metacarpal ACTION: -extend wrist -adduct wrist INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
extensor digitorum (communis) -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
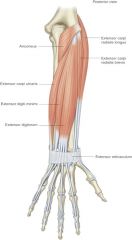
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus INSERTION: -via extensor hoods in dorsal aspect of middle and distal phalanges of 4 fingers ACTION: -extension at fingers INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
extensor digiti minimi -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
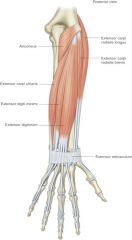
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus INSERTION: -via extensor hoods into dorsal aspect of middle and distal phalanges of 5th finger ACTION: -extend pinkie INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
what is the shape of extensor hoods? |
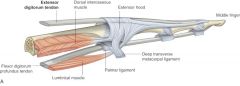
triangular |
|
|
extensor hoods borders |
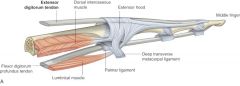
-apex: distal phalanx -central region: attached to middle phalanx -base: corner wrapped around MCP joint |
|
|
which muscles insert into extensor hoods? |
intrinsic muscles, allowing for fine movements |
|
|
extensor indicis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
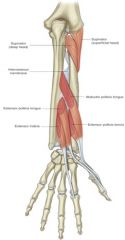
ORIGIN: -ulna and interosseous membrane INSERTION: -extensor hood of index finger ACTION: -extend index finger INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
supinator -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
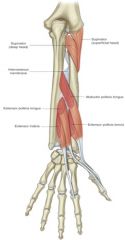
ORIGIN: -lateral epicondyle of humerus -proximal aspect of ulna below radial notch INSERTION: -lateral aspect of proximal end (radius) ACTION: -forearm supination INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
abductor pollicis longus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
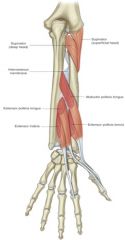
ORIGIN: -ulna -radius -interosseous membrane INSERTION: -base of 1st metacarpal ACTION: -abduct thumb -abduct wrist INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
extensor pollicis longus -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
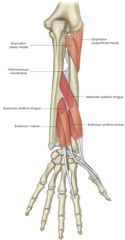
ORIGIN: -ulna -interosseous membrane INSERTION: -distal phalanx of thumb ACTION: -extend interphalangeal joints of thumb INNERVATION: -radial nerve |
|
|
extensor pollicis brevis -origin -insertion -actions -innervation |
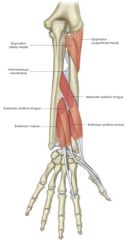
ORIGIN: -radius -interosseous membrane INSERTION: -proximal phalanx of thumb ACTION: -extend metacarpophalangeal joint of thumb -extend carpometacarpal joint of thumb |
|
|
what are the borders of anatomical snuffbox? |
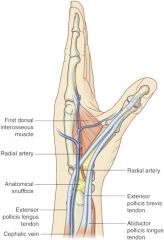
medial (ulnar) border -extensor pollicis longus tendon lateral (radial) border -abductor pollcis longus -extensor pollicis brevis tendons
|
|
|
what are contents of of anatomical snuffbox? |
radial artery (pulse can be taken in it) |
|
|
anatomical snuffbox is observed into which position of the hand? |
pronation |

