![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The area above the nose between the eyes is part of the forehead is called the
________. |
Glabellla
|
|
|
One feature of the frontal bone is very obvious is the little hole on either side above the eye socket is called the _______ _______.
|
Supraorbital foramen
|
|
|
Some people don't have the nice distinct hole from the supraorbital foramen. They have a little notch on the bone instead. This allows the ______ _______ to come out of the skull and to go across the forehead.
|
Superorbital nerves
|
|
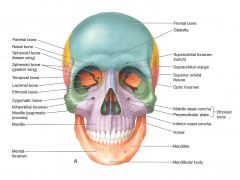
The _____ ______ is in the Aqua color
|
Frontal Bone
|
|
|
If you look at the anterior view of the skull you can see part of the 2 ____ _____?
|
Parietal Bones
|
|
|
If you look through the eye sockets you can see portions of the _____? The ____ has several parts one part is called the ____ _____, another part is called the ___ ___?
|
Sphenoid, sphenoid
Lesser wing, greater wing |
|
|
There are a number of important features with regard to the sphenoid. The 1st is that there is a round hole in the lesser wing called the ______ _______ or _____ _____?
|
Optic foramen or optic canal
|
|
|
Another important feature with regard to the sphenoid is that there are 2 slits which are _____ _____ and _____ ______?
|
superior orbital fissure, inferior orbital fissure
|
|
|
The _____ ______ ______ seperates the lesser wing from greater wing.
|
Superior orbital fissure
|
|
|
The reason the ______orbital fissure is important is that the ____nerves that control the movements of the _____ pass through there.
|
superior, three, eye
|
|
|
There are 3 nerves that come out from the brain and go to each eye and control the movement of the eyes ___, _____, ______ ___ ____ and they leave the brain and enter the boney ______ through the superior _______ fissures
|
Up, Down, side to side,
Orbit, Orbital |
|
|
There are two ____ _____, right and left.
|
Parietal bones
|
|
|
The right parietal bone extends all the way from the joint where it comes into contact with the ______ bone where the joint comes in contact with _______ bone.
|
frontal, occipital
|
|
|
Joints in the skull are known as _____
|
Sutures
|
|
|
Joint in the skull between the frontal bone and parietal is the _____ ______?(Think back when you studied the planes. The one that cut the head this way is the frontal/coronal plane so this is the ____?)
|
Coronal Suture
|
|
|
The second suture is the ____ ______. It is formed by a fibrous joint between the temporal and parietal bones on each side of the skull.
|
Squamous suture
|
|
|
The bone underneath the scalp is the ____ bone.
|
occipital
|
|
|
The 3rd suture you need to know is the ____ _____. It is the suture that runs at an angel. It seperates the _____ bone from the parietal and _____ bone.
|
lambdoid (LAMB DOID) suture,
occipital, temporal |
|
|
Another important feature of the temporal bone is a little piece that sticks down like a pen or stylus. It is called the ____ _____.
|
Styloid process
|
|
|
The _____ process is important because it serves as a site of attachment for some muscles.
|
Styloid
|
|
|
One feature of the temporal bone is the _______ process.
|
Zygomatic
|
|
|
The curve of the zygomatic process is called the ___ ____.
|
Zygomatic arch
|
|
|
The zygomatic arch is actually made up of two different bones. One piece comes from the _____ bone and the other part of the arch is made up of one of the facial bones called the ______ bone. (AKA high cheek bones)
|
Temporal, zygomatic
|
|
|
The temporal bone contributes the zygomatic process and the zygomatic bone contributes to the _____ _____.
|
Temporal process
|
|
|
The ___ ____ is important because it houses the pituitary gland.
|
Sella turcica
|
|
|
The ____ ____ is where the brain stem meets the spinal cord.
|
Foramen magnum
|
|
|
The plate with holes in it is the ________ plate.
|
Cribriform
|
|
|
The little holes in the cribriform plate are called _____ ______.
|
Olefactory foramina
|
|
|
What does olefaction mean?
|
Sense of smell
|
|
|
Inside the nose you have what's called olfactory _____. The mucosal _____ that lines the upper part of that _____ cavity contains _______ nerves.
|
Mucosa, membrane, olfactory, olfactory
|
|
|
The _____ _____ manaufactures a number of important hormones. Often times it is called the master gland of the body.
|
Pituitary gland
|
|
|
The ____ _____ of the temporal bone has little air cells and are small.
|
Mastoid process
|
|
|
The main or large air cells are known as ______ or _________ sinus.
|
Sinuses, paranasal
|
|
|
The superior and the middle nasal conca are parts of the ______ bone. The _______ nasal conca is not a part of the ethmoid bone. It is its own seperate _____ bone.
|
Ethmoid, inferior, facial
|
|
|
______ stands for rock.
|
Petrous
|
|
|
The ____ ____ goes through the temporal bone.
|
Ear canal
|
|
|
_____ ____ is the opening that allows the spinal cord to come up and go inside the skull where it joins with the brain stem.
|
Foramen magnum
|
|
|
What are the 4 sutures you need to know?
|
Coronal
Sagittal Lambdoid (LAMB DOID) Squamous |
|
|
The______ suture is the one that goes in the midsagittal line.
|
Sagittal
|
|
|
The soft spot/opening in a fetal skull are called _____.
|
Fontanelles
|
|
|
The _____ process which has those air cells could get infected and that would be mastoiditis.
|
Mastoid
|
|
|
The _____ looks like a bat, has the lesser and greater wing, the body bat
|
Sphenoid
|
|
|
The legs are made up of ______ plate. There is a _____ and a ______ on each side.
|
Pterygoid, lateral, medial
|
|
|
The ____ is oval in shape. The way to remember the order is to think ROS(S).
|
Ovale,
Rotundum Ovale Spinosum |
|
|
The middle ____ ____ is important because the meningeals cover the brain and sometimes people can sustain trauma to the head.
|
meningeal artery
|
|
|
What is your lower jaw called?
|
Mandible
|
|
|
What is the small bone that forms part of the lower nasal septum?
|
Vomer
|
|
|
What bone forms part of the face?
|
Maxillary
|
|
|
The _____ bones suggest form part of the pallet, the roof of your mouth is the _____.
|
Palatine, pallet
|
|
|
The palatine bone and then the ______ also contributes to the pallette.
|
Maxilla
|
|
|
What does lacrimation mean?
|
To tear (so anything that has to do with teraing you think LACRIMATION)
example: lacrimal bones |
|
|
There are two bones that make up the lacrimal bones. They have depressions and they are called lacrimal _____ that conects the tears. It helps to drain the tears in the _____ cavity.
|
Fossa, Nasal
|
|
|
The rest of the nasal septum, the middle section is actually made out of cartilage. What is the cartilage made out of?
|
Hyaline
|
|
|
Nasal and lacrimal are both ______ bones.
|
Facial
|
|
|
There are three sets of nasal concha. (SMI)
Each one is kind of a scrolled piece of bone. |
Superior nasal concha
Middle nasal concha Inferior nasal concha |
|
|
The _____ and _____ nasal concha are parts of the _______ but the inferior nasal concha are not part of the _______.
|
Superior, middle
Ethmoid Ethmoid |
|
|
_______ ______ _____ are not part of the ethmoid. They are their own bones. Their own seperate little bones.
|
Inferior nasal concha
|
|
|
in 29:29 she said to notice that there is a little notch here. This piece that sticks back here is called the ______ ______.Notice that it articulates with what bone?
|
Mandibular condyle,
Temporal |
|
|
The _______ joint is the joint between the mandibular condyle and the temporal bone.
|
Mandibular
|
|
|
The ____ ____ houses your spinal cord.
|
Vertebral column
|
|
|
The vertebral column is suppose to be straight when you look at it from the posterior view. If it curves to one side or to the other on the thoracic region or in the lumbar region that is what we call _____.
|
Scoliosis
|
|
|
There are 4 curvatures in the vertebral column which are?
They are normally present if you look at it from the side. |
1. Cervical
2. Thoracic 3. Lumbar 4. Sacral |
|
|
The cerivical portion of the vertebral has ____ vertebrae and there are ____ in the thoracic section
|
7,12
|
|
|
You have ____ pairs of ribs
|
12
|
|
|
The ______ consists of 5 vertebrae but they fuse together usually by the age of 25.
|
Sacrum
|
|
|
The _____ is your tailbone
|
coccyx
|
|
|
The coccyx is composed of ____ vertebrae that also fuse during childhood.
|
4
|
|
|
What if a person has a stroke and one side of the body is paralized the right or left. What do we call that?
|
hemiplegia
|
|
|
What seperates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal pelvic cavity and it is actually a muscle. It is responsible for breathing in
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
It turns out that every cervical vertebrae all 7 of them has _____ holes.
|
3
|
|
|
The central hole is the vertebral foramen through which the _____ cord goes. Then there are 2 holes here called the _______ foramina
|
Spinal
Transverse |
|
|
The transverse foramina transits something very important which is the ____ _____?
|
Vertebral artery
|

