![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
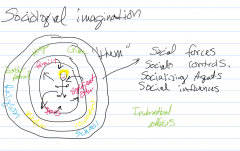
Sociological imagination
Interplay between individual and society. |
The task of sociologists regarding interpreting social problems is to realize that individual circumstances are inextricably linked to the structure/conditions of society.
the sociological imagination is the ability to see things socially and how they interact and influence each other. an individual needs to be able to pull him/herself away from the situation and to be able to think from an alternative point of view. It requires us to "think ourselves away from our daily routines and look at them anew". |
|
|
Labeling Process/Labeling theory
Labeling theory is based on the idea that behaviors are deviant only when society labels them as deviant. As such, conforming members of society, who interpret certain behaviors as deviant and then attach this label to individuals, |
1. Engage in deviant behavior-guilty by association. 2. Influential authority as adult-popular person as a child. 3. Spreads gossip. 4. Label returns back to original person. 5. Self-fulfilling prophecy-self doubt-engaging in act. |
|
|
Norm Violations
Social Conditions |
Acts and conditions that violate the norms and values found in a society.
Societally induced conditions that cause psychic and material suffering for any segment of the population. |
|
|
Institutional deviance |
Occurs when institution fail to fulfill the needs of the people. When government is run by the few for the benefit of the few, when businesses supposedly in competition fix prices to gouge the consumers, when criminal justice system is biased against the poor and people of color, then society is permitting what is called institutionalized deviance |
|
|
Deviant behavior
Norm Violations |
Actions that violate social norms.
Acts and conditions that violate the norms and values found in a society. |
|
|
Challenge Question:
Person blame approach
System blame approach |
Social problems are the result of corrupt, immoral pathological individuals.
Social problems result from corrupt social systems and poor social conditions. |
|
|
Cultural Deprivation |
Certain ethnic groups are inherently inferior and deficient. |
|
|
Sociological Theory |
Explanation based on scientific theory, in attempt to explain social problems.
A set of ideas that explains a range of human behavior and a variety of social and societal events based on sociological methods. |
|
|
Differential Fertility |
Refers to the differences in average number of children born to a woman by social category.
Fertility rate among the poor is exceptionally high.
Children and work in fields/farms, they can beg and they are cheap labor. |
|
|
Demographic transition
|
Countries that go through three stages as they become more developed which affects the population rate.
1. Agricultural stage-high birth/death rate resulting in low population growth. 2. Transition stage-high birth rates and low death rates resulting in population explosion. 3. Urbanization stage-low birth rate while death rates remain stable resulting in low population growth. Shift of people from rural to cities. |
|
|
Why is family planning difficult to implement? |
Modern contraceptives, education and abortions..
Religious beliefs forbade it. Fertility rates would decline when women were educated, work outside of home or to be in business with others. In hard times and political unrest couples delay marriage and accepting of birth control.
|
|
|
Underdeveloped nations lack life chances; the chances throughout one's life to experience "good things" |
Opportunities for a better life-increase life chances for other areas. |
|
|
Food and Hunger
• If everyone worldwide adopted a vegetarian diet, then the current food production could feed 10 billion people • Food production is grossly unevenly distributed… 1 in 3 persons worldwide are food deprived…WHY? |
1. Overpopulation
2. Conversion of farmland to urbanization and suburbanization 3. Dumping of food to maintain agricultural prices 4. People eating more meat, thus diverting grain to feed livestock |
|
|
The New Slavery
|
“New slavery” is characterized by ‘debt |
|
|
Corporate Dumping |
Situation where a firm exports outdated fashions, obsolete technology, or items banned in the home country to unsuspecting importers enticed by attractive prices. |
|
|
Biosphere |
The surface layer of the planet
|
|
|
Degradation of land |
•Topsoil—three-foot layer of soil that •Topsoil is being lost to wind and water erosion
|
|
|
Destruction of Rain Forests |
•Tropical rain forests house about half of all species on earth… |
|
|
Environmental Pollution
What is the solution??
|
•Chemical Pollution
|
|
|
Environmental Pollution
|
•Solid Waste Pollution 3. ‘Toxic sludge’ is produced—a mixture of human and industrial waste in washwater 5. Incinerating garbage has two benefits: reduces garbage by 90% and produces steam/electricity |
|
|
Environmental Pollution |
•Water Pollution
|
|
|
Environmental Racism
|
The trend of dumping where poor people reside,
|
|
|
Environmental Pollution |
•Radiation Pollution 2011 Japan |
|
|
Environmental Pollution |
•Air Pollution [Los Angeles, Mexico City, Seoul, Cairo]
|
|
|
GREENHOUSE EFFECT
|
When harmful gases accumulate in the earth’s atmosphere and act like a glass ceiling…resulting in warming of the earth, melting of glaciers, significant changing
|
|
|
Cultural Sources Sources of Environmental Problems |
1. Cornucopia View of Nature ‘nature is a vast storehouse awaiting it use’
|
|
|
Solutions to Environmental Problems |
1. Individual/Local Recycling, Govt Policies 2. Societal Level Solutions Funding, Education, Disposing waste properly 3. Global Level Solutions Dumping to other countries
|
|
|
Capital Flight |
Companies moving to low wage locales in rural areas and overseas. |
|
|
Urban Problems |
Redlining: Not providing loans or insurance in "undesirable" locations-urban ghettos.
Redlining, discrimination and disinvestment create urban job loss. |
|
|
Urban Problems |
Central city poverty areas: neighborhoods in which at least one in five households live below the poverty line 4. The inner-city poor adopt a lifestyle of crime for survival purposes |
|
|
Urban Problems |
• Urban Housing Crisis i. Gentrification: converting poor sections into up-scale condominiums, townhouses, lofts |
|
|
Urban Problems |
Urban Schools |
|
|
Urban Problems |
• Crimes, Drugs, and Gangs 4. Gangs are source of ‘meaningful relationships’ |
|
|
Triage |
Only treating the most urgent patients-others must wait for days/weeks to be treated. |
|
|
Suburban Problems
|
Suburban Sprawl
1. White Flight: suburbs growing with White, middle-class families causing major segregation, shrinking of innercities, and job loss for urbanites 2. Boomburg: a suburban city with a population of at least 100,00…has strip developments, office parks, and ‘bigbox’ retailers 3. Suburban Sprawl: low-density, automobile-dependent developments characterized by tract housing, fast-food franchises, and visual blight [a similar look, whether on outskirts of Phoenix, Detroit, Philadelphia] |
|
|
Suburban Problems |
Automobile Dependency |
|
|
Rural Problems |
Forestry, back country, back roads/hills Poverty and Jobs in Rural Areas |
|
|
Rural Problems Urban police-racial profiling Good ole boy town |
• Healthcare and Delivery
|
|
|
Rural Problems |
•Crime and Illicit Drugs |
|
|
Rural Problems
|
• Small-town Decline
1. Rural life use to center around the school, the town square, and the church…these social institutions have been replaced by commercialized, chain franchises—Walmart, McDonalds, Lowes, Big Lots, etc. 2. Rural residents must travel to the suburbs for work 3. Loss of a sense of community, solidarity, and identity 4. Rise of ‘colonias’ or shantytown settlements of Latino immigrants |

