![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
329 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Adrenaline |
1 mg in 1ml amp (1:1,000)
1mg in 10ml amp (1:10,000) |
|
Adrenaline Pharmacology |
A naturally occurring Alpha and Beta-adrenergic stimulant |
|
Adrenaline Actions |
Increases pulse rate by increasing S.A. Node firing rate (Beta 1)
Increases conduction velocity through the A.V. Node (Beta 1)
Increases myocardial contractility (Beta 1)
Increases irritability of ventricles (Beta 1)
Causes bronchodilatation (Beta 2)
Causes peripheral vasoconstriction (Alpha 1) |
|
Adrenaline Metabolism |
By monoamine oxidase and other enzymes in blood, liver and around nerve endings and excreted by the kidneys |
|
Adrenaline Primary Emergency Indications |
Persistent VF or unconscious pulseless VT
Asystole
Electro-mechanical dissociation/PEA
Inadequate perfusion (Cardiogenic)
Inadequate Perfusion (Non Cardiogenic - Non Hypovolaemic)
Bradycardia with poor perfusion
Anaphylactic reactions
Severe asthma
Unconscious asthma with no BP
Croup |
|
Adrenaline Contraindications |
Hypovolaemic shock without adequate fluid replacement |
|
Adrenaline Precautions |
Elderly pts
Pts with cardiovascular disease
Pts on monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors
Pts on Beta blockers as higher doses may be required |
|
Adrenaline Administration Route |
IV IM Nebulised ETT IV Infusion IO |
|
Adrenaline Side Effects |
Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular arrhythmias Ventricular arrhythmias Hypertension Pupillary dilatation May increase size of myocardial infarction Anxiety/palpitations in the conscious pt |
|
Adrenaline Special Notes |
IV Adrenaline should be reserved for life threatening situations |
|
Adrenaline Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 30 sec Peak: 3-5 min Duration: 5-10 min
IM Onset: 30 - 90 sec Peak: 4 -10 min Duration: 5-10 min |
|
Amiodarone Presentation |
150mg in 3ml ampoule |
|
Amiodarone Pharmacology |
A Class III anti-arrhythmic agent |
|
Amiodarone Actions |
Anti-arrhythmic |
|
Amiodarone Metabolism |
By the liver |
|
Amiodarone Primary Emergency Indications |
VF or Pulseless VT refractory to cardioversion
Sustained or recurrent VT |
|
Amiodarone Contraindications |
VF/Pulseless VT refractory to cardioversion - nil of significance in above indication
VT - inadequate perfusion - pregnancy
TCA overdose |
|
Amiodarone Precautions |
Following Fentanyl administration |
|
Amiodarone Administration Route |
IV |
|
Amiodarone Side Effects |
Hypotension
Bradycardia |
|
Amiodarone Special Notes |
Amiodarone is incompatible with saline. Glucose 5% must be used as dilutant when preparing an IV infusion.
An IV infusion of Amiodarone may be required during interhospital transfer. This will be prescribed by the referring physician and will normally be at a dose of 10 - 20 mg/kg/24 hr. |
|
Amiodarone Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 2 min Peak: 20 min Duration: 120 min |
|
Adenosine Presentation |
6 mg in 2 ml amp |
|
Adenosine Pharmacology |
A naturally occurring purine nucleoside found in all body cells |
|
Adenosine Actions |
Slows conduction velocity through the AV node resulting in termination of re-entry circuit activity within or including the AV nodal pathway |
|
Adenosine Metabolism |
By adenosine deaminase in red blood cells and vascular endothelium |
|
Adenosine Primary Emergency Indications |
AVNRT with adequate or inadequate perfusion but not deteriorating rapidly
AVRT and associated WPW or other accessory tract SVT with adequate or inadequate perfusion but not deteriorating rapidly |
|
Adenosine Contraindications |
Hypersensitivity Second degree or third degree AV block (may lead to prolonged sinus arrest/AV blockade) AF Atrial Flutter Ventricular tachyarrhythmias |
|
Adenosine Precautions |
Adenosine may provoke bronchospasm in the asthmatic pt Adenosine is antagonised by methylxanthines (eg coffee, theophyllines). The drug may not be effective in pts with large caffeine intakes or those on high doses of theophylline medication (is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma . It bears structural and pharmacological similarity to caffeine. |
|
Adenosine Administration Route |
IV |
|
Adenosine Side Effects |
Usually brief and transient: Transient arrhythmia (asystole, bradycardia, VE) Chest pain Dyspnoea Headache or dizziness Nausea Skin flushing |
|
Adenosine Special Notes |
Adenosine has a very short half life. It should be administered through an IV as close to the heart as practicable such as the cubital fossa. |
|
Adenosine Therapeutic Effects |
IV Duration less than 10 secs |
|
Aspirin Presentation |
300mg chewable tablets
300mg soluble or water dispersible tablets |
|
Aspirin Pharmacology |
Analgesic
anti-pyretic
anti-inflammatory and
antiplatelet aggregation agent |
|
Aspirin Actions |
To minimise platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in order to retard the progression of coronary artery thrombosis in acute coronary syndrome.
Inhibits synthesis of prostaglandins - anti-inflammatory actions |
|
Aspirin Metabolism |
Converted to salicylate in the gut mucosa and liver, excreted mainly by the kidneys. |
|
Aspirin Primary Emergency Indications |
ACS |
|
Aspirin Contraindications |
Hypersensitivity to aspirin/salicylates
Actively bleeding peptic ulcers
Bleeding disorders
Suspected dissecting aortic aneurysm
Chest pain associated with psychostimulant overdose if SBP less than 160 mmHg |
|
Aspirin Precautions |
Peptic ulcer
Asthma
Pts on anti-coagulants |
|
Aspirin Administration Route |
Oral |
|
Aspirin Side Effects |
Heartburn, nausea, gastrointestinal bleeding
Increased bleeding time
Hypersensitivity reactions |
|
Aspirin Special Notes |
Aspirin is contraindicated for use in acute febrile illness in children and adolescents.
The anti-platelet effects of Aspirin persist for the natural life of platelets. |
|
Aspirin Therapeutic Effects |
Duration: 8-10 days |
|

Atropine Presentation |
0.6 mg in 1ml amp
1.2 mg in 1ml amp |
|

Atropine Pharmacology |
An anticholinergic agent |
|

Atropine Actions |
Inhibits the actions of acetylcholine on post-ganglionic cholinergic nerves at the neuro-effector site, e.g. as a vagal blocker and allows sympathetic effect to:
- increase pulse rate by increasing S.A. Node firing rate - increase conduction velocity through the A.V. Node.
Antidote to reverse the effects of cholinesterase inhibitors, e.g. organophosphate insecticides, at the post-ganglionic neuro-effector sites of cholinergic nerves, i.e. reduces the excessive salivary, sweat, gastrointestinal and bronchial secretions and relaxes smooth muscles. |
|

Atropine Metabolism |
By the liver and excreted mainly by the kidneys |
|

Atropine Primary Emergency Indications |
Bradycardia with poor perfusion
Organophosphate poisoning with excessive cholinergic effects |
|

Atropine Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indications |
|

Atropine Precautions |
Atrial flutter
Atrial fibrillation
Do not increase heart rate above 100/min except in children under 6 years
Glaucoma |
|

Atropine Administration Route |
IV
ETT |
|

Atropine Side Effects |
Tachycardia
Palpitations
Hot, dry skin (in large doses)
Confusion, restlessness (in large doses)
Dry mouth
Dilated pupils
Visual blurring
Urine retention |
|

Atropine Special Notes |
Nil stated |
|

Atropine Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: less than 2 min Peak: less than 5 min Duration: 2 - 6 hrs |
|
Ceftriaxone Presentation |
1g sterile powder in a glass vial |
|
Ceftriaxone Pharmacology |
Cephalosporin antibiotic |
|
Ceftriaxone Actions |
Antibiotic |
|
Ceftriaxone Metabolism |
Excreted unchanged in urine (33% - 67%) and in bile |
|
Ceftriaxone Primary Emergency Indications |
Suspected meningococcal septicaemia
Severe sepsis (consult only) |
|
Ceftriaxone Contraindications |
Allergy to cephalosporin antibiotics |
|
Ceftriaxone Precautions |
Allergy to Penicillin antibiotics |
|
Ceftriaxone Route Of Administration |
IV (preferred)
IM (if IV is unable to be attained) |
|
Ceftriaxone Side Effects |
Nausea
Vomiting
Skin rash |
|
Ceftriaxone Special Notes |
Usual dose: Adult 1gm and child 50mg/kg (max 1 gm).
Ceftriaxone IV must be made up to 10ml using sterile water and dose administered over 2 min.
Ceftriaxone IM must be made up to 4ml using 1% Lignocaine and dose administered in lateral upper thigh. |
|
Ceftriaxone Therapeutic Effects |
Not stated |
|
Dexamethasone Presentation |
8mg in 2ml glass vial |
|
Dexamethasone Pharmacology |
A corticosteroid secreted by the adrenal cortex |
|
Dexamethasone Actions |
Relieves inflammatory reactions and provides immunosuppression |
|
Dexamethasone Metabolism |
By the liver and other tissues and excreted predominantly by the kidneys |
|
Dexamethasone Primary Emergency Indications |
Bronchospasm associated with acute respiratory distress not responsive to nebulised Salbutamol
Anaphylaxis
Acute exacerbation of COPD |
|
Dexamethasone Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity to Dexamethasone |
|
Dexamethasone Precautions |
Solutions which are not clear or are contaminated should be discarded |
|
Dexamethasone Administration Route |
IV
IM |
|
Dexamethasone Side Effects |
Nil of significance in the above indications |
|
Dexamethasone Special Notes |
Does not contain an antimicrobial agent, therefore use solution immediately and discard any residue |
|
Dexamethasone Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 30 - 60 min Peak: 2 hr Duration: 36 -72 hrs |
|
Dextrose 5%
Presentation |
100ml infusion soft pack |
|
Dextrose 5%
Pharmacology |
An isotonic crystalloid solution comprising of:
Sugar 5% Dextrose
and water |
|
Dextrose 5%
Actions |
Provides a small source of energy
Supplies body water |
|
Dextrose 5%
Metabolism |
Dextrose: Broken down in most tissues Stored in liver and muscle as glycogen
Water: Excreted by the kidneys. Distributed throughout total body water, mainly in the extracellular fluid compartment |
|
Dextrose 5%
Primary Emergency Indications |
Vehicle for dilution and administration of IV emergency drugs |
|
Dextrose 5%
Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|
Dextrose 5%
Precautions |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|
Dextrose 5%
Administration Route |
Intravenous infusion |
|
Dextrose 5%
Side Effects |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|
Dextrose 5%
Special Notes |
Nil stated |
|
Dextrose 5%
Therapeutic Effects |
Intravascular half life:
approximately 20 - 40 min. |
|

Dextrose 10%
Presentation |
25 g in a 250 ml infusion soft pack |
|

Dextrose 10%
Pharmacology |
A slightly hypertonic crystalloid solution.
Composition: 10% Dextrose and water |
|

Dextrose 10%
Actions |
Provides a source of energy
Supplies body water |
|

Dextrose 10%
Metabolism |
Dextrose: Broken down in most tissues Stored in liver and muscle as glycogen
Water: Excreted by the kidneys. Distributed throughout total body water, mainly in the extracellular fluid compartment |
|

Dextrose 10% Primary Emergency Indications |
Diabetic hypoglycaemia (BGL less than 4mmol/l) in pts with an altered conscious state who are unable to self-administer oral glucose |
|

Dextrose 10%
Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|

Dextrose 10%
Precautions |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|

Dextrose 10%
Administration Route |
IV infusion |
|

Dextrose 10%
Side Effects |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|

Dextrose 10%
Special Notes |
Nil stated |
|

Dextrose 10%
Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 3 min Peak: Duration: Depends on severity of hypoglycaemic episode |
|
Fentanyl Presentation |
100mcg in 2ml amp
600mcg in 2ml (IN use only) |
|
Fentanyl Pharmacology |
A synthetic narcotic analgesic |
|
Fentanyl Actions |
CNS effects: Depression - leading to analgesia Respiratory depression - leading to apnoea Dependence - leading to addiction
Cardiovascular effects: Decreases conduction velocity through the A.V. Node |
|
Fentanyl Metabolism |
By the liver and excreted by the kidneys |
|
Fentanyl Primary Emergency Indications |
Analgesia IV/IN
IFS
RSI
Maintain intubation |
|
Fentanyl Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity
IV Amiodarone |
|
Fentanyl Precautions |
Asthma - current
Addiction to narcotics
Amiodarone - oral
Elderly pts
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MOAI's)
Respiratory depression e.g. COPD
Renal/hepatic function impairment
Rhinorrhoea, rhinitis or facial trauma (IN use) |
|
Fentanyl Administration Route |
IV
IN |
|
Fentany lSide Effects |
Apnoea
Respiratory depression
Rigidity of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles
Bradycardia |
|
Fentanyl Special Notes |
Fentanyl is a Schedule 8 drug under the Poisons Act and its use must be carefully controlled with accountability and responsibility.
Respiratory depression can be reversed with Naloxone 100mcg Fentanyl is equivalent in analgesic activity to 10mg Morphine. |
|
Fentanyl Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: Immediate Peak: less than 5 min Duration: 30-60 min
IN Peak: 2 min |
|
Frusemide Presentation |
40 mg in 4ml amp |
|
Frusemide Pharmacology |
A diuretic |
|
Frusemide Actions |
Causes venous dilatation and reduces venous return
Promotes diuresis |
|
Frusemide Metabolism |
Excreted by the kidneys |
|
Frusemide Primary Emergency Indications |
Acute left ventricular failure |
|
Frusemide Contraindications |
Nil of signifcance in the above indication |
|
Frusemide Precautions |
Hypotension |
|
Frusemide Administration Route |
IV |
|
Frusemide Side Effects |
Hypotension |
|
Frusemide Special Notes |
The effect of vasopressor drugs will often be reduced after treatment with Frusemide. |
|
Frusemide Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 5 min Peak: 20-60 min Duration: 2-3 hr |
|
Glucagon Presentation |
1mg (IU) in 1ml hypokit |
|
Glucagon Pharmacology |
A hormone normally secreted by the pancreas |
|
Glucagon Actions |
Causes an increase in blood glucose concentration by converting stored liver glycogen to glucose |
|
Glucagon Metabolism |
Mainly by the liver, also by the kidneys and in the plasma |
|
Glucagon Primary Emergency Indications |
Diabetic hypoglycaemia (BGL less than 4mmol/l) in pts with an altered conscious state who are unable to self-administer oral glucose |
|
Glucagon Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|
Glucagon Precautions |
Nil of significance in the above indication |
|
Glucagon Administration Route |
IM |
|
Glucagon Side Effects |
Nausea and vomiting (rare) |
|
Glucagon Special Notes |
Not all pts will respond to Glucagon for example those with inadequate glycogen storage in the liver: - alcoholics - malnourishment. |
|
Glucagon Therapeutic Effects |
IM Onset: 3-5 min Peak: Duration: 12-25 min |
|

GTN Presentation |
0.6mg tablets
Transdermal GTN patch 50 mg (0.4mg/hr) |
|

GTN Pharmacology |
Principally a vascular smooth muscle relaxant |
|

GTN Actions |
Venous dilatation promotes venous pooling and reduces venous return to the heart (reduces preload).
Arterial dilatation reduces systemic vascular resistance and arterial pressure (reduces afterload).
THE EFFECTS OF THE ABOVE ARE: - reduced myocardial oxygen demand - reduced systolic, diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure, whilst usually maintaining coronary perfusion pressure - mild collateral coronary arterial dilatation may improve blood supply to ischaemic areas of myocardium -mild tachycardia secondary to slight fall in blood pressure.
Pre-term labour - Uterine quiescence in pregnancy. |
|

GTN Metabolism |
By the liver |
|

GTN Primary Emergency Indications |
Chest pain associated with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Hypertension associated with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute left ventricle failure
Autonomic dysreflexia
Preterm labour (consult) |
|

GTN Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity
Systolic blood pressure less than 110 (tablet)
Systolic blood pressure less than 90 (patch)
"Viagra" or "Levitra" administration in the previous 24 hr or "Cialias" administration in the previous 4 days (PED5 inhibitors)
Heart rate greater than 150
Bradycardia HR less than 50 (excluding Autonomic Dysreflexia)
Ventricular Tachycardia
Inferior STEMI with systolic BP less than 160
Right ventricular infarct |
|

GTN Precautions |
No previous administration
Elderly pts
Recent acute myocardial infarction
Concurrent use with other tocolytics |
|

GTN Administration Route |
Buccal/Sub-lingal
Transdermal
IV Infusion |
|

GTN Side Effects |
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Headache
Skin flushing (uncommon)
Bradycardia (occasionally) |
|

GTN Special Notes |
Glyceryl Trinitrate is susceptible to heat and moisture. Make sure that tablets are stored in their original, light-resistant, tightly sealed bottles. Foil of the patches should be intact. Tablets should be discarded and replaced after 1 month. The foil pack of the patches should be intact. Patches should be discarded prior to use by date. Do not administer the patient's own medication, as its storage may not have been in optimum conditions or may be old. Since both men and women can be prescribed VIAGRA, LEVITRA or CILIAS, all patients should be asked if and when they last had the drug to determine if GTN is contra-indicated.Cialis may also be prescribed for benign prostatic hypertrophy for men.GTN by intravenous infusion may be required for an interhospital transfer as per the treating doctors orders
The IV dosage is to be prescribed and signed by the referring hospital Medical Officer. Usually in the range of 5mcg/min to 200mcg/min and increased 3-5mcg/min. |
|

GTN Therapeutic Effects |
BUCCAL Onset: 30 sec - 2 min Peak: 5-10 min Duration: 15-30 min
TRANSDERMAL Onset: up to 30 min Peak: 2 hr |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Presentation |
250mcg in 1ml nebule or polyamp |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Pharmacology |
Anticholinergic bronchodilator |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Actions |
Allows bronchodilatation by inhibiting cholinergic bronchomotor tone (i.e. blocks vagal reflexes which mediate bronchoconstriction) |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Metabolism |
Excreted by the kidneys |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Primary Emergency Indications |
Severe respiratory distress associated with bronchospasm |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity to Atropine or its derivatives |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Precautions |
Glaucoma
Avoid contact with eyes |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Administration Route |
Nebulised in combination with Salbutamol |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Side Effects |
TPHANDS
Tachycardia (rare) Palpitations (rare) Headache Acute angle closure glaucoma secondary to direct eye contact (rare) Nausea Dry mouth Skin Rash |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Special Notes |
There have been isolated reports of ocular complications (mydriasis, increased intraocular pressure, acute angle glaucoma, eye pain) as a result of direct eye contact of Ipratropium Bromide formulations. The nebuliser mask must therefore be fitted properly during inhalation and care taken to avoid Ipratropium Bromide solution entering the eyes. Ipratropium Bromide must be nebulised in conjunction with Salbutamol and is to be administered as a single dose only. |
|
Ipratropium Bromide Therapeutic Effects |
Nebules Onset: 3-5 min Peak: 1.5 - 2 hours Duration: 6 hrs |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Presentation |
50mg in 5ml amp (1%) |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Pharmacology |
A local anaesthetic agent |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Actions |
Prevents initiation and transmission of nerve impulses causing local anaesthesia |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Metabolism |
By the liver (90%)
Excreted unchanged by the kidneys (10%) |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Primary Emergency Indications |
Diluent for Ceftriaxone for IM administration in suspected meningococcal disease |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Precautions |
When using Lignocaine 1% as diluent for IM Ceftriaxone, it is important to rule out inadvertent IV administration due to potential CNS complications. |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Administration Route |
Intramuscular with Ceftriaxone only |
|
|
Lignocaine 1% IM Side Effects |
Nil - unless inadvertent IV administration |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Special notes |
Nil |
|

Lignocaine 1% IM Therapeutic Effects |
IM Onset: Rapid Peak: Duration: 60 - 90 min |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Presentation |
50mg in 5ml amp (1%) |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Pharmacology |
A local anaesthetic agent |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Actions |
Prevents initiation and transmission of nerve impulses causing local anaesthesia |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Metabolism |
By the liver (90%)
Excreted unchanged by the kidneys (10%) |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Primary Emergency Indications |
To reduce the pain of intraosseous drug and fluid administration in the responsive patient |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Precautions |
Hypotension and poor perfusion
Chronic LVF
Liver disease |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Administration Route |
Intraosseous |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Side Effects |
IO administration (1% solution) CNS effects (common): - drowsiness - disorientation - decreased hearing - blurred vision - change or slurring of speech - twitching or agitation - convulsions
Cardiovascular effects (uncommon): - hypotension - bradycardia - sinus arrest - AV block
Respiratory Effects (uncommon): - difficult breathing - respiratory arrest |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Special Notes |
Nil |
|

Lignocaine 1% IO Therapeutic Effects |
IO Onset: 1 - 4 min Peak: 5 -10 min Duration: 20 min |
|
Methyoxyflurane Presentation |
3ml glass bottle |
|
Methyoxyflurane Pharmacology |
Inhalation analgesic agent at low concentrations |
|
Methyoxyflurane Actions |
Analgesic agent |
|
Methyoxyflurane Metabolism |
By the liver
Excreted mainly by the lungs |
|
Methyoxyflurane Primary Emergency Indications |
Pain relief |
|
Methyoxyflurane Contraindications |
Pre-existing renal disease/renal impairment
Concurrent use of tetracycline antibiotics
Exceeding total dose of 6ml in a 24 hr period |
|
Methyoxyflurane Precautions |
The Penthrox inhaler must be hand-held by the patient so that if unconsciousness occurs it will fall from the patient's face.
Occasionally the operator may need to assist but must continuously assess the level of consciousness.
Pre-eclampsia |
|
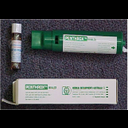
Methyoxyflurane Administration Route |
Self-administration under supervision using the hand held Penthrox Inhaler with or without oxygen supplementation. |
|
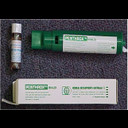
Methyoxyflurane Side Effects |
Drowsiness
Decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia (rare)
Exceeding the max. total dose of 6ml in a 24 hr period may lead to renal toxicity. |
|
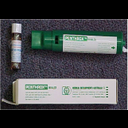
Methyoxyflurane Special Notes |
The max. initial priming dose for Methoxyflurane is 3ml. This will provide approximately 25min of analgesia and may be followed by one further 3ml dose once the initial dose is exhausted if required.
Do not administer in a confined space - ensure adequate ventilation in ambulance. |
|
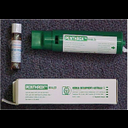
Methyoxyflurane Therapeutic Effects |
Analgesia after 8 -10 breaths.
Lasts approx 3 - 5 mins once discontinued. |
|

Metoclopramide Presentation |
10mg in 2ml polyamp |
|

Metoclopramide Pharmacology |
Anti-emetic |
|

Metoclopramide Actions |
Accelerates gastric emptying and peristalsis
Dopamine receptor antagonist |
|

Metoclopramide Metabolism |
By the liver and excreted by the kidneys |
|

Metoclopramide Primary Emergency Indications |
Nausea and vomiting associated with:
Chest pain/discomfort of a cardiac nature Opioid administration for pain Previously diagnosed migraine Cytotoxic or radiotherapy Severe gastroenteritis
Treatment or prophylaxis in:
awake spinal immobilised pts and eye trauma |
|

Metoclopramide Contraindications |
Children
Suspected bowel obstruction or perforation
GI haemorrhage |
|

Metoclopramide Precautions |
Undiagnosed abdominal pain
Adolescents (less than 20 years)
Administer slowly over 1 min. to minimise of extrapyramidal reactions |
|

Metoclopramide Administration Route |
IV
IM |
|

Metoclopramide Side Effects |
EDDM
Extrapyramidal reactions (usually the dystonic type)
Drowsiness/lethargy
Dry mouth
Muscle tremor |
|

Metoclopramide Special Notes |
Not effective for established motion sickness.
Not effective for nausea prophylaxis in the setting of narcotic administration. |
|

Metoclopramide Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 1-3 min Peak: Duration: 10 - 30 min
IM Onset: 10 - 15 min Peak: Duration: 1-2 hr |
|
Midazolam Presentation |
5mg in 1ml amp
15mg in 3ml amp |
|
Midazolam Pharmacology |
Short acting CNS depressant |
|
Midazolam Actions |
Anxiolytic
Sedative
Anti-convulsant |
|
Midazolam Metabolism |
In the liver
Excreted by the kidneys |
|
Midazolam Primary Emergency Indications |
Continuous/recurrent seizures
Sedation to enable intubation - IFS
Rapid Sequence Intubation
Sedation to maintain intubation
Sedation to enable synch cardioversion
Sedation in the agitated patient
Sedation in psychostimulant overdose |
|
Midazolam Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines |
|
Midazolam Precautions |
Reduced doses may be required for:
- elderly pts - chronic renal failure - CCF - shock.
The CNS depressant effects of benzodiazepines are enhanced in the presence of narcotics and other tranquillisers including alcohol.
Can cause severe respiratory depression in pts with COPD.
Pts with myasthenia gravis. |
|
Midazolam Administration Route |
IM
IV |
|
Midazolam Side Effects |
Depressed level of consciousness
Loss of airway control
Respiratory depression
Hypotension |
|
Midazolam Special Notes |
Midazolam is not permitted for use to facilitate the transport of pts who have been recommended for transport under the Mental Health Act. If sedation is required in these circumstances then the Act requires that this only be administered by a prescribed Medical Practitioner or Registered Nurse. |
|
Midazolam Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 1-3 min Peak: 10 min Duration: 20 min
IM Onset: 3-5 min Peak: 15 min Duration: 30 min |
|

Misoprostol Presentation |
200 mcg tablet |
|

Misoprostol Pharmacology |
Synthetic prostaglandin |
|

Misoprostol Actions |
Enhances uterine contractions |
|

Misoprostol Metabolism |
Converted to active metabolite Misoprostol acid in the blood
Metabolised in the tissues and excreted by the kidneys. |
|

Misoprostol Primary Emergency Indications |
Primary post partum haemorrhage |
|

Misoprostol Contraindications |
Allergy to prostaglandins
Ensure multiple pregnancy excluded before drug administration |
|

Misoprostol Precautions |
History of asthma |
|

Misoprostol Administration Route |
Oral |
|

Misoprostol Side Effects |
Hyper-pyrexia
Shivering
Abdominal pain
Diarrhoea |
|

Misoprostol Special Notes |
Side effects more likely with greater than 600 mcg oral dose |
|

Misoprostol Therapeutic Effects |
Oral Onset: 8 - 10 min Peak: Duration: 2 - 3 hr |
|

Morphine Presentation |
10mg in 1ml amp |
|

Morphine Pharmacology |
A opiod analgesic |
|

Morphine Actions |
CNS effects: Depression - leading to analgesia Respiratory depression Depression of cough reflex Stimulation - changes of mood, euphoria/dysphoria, vomiting, pin-point pupils Dependence - addiction
Cardiovascular effects: Vasodilatation Decreases conduction velocity through the AV Node |
|

Morphine Metabolism |
By the liver
Excreted by the kidneys |
|

Morphine Primary Emergency Indications |
Pain relief
Acute LVF with shortness of breath and full field crackles
Sedation to enable intubation
RSI
Sedation to maintain intubation |
|

Morphine Contraindications |
Known hypersensitivity
Late second stage of labour |
|

Morphine Precautions |
Asthma - current
Addiction to narcotics
Acute alcoholism
Elderly pts
Hypotension
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MOAI's)
Respiratory depression
Respiratory tract burns |
|

Morphine Administration Route |
IV
IM
Intravenous infusion |
|

Morphine Side effects |
CNS effects: Drowiness Respiratory depression Euphoria Nausea/vomiting Depression of cough reflex Pin-point pupils Addiction
Cardiovascular effects: Hypotension Bradycardia |
|

Morphine Special Notes |
Morphine Sulphate is a Schedule 8 drug under the Poisons Act and its use must be carefully controlled with accountability and responsibility
Side effects of Morphine Sulphate can be reversed with Naloxone
Occasional wheals are seen in the line of the vein being used for IV injection. This is not an allergy, only a histamine release. |
|

Morphine Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 2-5 min Peak: 10 min Duration: 1-2 hr
IM Onset: 10 -30 min Peak: 30- 60 min Duration: 1-2 hr |
|
Narcan Presentation |
0.4mg in 1ml amp
2 mg in 5 ml prepared syringe |
|
Narcan Pharmacology |
A opiod antagonist |
|
Narcan Actions |
Prevents or reverses the effects of opiods |
|
Narcan Metabolism |
By the liver |
|
Narcan Primary Emergency Indications |
Altered conscious state and respiratory depression secondary to administration of opiods or related drugs |
|
Narcan Contraindications |
Nil of signifcance in the above indication |
|
Narcan Precautions |
If pt is known to be physically dependent on opiods, be prepared to deal with a combative pt after administration
Neonates |
|
Narcan Administration |
IM
IV |
|
Narcan Side effects |
Symptoms of narcotic withdrawal: Sweating Goose flesh Tremor Nausea and vomiting Agitation Dilatation of pupils Excessive lacrimation Convulsions |
|
Narcan Special Notes |
Since the duration of action of Naloxone is often less than that of the opiod used repeated doses may be required.
Naloxone reverses the by other opiod antagonists when no opiod is present in the body. (For example, it does not depress respiration or cause pupillary constriction). In the absence of opiates, Naloxone has no perceivable effects.
Following a opiod associated cardiac arrest Naloxone should not be administered. Maintain assisted ventilation.
Following head injury Naloxone should not be administered. Maintain assisted ventilation if required. |
|
Narcan Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 1-3 min Peak: Duration: 30 - 45 min
IM Onset: 1-3 min Peak: Duration: 30 - 45 min |
|

Normal Saline Presentation |
10 ml polyamp
500 ml and 1000 ml infusion soft pack |
|

Normal Saline Pharmacology |
An isotonic crystalloid solution
Composition: Electrolytes, sodium and chloride in a similar concentration to that of extracellular fluid. |
|

Normal Saline Actions |
Increases the volume of the intravascular compartment |
|

Normal Saline Metabolism |
Electrolytes: Excreted by the kidneys
Water: Excreted by the kidneys and distributed throughout total body water, mainly in the extracellular fluid compartment |
|

Normal Saline Primary Emergency Indications |
As a replacement fluid in volume depleted patients
To expand intravascular volume in the non cardiac, non-hypovolaemic, hypotensive pt - e.g. anaphylaxis, burns, sepsis
As a fluid challenge in unresponsive non-hypovolaemic hypotensive pts, other than LVF - e.g. PEA, asthma
Vehicle for diluting and intravenous administration of emergency drugs
Fluid to keep vein open for IV administration of emergency drugs |
|

Normal Saline Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indications |
|

Normal Saline Precautions |
Consider modifying factors when administering for hypovolaemia |
|

Normal Saline Administration Route |
IV
IO |
|

Normal Saline Side Effects |
Nil of significance in the above indications |
|

Normal Saline Special Notes |
Nil stated |
|

Normal Saline Therapeutic Effects |
Intravascular half life: Approximately 30 - 60 min |
|
Oxytocin Presentation |
10 units in a 1 ml ampoule |
|
Oxytocin Pharmacology |
A synthetic oxytocic |
|
Oxytocin Actions |
Stimulates smooth muscle of the uterus producing contractions |
|
Oxytocin Metabolism |
By the liver
Extreted by the kidneys |
|
Oxytocin Primary Emergency Indications |
Primary post partum haemorrhage |
|
Oxytocin Contraindications |
Previous hypersensitivity
Severe toxaemia (pre-eclampsia)
Ensure multiple pregnancy excluded before drug administration
Cord prolapse |
|
Oxytocin Precautions |
If given IV, may cause transient hypotension
Concurrent use with Methyoxyflurane may cause hypotension |
|
Oxytocin Administration Route |
IM |
|
Oxytocin Side Effects |
Uncommon via the IM route:
Tachycardia Bradycardia Nausea |
|
Oxytocin Special Notes |
Concomitant use with prostaglandins (Misoprostol) may potentiate uterotonic effect
MUST be stored between 2° to 8° C. |
|
Oxytocin Therapeutic Effects |
IM Onset: 2 - 4 min Peak: Duration: 30 - 60 min |
|

Pancuronium Presentation |
4mg in 2ml polyamp |
|

Pancuronium Pharmacology |
A non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking agent |
|

PancuroniumActions |
Blocks transmission of impulses at the neuromuscular junction of striated muscles resulting in skeletal muscle paralysis.
Due to weak vagolytic action, a slight rise in pulse rate and mean arterial pressure may be expected |
|

Pancuronium Metabolism |
By the kidneys
Excreted mainly unchanged in the urine |
|

Pancuronium Primary Emergency Indications |
To maintain skeletal muscle paralysis and allow mechanical ventilation in intubated pts following:
- IFS - RSI - or during interhospital transport of ventilated pts. |
|

Pancuronium Contraindications |
Pancuronium must not be given if continuous monitoring of pt vital signs including pulse oximetry and end tidal CO2 monitoring are not available
Status Epilepticus |
|

Pancuronium Precautions |
Ensure patency of IV access
Sedatives must always be administered prior to Pancuronium
ETT placement, adequacy of ventilation, oxygen saturation, end tidal CO2, pulse and blood pressure must be continuously monitored
Pts with myasthenia gravis should be given much smaller doses and monitored carefully due to the potential of increased degree of neuromuscular block
Care should be exercised in pts with renal impairment. |
|

Pancuronium Administration Route |
IV
IO |
|

Pancuronium Side Effects |
Slight increase in heart rate
Slight increase in mean arterial pressure
Localised reaction at injection site (rare) |
|

Pancuronium Special Notes |
Allergic reactions such as urticaria, laryngeal oedema, bronchospasm and anaphylactic shock have been reported.
Pancuronium infusions required during interhospital transfers are to be prescribed and signed by the referring hospital medical offcer. The initial dose is usually 0.1mg/kg. |
|

Pancuronium Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 2-3 min Peak: 8-10 min Duration: 35-45 min |
|
Prochlorperazine Presentation |
12.5mg in 1ml amp |
|
Prochlorperazine Pharmacology |
Antiemetic |
|
Prochlorperazine Actions |
Acts on several central neuro-transmitter systems |
|
Prochlorperazine Metabolism |
Metabolised by the liver and excreted by the kidneys |
|
Prochlorperazine Primary Emergency Indications |
Treatment or prophylaxis for:
- Motion sickness - Planned aeromedical evacuation - Known allergy or contraindication to Metoclopramide - Headache irrespective of nausea or vomiting - Vertigo |
|
Prochlorperazine Contraindications |
Previous hypersensitivity
Children
Circulatory collapse
CNS depression |
|
Prochlorperazine Precautions |
Hypotension
Epilepsy
Pts effected by alcohol or on anti-depressants |
|
Prochlorperazine Administration Route |
IM |
|
Prochlorperazine Side Effects |
BREDTH
Blurred vision Rash Extrapyramidal reactions, usually the dystonic type Drowsiness Tachycardia Hypotension |
|
Prochlorperazine Special Notes |
Nil |
|
Prochlorperazine Therapeutic Effects |
IM Onset: 20 min Peak: 40 min Duration: 6 hr |
|
Salbutamol Presentation |
5 mg in 2.5ml polyamp
500 mcg in 1ml amp
5 mg in 5ml amp
pMDI |
|
Salbutamol Pharmacology |
A synthetic Beta-adrenergic stimulant, with primarily Beta 2 effects |
|
Salbutamol Actions |
Causes bronchodilatation |
|
Salbutamol Metabolism |
By the liver
Excreted by the kidneys |
|
Salbutamol Primary EmergencyIndications |
Respiratory distress with suspected bronchospasm, associated with:
- Asthma - Anaphylaxis - COPD - Smoke inhalation - Oleoresin capsicum spray exposure |
|
Salbutamol Contraindications |
Nil of significance in the above indications |
|
Salbutamol Precautions |
Large doses of IV Salbutamol have been reported to cause intracellular metabolic acidosis. |
|
Salbutamol Administration Route |
Nebulised
IV
IO
IV
Infusion
ETT
Pressurised Metered Dose Inhaler (pMDI) |
|
Salbutamol Side Effects |
Sinus tachycardia
Muscle tremor (common) |
|
Salbutamol Special Notes |
Salbutamol Nebules/Polyamps have a shelf life of one month after the wrapping is opened. The date of opening of the packaging should be recorded and the drug should be stored in an environment of <30°C.
IV Salbutamol has no advantage over nebulised Salbutamol provided that adequate ventilation is occurring.
Although infrequently used, Salbutamol by intravenous infusion may be required during interhospital transfers of some women in premature labour. The dose is to be prescribed and signed by the referring hospital medical officer. |
|
Salbutamol Therapeutic Effects |
Nebuliser Onset: 5 - 15 min Peak: Duration: 15 - 50 min
IV Onset: 1-2 min Peak: Duration: 30 - 60 min. |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Presentation |
50ml prepared syringe (8.4%)
100 ml glass bottle |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Pharmacology |
A hypertonic crystalloid solution
Contains sodium and bicarbonate ions in a solution of high pH |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Actions |
Raises pH |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Metabolism |
Sodium: Excreted by the kidneys
Bicarbonate: Excreted by the kidneys as bicarbonate ion and by the lungs as carbon dioxide |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Primary Emergency Indications |
Cardiac arrest after 15 minutes of AV CPR
Symptomatic TCA OD |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Contraindications |
Hypothermia less than 30 oC |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Precautions |
Administration of Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% must be accompanied by effective ventilation and ECC if required.
Since Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% causes tissue necrosis, care must be taken to avoid leakage of the drug into the tissues.
Because of the high pH of this solution do not mix or flush any other drug or solution with Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4%. |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Administration Route |
IV |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Side Effects |
Sodium overload may provoke pulmonary oedema.
Excessive dosage of Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4%, especially without adequate ventilation and circulation, may cause an intracellular acidosis. |
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4% Special Notes |
Nil stated |
|
|
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.4%Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 1-2 min Peak: Duration: Depends on cause and patient's perfusion. |
|

Suxamethonium Presentation |
100mg in 2ml polyamp |
|

Suxamethonium Pharmacology |
Depolarising neuromuscular blocking agent |
|

Suxamethonium Actions |
Short acting muscular relaxant |
|

Suxamethonium Metabolism |
Pseudo-cholinesterase in plasma |
|

Suxamethonium Primary Emergency Indications |
Complete muscle relaxation to allow endotracheal intubation |
|

Suxamethonium Contraindications |
KKKUSPEBOR
Known hypersensitivity
Known history of Suxamethonium apnoea
Known history of malignant hyperthermia
Upper airway obstruction
Severe respiratory distress
Penetrating eye injury
ECG signs of hyperkalaemia in conditions such as muscle necrosis and renal failure
Burns > 24hrs post injury
Organophosphate poisoning
Ruptured AAA |
|

Suxamethonium Precautions |
PLACE
Pts who have not fasted
Liver disease
Airway trauma
Crush injuries
Elderly Pts |
|

Suxamethonium Administration Route |
IV
IO |
|

Suxamethonium Side Effects |
Muscular fasciculation
Increase in intraocular pressure
Increase in intragastric pressure
Elevated serum potassium levels |
|

Suxamethonium Special Notes |
Sedation is required prior to use.
Atropine (600mcg) should be administered prior to Suxamethonium administration in adult pts with a HR less than 60.
Atropine 20mcg/kg should be administered prior to Suxamethonium administration in children
A second dose of Suxamethonium usually causes profound bradycardia
Refrigeration of Suxamethonium is required - requires weekly rotation or disposal when not refrigerated.
Adult doses 1.5 mg/kg IV |
|

Suxamethonium Therapeutic Effects |
IV Onset: 20 - 40 sec Peak: 60 sec Duration: 4 - 6 min |
|
Water for injection Presentation |
10ml polyamp |
|
Water for injection Pharmacology |
Water for Injection is a clear, colourless, particle free, odourless and tasteless liquid.
It is sterile, with a pH of 5.6 to 7.7 and contains no antimicrobial agents. |
|
Water for injection Actions |
Nil |
|
Water for injection Metabolism |
Distributed throughout the body and excreted by the kidneys |
|
Water for injection Primary Emergency Indications |
Used to dissolve Ceftriaxone in preparation for IV injection |
|
Water for injection Contraindications |
Nil |
|
Water for injection Precautions |
Nil |
|
Water for injection Administration Route |
IV |
|
Water for injection Side Effects |
Nil |
|
Water for injection Special Notes |
Nil |

