![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diagram: central processing, efferent pathways, controlled variable, afferent pathways
|
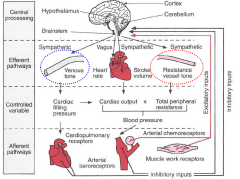
|
|
|
What neurotransmitters make up the sympathetic triad and what are their receptors?
|
Neuropeptide Y - Y receptor (GPCR)
Noradrenaline - alpha-1 receptor (GPCR) Adenosine triphosphate - P2x receptor (ion channel receptor) |
|
|
Adrenergic/purinergic cotransmission
|
When NA and ATP are released together there in adrenergic/purinergic cotransmission.
- NA and ATP together give a big contraction: synergy, boost one another. - If NPY is added at a concentration to low to create its own contraction, with NA and ATP it gives a big attenuation. |
|
|
CGRP
|
Calcitonin gene related peptide is produced in central and peripheral neurons and gives vasodilation. Functions by a GPCR.
Generally: - Sympathetic: vasoconstriction - Parasympathetic: vasodilation |
|
|
Formation of neurotransmitters
|
Synthesis starts in the varicosity and is finished in the vesicle.
Small molecules e.g. ACh synthesised in the axon terminal Neuropeptides are synthesised in the cell body |
|
|
Synthesis of small molecule neurotransmitters
|
Small molecule neurotransmitters are synthesised locally around the axon terminal.
- some of the precursors are taken up by selective transport on the membrane of the terminal - others are cellular byproducts - Enzymes are produced in cell body and brought to the terminal by slow axonal transport |
|
|
Synthesis of neuropeptides
|
Neuropeptides are derived from large precursors with no biological activity. These are in the cell body, packaged into vesicles and moved into the terminals and varicosities, where they are cleaved by peptidases.
|
|
|
peptidergic
|
Neuron that releases one or more neurotransmitters
|
|
|
Neuromodulation
|
Neuropeptides are formed with another neurotransmitter and can be neuromodulators.
|

