![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
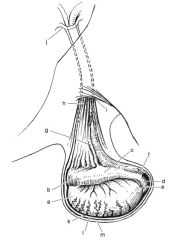
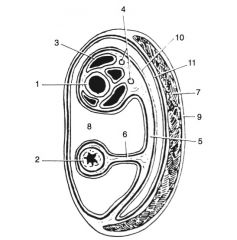
Components of the male reproductive anatomy:
|
scrotum, testis, epididymis, inguinal canal, tunics, gubernaculum, and spermatic cord
|
|
|
What is the tunica dartos?
|
muscle that relaxes with heat and contracts with cold to held regulate testicular temperature and change the size of the scrotum, in the median plane of the tunica dartos divides the scrotum into left and right halves
|
|
|
Scrotal arterial supply:
|
external pudendal artery
|
|
|
Nervous supply to scrotum:
|
genitofemoral nerve
|
|
|
How do the left and right testes differ?
|
left is usually larger and more caudal than the right
|
|
|
What is the tunica albuginea?
|
inelastic capsule over the testis, which forms septa of connective tissue to divide the testis into lobules
|
|
|
What is contained in each testicular lobule?
|
seminiferous tubules, sertoli cells, and interstitial cells
|
|
|
What lines seminiferous tubules?
|
spermatogonia attached to a basement membrane. As the spermatogonia mature they are pushed toward the lumen to emerge as spermatozoa
|
|
|
What stimulate emergence of spermatozoa from the seminiferous tubule?
|
FSH
|
|
|
Function of sertoli cells:
|
provide mechanical and nutrition support to the developing spermatozoa
|
|
|
Function of interstitial cells:
|
produce androgens and estrogens
|
|
|
Alterntive name for interstitial cells:
|
leydig cells
|
|
|
Regions of the epididymis:
|
head, body and tail
|
|
|
Where is the head of the epididymis?
|
cranial pole of the testis
|
|
|
What is the head of the epididymis composed of?
|
efferent ductules of the testis unite to form a single coiled tube, which are the body and tail of the epididymis
|
|
|
Where is the body of the epididymis?
|
dorsolateral surface of the testis
|
|
|
Where is the tail of the epididymis?
|
projects beyond the caudal border of the testis, wraps medially
|
|
|
What is the continuation of the epididymis?
|
ductus deferens
|
|
|
Function of the epididymis:
|
receives immature sperm and with ejaculation, peristaltic motion force sperm from the epididymis to the ductus deferens
|
|
|
What is in the inguinal canal?
|
spermatic cord, genitofemoral nerve, external pudendal vasculature, and efferent lymphatics pass through the canal
|
|
|
What are the borders of deep inguinal ring?
|
caudal edge of the IAO is the cranial border, the rectus abdominus and prepubic tendon (prepubic tendon is the tendon of insertion of the rectus abdominus) are the ventral and medial border and the inguinal ligament is the caudal border
|
|
|
What is the external opening of inguinal canal?
|
superficial inguinal ring is slit in the external abdominal oblique muscle
|
|
|
How are the deep and superficial inguinal rings aligned?
|
medial are aligned but the lateral borders are divergent making the medial aspect of the canal shorter than the lateral aspect
|
|
|
What is the tunica vaginalis?
|
extension of the peritoneum, and has a visceral and parietal surface
|
|
|
What is the vaginal process?
|
Sac formed of the visceral surface adhered to the tunica albuginea and the parietal surface is continuous with the parietal periton
|
|
|
What is the vaginal ring?
|
ring that forms as the peritoneum invaginates into the canal through the deep inguinal ring
|
|
|
What is the gubernaculum?
|
fetal cord that extends from the fetal testis to the scrotum and guides decent into the scrotum
|
|
|
When do the fetal gonads arise during gestation?
|
Day 40
|
|
|
What and when does the vaginal process form during gestation?
|
gubernaculum extends from the caudal pole of the testis and ends in an expansion between the internal and external abdominal oblique muscles, with peritoneal lining penetrating this area around day 45 of gestation
|
|
|
What begins at 5 months of gestation?
|
testicle hypertrophies under the influence of the leydig cells, the cephalic (suspensory) ligament atrophies, and the epididymis begins decent into the vaginal process
|
|
|
What occrurs at 8.5 months of gestation?
|
gubernaculum begins to shorten and the testicle shrinks in size due to loss of leydig cells. The epididymis and subperitoneal gubernaculum dilate the vaginal ring and inguinal canal
|
|
|
When does the testicle passes into the inguinal canal?
|
around 270-300 days of gestation
|
|
|
When does the testicle descend into the scrotum?
|
Within a few days of birth
|
|
|
When does the vaginal ring contract?
|
within a few weeks of life
|
|
|
What are the parts of fetal gubernaculum?
|
Cranial, middle, caudal
|
|
|
Where is the cranial portion of the gubernaculum?
|
between the testis and the epididymis
|
|
|
What does the cranial portion of the gubernaculum become?
|
proper ligament of the testis.
|
|
|
Where is the middle portion of the gubernaculum?
|
between the epididymis and the point of entry of the gubernaculum at the inguinal ring
|
|
|
What does the middle portion of the gubernaculum become?
|
ligament of the tail of the epididymis
|
|
|
Function of the ligament of the tail of the epididymis?
|
connects the tail of the epididymis to the parietal tunic
|
|
|
Where is the caudal portion of the gubernaculum?
|
extends from the abdominal wall to the scrotum
|
|
|
What does the caudal portion of the gubernaculum become?
|
scrotal ligament,
|
|
|
Function of the scrotal ligament?
|
connecting the parietal tunic to the scrotum
|
|
|
What is the scrotal ligament called in a cryptorchid?
|
inguinal extension of the gubernaculum testis
|
|
|
Components of the spermatic cord:
|
tunica vaginalis, vessels, nerves, and lymphatics, and the ductus deferens
|
|
|
Function of the cremaster?
|
contracts to retract the testicle
|
|
|
Arterial supply to the cremaster?
|
cremasteric artery
|
|
|
What is the mesorchium?
|
fold of the parietal tunic enclosing the neurovascular portions of the cord
|
|
|
What is the mesoductus ?
|
fold of the parietal tunic enclosing the ductus deferens
|
|
|
What is the mesofuniculum?
|
thin portion of the mesorchium between the mesoductus and the parital tunic
|
|
|
Arterial supply to the ductus deferens:
|
deferential branch of the umbilical artery
|
|
|
What are the branches of ehe testicular artery?
|
epididymal artery
|
|
|
Arterial supply to the testicle?
|
Testicular artery, epidydmal artery cremasteric artery, deferential artery
|
|
|
What is the panpiniform plexus?
|
Tortuous portions of the testicular artery and vein in the cord
|
|
|
Where does the testicular artery empty?
|
right testicular vein drains to the caudal vena cava and the left testicular vein drains to the left renal vein
|

