![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
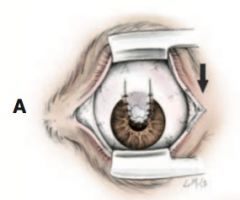
|
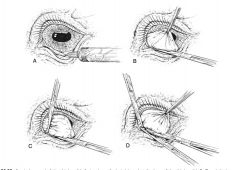
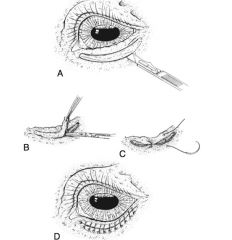
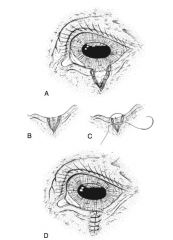
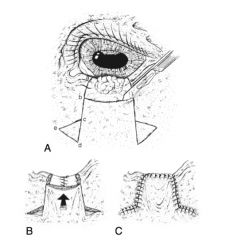
conjunctival advancement pedicle graft
|
|

|

|
|
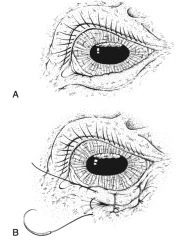
|

|
|
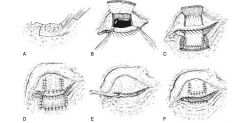
|

|
|

|
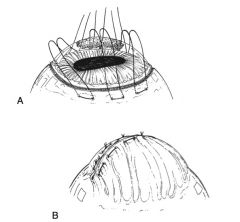
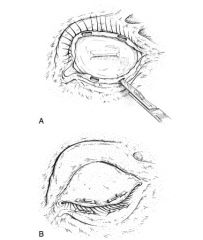
guyton park eyelid speculum
|
|
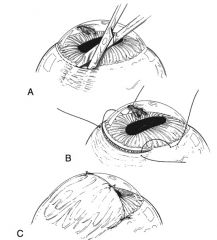
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
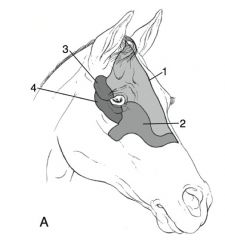
Function of orbicularis oculi muscle:
|
close eyelids
|
|
|
Innervation of orbicularis oculi:
|
palpebral branch of facial nerve (VII)
|
|
|
Muscles that open eyelids:
|
levator anguli oculi, levator palpebrae superioris, frontalis, malaris, muller’s
|
|
|
What is muller’s muscle associated with?
|
Levator palpebrae superioris
|
|
|
Innervation of levator anguli oculi:
|
palpebral branch of facial nerve (VII)
|
|
|
Innervation of levator palpebrae superioris:
|
dorsal branch of oculomotor (III)
|
|
|
Innervation of muller’s muscle:
|
sympathetic
|
|
|
Innervation of frontalis:
|
palpebral branch of facial nerve (VII)
|
|
|
Innervation of malaris:
|
dorsal buccal branch of facial nerve (VII)
|
|
|
Sensory innervation of upper eyelid:
|
branches (supraorbital nerve, lacrimal nerve, infratrochlear nerve) of ophthalmic portion of trigemical nerve (V)
|
|
|
Sensory innervation of lower eyelid:
|
zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary portion of the trigeminal nerve (V)
|
|
|
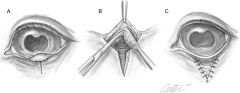
Entropion:
|
inward turning of eyelid
|
|
|
Repair of entropion:
|
temporary: everting vertical mattress suture permanent: Y to V plasty, modified Hotz-celsus
|
|
|
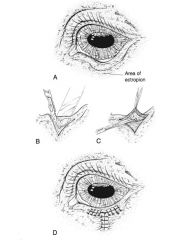
Ectropion:
|
out turning of eyelid
|
|
|
Repair of ectropion:
|
V to Y plasty
|
|
|
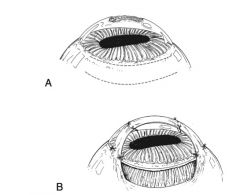
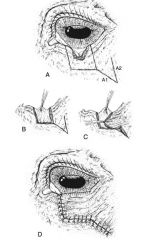
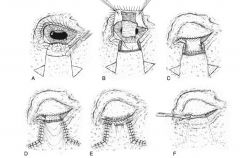
Types of reconstructive blepharoplasty techniques:
|
sliding skin flap, conjunctival advancement flap, full thickness eyelid graft, rhomboid graft flap, sliding z flap
|
|
|
Indications for reconstructive blepharoplasty:
|
extensive eyelid lacerations or closure of large defects after neoplasia removal
|
|
|
Sensory innervation to 3rd eyelid:
|
infratrochlear nerve
|
|
|
Complications of 3rd eyelid resection:
|
orbital fat prolapse, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, superficial keratitis
|
|
|
Arterial supply to conjunctiva:
|
anterior ciliary arteries, branches of ophthalmic artery
|
|
|
Innervation of bulbar conjunctiva:
|
long ciliary branch of ophthalmic portion of trigeminal (V)
|
|
|
Innervation of superior palpebral conjunctiva:
|
frontal and lamcrimal branches of ophthalmic portion of trigeminal (V)
|
|
|
Innervation of inferior palpebral conjunctiva:
|
lacrimal and infraorbital branch of maxillary portion of trigeminal (V)
|
|
|
Vascular supply to sclera:
|
anterior and posterior ciliary arteries from ophthalmic artery
|
|
|
Sensory innervation of anterior sclera:
|
long posterior ciliary nerve branch from ophthalmic nerve
|
|
|
Sensory innervation of posterior sclera:
|
short posterior ciliary nerve from cilary ganglion
|
|
|
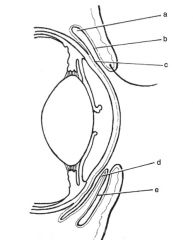
Layers of cornea:
|
epithelium, stroma, descemet’s membrane, endothelium
|
|
|
Innervation of cornea:
|
long ciliary nerve
|
|
|
Ocular hemostasis:
|
wicking sponges, 2.5% phenylephrine on cotton applicator, 1:10,000 epinephrine on cotton applicator
|
|
|
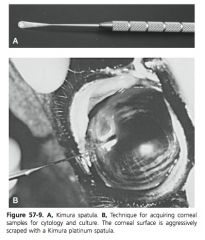
What is a superficial keratectomy?
|
Surgical excision of a superficial layer of corneal tissue including epithelium and anterior stroma
|
|
|
Indications for superficial keratectomy:
|
Dermoids, infection, corneal malacia, superficial corneal abscess, corneal neoplasia
|
|
|
Complications of superficial keratectomy:
|
excessive neovascular response, scarring, infection, corneal perforation
|
|
|
What is the depth of corneal suturing?
|
80-90%
|
|
|
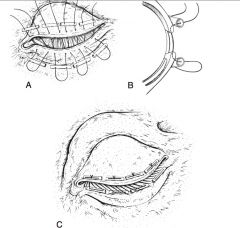
What are conjunctival grafts?
|
Transposition of a portion of conjunctival tissue to cover a corneal defect
|
|
|
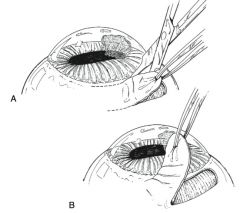
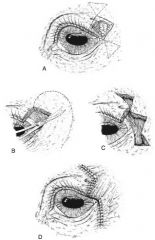
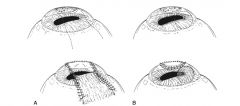
Types of conjunctival grafts:
|
rotation pedicle graft, advancement pedicle graft, tarsoconjunctival grafts, bipedicle graft, bridge graft, hood graft, free island graft, 360 degree graft
|
|
|
Indication for rotation pedicle conjunctival graft:
|
centrally located corneal defects
|
|
|
Indication for advancement pedicle conjunctival graft:
|
corneal defects closer to the limbus
|
|
|
Indication for bipedicle or bridge conjunctival grafts:
|
linear and large abaxial located corneal defects
|
|
|
Indication for hood conjunctival graft:
|
large corneal defect closer to limbus
|
|
|
Disadvantage of free island and 360 degree conjunctival grafts:
|
absence of blood supply, preclude vision, prevent visualization of globe
|
|
|
Complications of conjunctival grafts:
|
dehiscence, infection, effects on vision
|
|
|
When is trimming of the conjunctival graft performed?
|
6-8 weeks post-op
|
|
|
Indication for sliding lamellar keratoplasty:
|
repair of deep corneal defect where surrounding cornea is healthy and clear axial cornea is desired
|
|
|
Indication for corneal grafting:
|
deep corneal stromal abscess, corneal endothelial disease, large corneal perforation
|
|
|
Donor for corneal grafting:
|
harvested fresh or frozen corneas
|
|
|
Types of corneal grafts:
|
penetrating keratoplasty, posterior lamellar keratoplasty, deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty
|

