![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CPA services |
Preparation - no assurance, no report Compilation - disclaimer of assurance Review - limited assurance Examination - positive assurance or opinion Agreed upon procedures - results, no assurance |
|
|
Pronouncements |
Statements on auditing standards- audits of non issuers, auditing standards board Statements on standards for accounting review services - prep, compilation, and reviews of nonissuers , aicpa- review board Statements on standards for attestation engagements- exam, reviews, agreedupok procedures , aicpa - audit board |
|
|
Sox 2002 |
Engagement responsibilities of auditors of public firms,
Created pcaob - create standards for issues with sec If audit a public company must have quality control 2nd partner review and approval Lead and review partner must rotate every 5 years Independence CEO and CFO must certify Penalties for destroying evidence Managment assess internal control and it be audited |
|
|
Objectives of auditor |
Obtain reasonable assurance are fairly presented free from material misstatement from error or fraud Report on audit findings Independence |
|
|
Professional skepticism |
Questioning mind Alert to conditions Critical of evidence |
|
|
Assertions classes of transactions and events |
Income statement and cash flows Occurence- events happened Completeness- all events have been recorded Accuracy - amounts and other info Cutoff- in proper period Classification- in proper account |
|
|
Assertions about account balances |
Balance sheet Existance- Rights and obligations- holds control or obligation Completeness- all assets or liabilities are recorded Valuation and allocation- appropriate value |
|
|
Assertions about presentation and disclosure |
Notes Occurence, rights, obligation- occured and exist Completeness- includes all that should be Classification, understandable- clearly expressed Accuracy, valuation - appropriate amounts |
|
|
Audit evidence assertions |
Existence Completelnes Valuation Rights and obligations Presentation and disclosure |
|
|
Attestation engagements |

|
|
|
Standards on consulting services |
Client interest- serve client maintain integrity Understanding with client - written or oral Communication with client- conflicts of interest and findings |
|
|
Elements of quality control |
Leadership responsibilities (tone at the top) Relevant ethical requirements Acceptance and continuance of client relationships Human resources Engagement performances Monitoring |
|
|
Auditing principals |
Responsibilities Public interest Integrity Objective and independent Due care Scope and nature of services |
|
|
Types of threats |
Adverse interest- Advocacy threat- threat of independence doesn't exist Familiarity threat- synathetic if client for too long and develop relationship Management participation threat - assumes management roles Self interest threat- conflict of interest Self review threat- does work then reviews it Indue influence threat- actual threats |
|
|
Independence impairment |
Loans - unless from financial institutions for cars, cash surrender value, credit card balance < 10k Material indirect financial interest- immediate family Owns > 5% of client Simultaneous employment during services Formerly employed by client Subsequent employment |
|
|
Preconditions for audit |
Client follows GAAP Client responsible for prep and fair presentation Client responsible for design, implementation and maintain internal control Client must provide info deemed necessary |
|
|
Engagement letter contents |
Objective and scope Responsibilities for both sides Inherent limitations of audit Reporting framework Form and content of audit report |
|
|
Predecessor auditor info to request |
Audit docs on Planning Risk assessment Audit procedures Results Other matters of significance |
|
|
Audit risks |
Inherent- risk of an assertion being materially misstated Control - risk internal control will not prevent, detect and correct a misstatement Detection- auditor won't find misstatement Inherent x control = detection |
|
|
3 levels of materiality |
Financial statement level- whole $ value of misstatement Balances, classes, or disclosures- benchmarks ( 1% of assets) Performance- another level |
|
|
5 sources of information |
1)Financials from comparable prior period - trends 2)Anticipated results- budgets 3)Relationships among elements of financial info(sales and accounts reciveable) 4)Comparable info from industry 5)Relationship between financial and relevant nonfinancial info. (Hours increased, wages should) |
|
|
Fraud triangle |
Pressures/incentives Opportunity Rationalization |
|
|
Components of internal control |
CRIME Control activities- policies and procedures Risk assessment- ID and analyze risks Info system- ID, capture and exchange of info Monitoring- effectiveness Environment- tone at the top, |
|
|
Elements of a control environment |
1, communication of ethics and integrity 2, commitment to competence 3, participation of management 4, management philosophy 5, organizational structure 6, assignment of authority and responsibility 7. HR policies |
|
|
Control activities |
Authorization Performance reviews Info processing Physical controls Segregation of duties |
|
|
Auditors documentation on understanding of internal controls |
Discussion of team members of risks Understanding entity and control components Assessed RMMs and assertions Significant risks and controls to be evaluated |
|
|
What duties should be segregated |
Authorization Recording Custody |
|
|
What increases a risk to significant |
Fraud Recent developments- economic Complex transactions Related party transactions High degree of uncertainty or subjectivity Non routine transactions, unusual infrequent |
|
|
Response to financial statement level RMMs |
More professional skepticism on evidence Increased supervision Staff with greater experience and expertise Greater unpredictability on further procedures Changing NET of audit procedures |
|
|
Audit approaches |
Substantive - ignores test of controls Combined- uses test of controls to decrease substantive procedures (both) |
|
|
Tests of controls |
Inquiry Inspection Observation Reperformance Recalculation |
|
|
Determining extent of test of controls |
Frequency of use Expectated rate of control deviations Relevance and reliability of evidence Evidence from tests of other controls Planned reliance on control Time during the period |
|
|
Testing computer control methods |
Test data, one moment compare outputs to know outcome Parallel simulation, info through clients and auditors at same time and compare Integrated- dummy records in clients computer Embedded- continuous audit procedures |
|
|
Direction of audit testing |

Existence/ occurence - from records to proof of event Completeness- from proof of event to records |
|
|
External confirmations are used for |
Accounts receivable Bank balances Inventories Investments Accounts payable and loans |
|
|
Positive vs negative confirmation requests |
Positive - respond if agree, can be blank Negative- only respond if disagree- only if risk is low |
|
|
When should audit documentation be completed |
60 days after report date , 45 for issuers Retained for at least 5 years, 7 years for issuers |
|
|
What are general audit software systems used for |
ACL and IDEA Aging of records Checking for duplicates Export to another software Extract for exception analysis Gap ID Joining and merging files Sampling Sorting Stratification Summarization Totalling |
|
|
Types of audit artificial intelligence AI |
Expert- interactive, help be efficient and effective, help choose: audit plan, sample size, level of misstatement, analytical procedures, judgements Neural- learning system that relies on programmed rules |
|
|
Assertions on sales and AR, cash balances |
CAVE CROC Completeness Accuracy Valuation and allocation Existence Cutoff Rights and obligations Occurence Classification |
|
|
Auditing going concern |
Substantial doubt for reasonable period of time (1 yr) Obtains management's plans to mitigate Include an emphasis of matter paragraph after opinion paragraph |
|
|
Sampling statistical vs non |
Nonstatistic- judgement, choosing material and riskier samples Statistical- random, |
|
|
Sampling risks |
Over reliance on controls, incorrect acceptance - risk in opinion Under reliance on controls, inefficient work |
|
|
Auditors report for nonissuer |
Title Addressee Intro- entity, financial statements, title, time period Management responsibility Auditors responsibility Opinion Signature Auditors address Date |
|
|
Audit report for issuer |
Title Addressee Intro Scope paragraph Opinion Signature Auditors address Date No headings |
|
|
If auditor reports on more than just financial statements where is it reported |
In auditors report after opinion paragraph with subtitle |
|
|
Auditors opinions |
Unmodified- a good report Qualified opinion- material misstatements not pervasive, inability to obtain evidence on material misstatements but believed no pervasive Adverse opinion- know pervasive material misstatements Disclaimer- pervasive inability to obtain enough evidence for opinion |
|
|
Examples that lead to qualified opinions |
Inability to obtain sufficient evidence on material misstatement not pervasive Material misstatements that are not pervasive 1, inappropriate accounting principals 2, inappropriate application of principals 3, unjustified change in principals 4, inadequate disclosure 5, failure to provide financial statement like cashflows |
|
|
Auditor report that includes other modifications |

|
|
|
Objective of review |
If material modification is needed Analytical and inquiry Not testing controls, corroborating evidence, Not Express opinion, provide assurance about controls |
|
|
Form and content of comfort letters |
Date- same as underwriting agreement Addressed Refer but not repeat audit opinion Independence Compliance with sec Provides negative assurance |
|
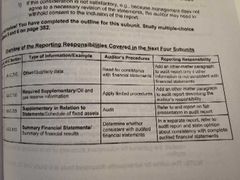
|
Read |
|
|
Human resources in quality control |
Professional development |
|
|
Attest engagements are for what |
Report on subjects other than traditional statements |
|
|
Disagreements between audit partner and assistant |
Expand details about assistants position and how to was resolved |
|
|
SSARSs must be followed when ... |
Prep, compile, review services |
|
|
Common stock subsequently mv drops |
No adjustment or disclosure necessary |
|
|
Calculate sample size |
Recorded balance × Confidence factor from table / tolerable misstatement |

