![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Posterior network |
Had to do with orienting and shifting attention |
|
|
Anterior network |
Serves as the detection system, involves detecting stimuli either from sensory events or from memory |
|
|
Alerting network |
Subserved by the ARAS, can influence the anterior and posterior networks, operating at high and low levels of arousal |
|
|
Delirium |
Waxing and waning deficits in attention Includes increased distractibility, poor awareness, persistent confusion |
|
|
ARAS |
Responsible for arousal and attention |
|
|
Anterior cingulate (and limbic system) |
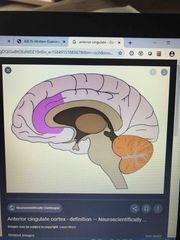
Determines salience of stimuli and associated emotion/motivation |
|
|
Prefrontal |
Response selection, control, sustained attention, focus, switching, searching, and alternating attention |
|
|
Orbitofrontal |
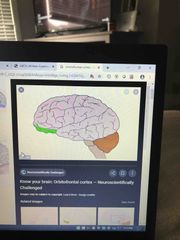
Inhibition of responses |
|
|
Dorsolateral prefrontal |
Initiation of responses |
|
|
Superior colliculus |
Shifting attention, eye movements |
|
|
Lateral pulvinar (thalamic nucleus) |
Extracting information from the target location and filtering distractors |
|
|
Inferior and posterior parietal |
Underlies disengagement from a stimulus and the representation of space Damage is associated with hemispatial inattention/neglect |
|
|
Right hemisphere |
Spatial attention Associated with hemispatial inattention/neglect |
|
|
Hemispatial inattention (neglect) |
Impairment in awareness of visual (and other) stimuli on the side contralateral to a brain lesion that is not the result of a primary sensory deficit and is manifested in hemi-inattention |
|
|
Anosognosia |
Denial of illness, extinction of stimuli |
|
|
Asomatognosia |
Denial of body part |
|
|
Hemispatial inattention is associated with damage to what part of the brain? |
Temporal-parietal region, but not exclusively |
|
|
Sensory neglect |
An acquired inattention or unawareness to part (typically half) of space |
|
|
Motor neglect |
Involves a failure to respond or initiate movement (akinesia) to stimuli |

