![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
224 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Multiplexing
|
Tracking A/D converter |
|
|
|
Demulyiplexing |
Separating data from a single line to different outputs |
|
|
|
First concept of computers |
Used vacuum tubes that were unreliable and expensive |
|
|
|
3 categories of computers |
Macro, mini, micro |
|
|
|
Microprocessor made of |
Input, control, memory, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), output |
|
|
|
Control |
Used for synchronizing processes |
|
|
|
ALU |
Calculates circuitry of computer |
|
|
|
Memory contains |
Data, instructions. Information |
|
|
|
Bus |
Path for info or data groups by function |
|
|
|
Status flag register |
Indicates status of ALU |
|
|
|
General purpose registers |
Used for temporary storage |
|
|
|
Address refisters |
Access location of data and enable a specific I/O port |
|
|
|
Program counter |
Has address of next instruction to be executed |
|
|
|
Smallest unit of data microprocessor rexognies |
Bit |
|
|
|
Address bus |
Determines how much memory can be addressed |
|
|
|
Staris |
Condition of ALU |
|
|
|
When control section directs a word to memory... |
An address determines where it will go |
|
|
|
Microprocessors are generally used by... |
Small businesses |
|
|
|
Basic sections of a computer |
Control, input, output |
|
|
|
Two primary forms of memory |
ROM & RAM |
|
|
|
Data stored in ROM is called |
Firmware |
|
|
|
Static RAM is made from |
Flip flops |
|
|
|
Dynamic RAM is made from |
Capacitors |
|
|
|
Extended memory |
All memory beyond original 1M |
|
|
|
XMS |
Extended memory specification |
|
|
|
What was used before XMS |
Expanded memory specification (EMS) |
|
|
|
Why is EMS not accessed same as conventional and XMS? |
It cannot be directly accessed by the processor |
|
|
|
Caches ste |
Extremely fast RAM |
|
|
|
L1 cache |
Internal to processor |
|
|
|
L2 cache |
External to processor |
|
|
|
Personal computer contains |
Mouse, keyboard, monitor, and system unit |
|
|
|
System unit is primary system component and contains |
CPU, power supply, memory and ROM BIOS |
|
|
|
Operating system is... |
Software, main program Used is kernel, purpose is to manage operation of computer |
|
|
|
System case most important functions |
Structure, protection, cooling |
|
|
|
Parts of case |
Chassis and enclosure |
|
|
|
What case has best cooling |
Full tower |
|
|
|
Why is mini tower good? |
Small and minimal space taken up on desk |
|
|
|
UNIX |
Network operating system that has been modified by different companies |
|
|
|
BIOS |
Set of instruction that tells CPU how to access devices that let it cpunicTe with rest of world |
|
|
|
Purpose of CPU |
Preform system's calculating and processing |
|
|
|
CMOS used for clock chip because |
Takes little power to operate it |
|
|
|
Interrupt |
Suspension of a process going on in CPU |
|
|
|
Important characteristics of bus: |
Sore an width |
|
|
|
Local bus |
Bus that allows peripherals to connect to processor bus |
|
|
|
Universal Serial Bus (USB) |
Can include up to 127 devices at once; peripherals can be connected w/o having to shut down/restart and individual device don't need individual sets of system resources |
|
|
|
Software application |
Set of instructions for accomplishing a Sequence of actions |
|
|
|
Software application categories |
Productivity, utility and communication |
|
|
|
Configuration of typical Ethernet jack |
8-pin |
|
|
|
Client/server relationship involves |
Resource sharing and data flow control |
|
|
|
If client account has full rights to a network client limitations are |
Minimal |
|
|
|
Photons |
Light form of electromagnetic radiation containing bits of massless energy |
|
|
|
Light is |
reflected, refracted and absorbed by all materials |
|
|
|
Refraction |
Benson of a beam of light as it travels from one medium to another due to change in speed of light |
|
|
|
Law of relfectance |
Angle of relfectance=angle of incidence |
|
|
|
Fiber optic systems contain |
Transmitter, transmission and receiver sections |
|
|
|
LEDs and lasers |
Capable of light emissions in visible and infrared ranges (lasers also ultraviolet ranges) |
|
|
|
PIN photodiode and APD's |
Most common employed in fiberoptics |
|
|
|
PIN photodiodez |
Have increased f response it lower quantum efficiency |
|
|
|
APDs |
Have other responsibility and efficiency but need higher V bias |
|
|
|
Optical detector terms |
Responsitivity, response time, numerical aperture, quantum efficiency, dark I |
|
|
|
Dark current |
Current produced by photodiode when no V applied |
|
|
|
Attenuation |
Ability to maintain integrity of signal; measure in decibels/kilometers |
Loss |
|
|
Attenuation is affected by |
Absorption, scattering an micro end losses |
|
|
|
Single mode optical fiber |
Only one light path |
|
|
|
Multimodal grade index optical fiber |
(Or multimode step index) allows several light paths |
|
|
|
Multimode step index |
Not good for high speed or log distance |
|
|
|
Signal processing includes |
Amplification, filtering, reshaping, modulation/demodulation, multiplexing/demultiplexing |
|
|
|
Intensity modulation |
Modulated signal transmitted by ranging intensity of light wave |
|
|
|
Misalignment types |
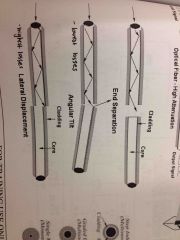
|
|
|
|
Heterojunction LEDs |
Confine and direct light better w/ a different type of material on at least one side of PN |
|
|
|
Quality measurements |
Analog SNR, digital BER |
|
|
|
Quality measurements |
Analog SNR, digital BER |
|
|
|
RADAR |
RAdio Detection And Ranging |
|
|
|
RF reflected from object gives |
Bearing, range, elevation and velocity |
|
|
|
RF reflected from object gives |
Bearing, range, elevation and velocity |
|
|
|
Echo |
Reflected energy from object |
|
|
|
RF reflected from object gives |
Bearing, range, elevation and velocity |
|
|
|
Echo |
Reflected energy from object |
|
|
|
Line of sight length |
Range |
|
|
|
RF reflected from object gives |
Bearing, range, elevation and velocity |
|
|
|
Echo |
Reflected energy from object |
|
|
|
Line of sight length |
Range |
|
|
|
Surface search radar |
Cannot supply altitude |
|
|
|
RF reflected from object gives |
Bearing, range, elevation and velocity |
|
|
|
Echo |
Reflected energy from object |
|
|
|
Line of sight length |
Range |
|
|
|
Surface search radar |
Cannot supply altitude |
|
|
|
Two types of radar transmissions |
Pulsed and continuous wave (CW) |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Dielectric loss |
Due to capacitance formed between transmission lines |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Dielectric loss |
Due to capacitance formed between transmission lines |
|
|
|
Waveguides are |
Manufactured from conductive materials and may be rectangular, circular, or elliptical |
|
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Dielectric loss |
Due to capacitance formed between transmission lines |
|
|
|
Waveguides are |
Manufactured from conductive materials and may be rectangular, circular, or elliptical |
|
|
|
a dimension |
f range |
In waveguides |
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
b dimension |
Power capability |
In waveguides |
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Dielectric loss |
Due to capacitance formed between transmission lines |
|
|
|
Waveguides are |
Manufactured from conductive materials and may be rectangular, circular, or elliptical |
|
|
|
a dimension |
f range |
In waveguides |
|
|
Discharge time of Pulse Forming Network (PFN) |
PW of radar |
|
|
|
b dimension |
Power capability |
In waveguides |
|
|
Antenna |
A conductor or group of conductors used for radiating electromagnetic energy transferred by the transmission line into space |
|
|
|
Good transmission line |
Has max transfer with minimum loss |
|
|
|
Transmission line properties |
Resistive loss, induction loss, radiation loss, capacitive loss |
|
|
|
Copper loss |
Due to resistance(especially in long lines) |
|
|
|
Radiation loss |
Portion of electric energy lost to the atmosphere (not object nearby) |
|
|
|
Characteristic impedance of transmission line |
Distributes inductance and capacitance |
|
|
|
Skin wffect |
At hight f's electrons go to outer surface |
|
|
|
Dielectric loss |
Due to capacitance formed between transmission lines |
|
|
|
Waveguides are |
Manufactured from conductive materials and may be rectangular, circular, or elliptical |
|
|
|
a dimension |
f range |
In waveguides |
|
|
Most common antenna type for microwave |
Horn |
|
|
|
Horn antenna |
Has power gain and matches waveguide impedance to space |
|
|
|
Parabolic reflector antenna |
Produce narrow beam in both planes |
|
|
|
Parabolic reflector antenna |
Produce narrow beam in both planes |
|
|
|
Orange peel parabolic reflector |
Narrow horizontal and wide vertical |
|
|
|
Parabolic reflector antenna |
Produce narrow beam in both planes |
|
|
|
Orange peel parabolic reflector |
Narrow horizontal and wide vertical |
|
|
|
Cavity resonator |
Is a parallel LC circuit |
Resonator... Resonance... Resonance frequency |
|
|
Special vacuum Tubes |
Klystron and magnetron |
|
|
|
Special vacuum Tubes |
Klystron and magnetron |
|
|
|
Klystron |
Buncher grids San cavity cause electrons to accelerate and decelerate |
|
|
|
Special vacuum Tubes |
Klystron and magnetron |
|
|
|
Klystron |
Buncher grids San cavity cause electrons to accelerate and decelerate |
|
|
|
Magnetrom |
Uses resonant cavities to produce oscillators; causes electrons to flow in a curved path |
|
|
|
Special vacuum Tubes |
Klystron and magnetron |
|
|
|
Klystron |
Buncher grids San cavity cause electrons to accelerate and decelerate |
|
|
|
Magnetrom |
Uses resonant cavities to produce oscillators; causes electrons to flow in a curved path |
|
|
|
EMC can be divide to: |
Denials and deception and each into passive and active |
|
|
|
Special vacuum Tubes |
Klystron and magnetron |
|
|
|
Klystron |
Buncher grids San cavity cause electrons to accelerate and decelerate |
|
|
|
Magnetrom |
Uses resonant cavities to produce oscillators; causes electrons to flow in a curved path |
|
|
|
EMC can be divide to: |
Denials and deception and each into passive and active |
|
|
|
Active denial ECM |
Electronic jamming devices used to produce signals to prevent tracking and detection of targets |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 2 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 2 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 3 cooling sustem |
CW/DW Heat exchange with a CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 2 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 3 cooling sustem |
CW/DW Heat exchange with a CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Minimum range of radar |
Determined by receiver recovery time and pulse width |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 2 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 3 cooling sustem |
CW/DW Heat exchange with a CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Minimum range of radar |
Determined by receiver recovery time and pulse width |
|
|
|
Radar accuracy affected most by |
Radar system resolution |
|
|
|
Type 1 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with SW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 2 cooling system |
SW/DW heat exchange with CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Type 3 cooling sustem |
CW/DW Heat exchange with a CW/DW heat exchange standby |
|
|
|
Minimum range of radar |
Determined by receiver recovery time and pulse width |
|
|
|
Radar accuracy affected most by |
Radar system resolution |
|
|
|
Range resolution |
Deprecate multiple targets on same bearing (determined by PW) |
|
|
|
Bearing resolution |
Separate multiple targets on same range determined by Beam width |
|
|
|
Superheterodyne receiver |
Most used |
|
|
|
Superheterodyne receiver |
Most used |
|
|
|
IF produced by |
Mixer (first detector) |
|
|
|
Superheterodyne receiver |
Most used |
|
|
|
IF produced by |
Mixer (first detector) |
|
|
|
Video produced by |
Video detector (second detector) |
|
|
|
Superheterodyne receiver |
Most used |
|
|
|
IF produced by |
Mixer (first detector) |
|
|
|
Video produced by |
Video detector (second detector) |
|
|
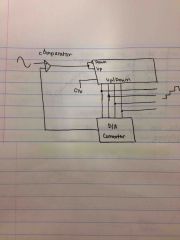
What is this? |
Tracking A/D converter |
|
|
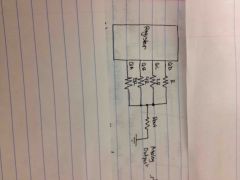
What is this? |
Binary weighted input D/A converter |
|
|
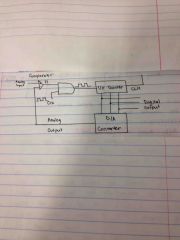
What is this |
Stair step A/D converter or ramp converter |
|
|
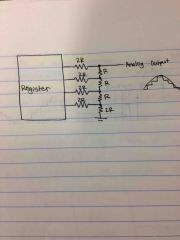
What is this |
R/2R D/A or ladder or scaling |
|

