![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Periods |
Horizontalarrangement of the elements. Elementsin the same period have the same number of electrons shells
|
|
|
Groups (families) |
Verticalarrangement of the elements. Elements in same group have same number valanceelectrons and same chemical properties.
|
|
|
Electronegativity |
a measure of anatom’s ability toattract (or gain) electrons
|
|
|
Electronegativity Trend |
Increases across a period Decreases down a group |
|
|
Ionization Energy |
energy toremove the most looselyboundelectron from an atom; ability to keep the electrons an atom has
|
|
|
Ionization Trend |
Increases across a period Decreases down a group |
|
|
Atomic Radius |
distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell |
|
|
Physical Properties of Metals |
Malleable, Ductile, High Luster, High Conductivity
|
|
|
Physical Properties of Nonmetals |
Brittle, dull and poor conductors |
|
|
Period Trends Left to right: properties that increase |
Ionization energy, electronegativitynonmetallic properties, nuclear charge
Reactivity (for nonmetals) |
|
|
Period Trends Left to right: properties that decrease |
Atomic radius Reactivity (for metals) |
|
|
Groups Trends Top to bottom: properties that increase |
nuclear charge, atomic radius Reactivity (for metals) |
|
|
Group Trends Top to bottom: properties that decrease |
electronegativity, ionization energy Reactivity (for nonmetals) |
|
|
Shielding |
the blocking affect that core electrons have on the valence electrons; prevents pull of nucleus |
|
|
Nuclear charge |
this is the force or pull that the nucleus provides on the electrons |
|
|
alkali metals; one valence electron |
|
|
alkaline earth metals; two valence electrons |
|

|
transition metals |
|
|
Group 7A; Halogens; 7 valence electrons |
|
|
Group 8A; Noble gases; inert; 8 valence electrons |
|
|
Most Reactive Metal |
Francium |
|
|
Most Reactive Nonmetal |
Fluorine |
|
|
Atoms become ions to |
have a stable arrangement; full valence shell |
|
|
Proton |
positive subatomic particle; weighs 1amu; is the identity of the atom (never changes = atomic number); in the nucleus |
|
|
Neutron |
neutral subatomic particle; weighs 1 amu; varying amounts of these yield isotopes; in the nucleus |
|
|
Electron |
negative subatomic particle; negligible mass; found in clouds around the nucleus |
|
|
Mass number |
the amount of particles in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Isotope |
Atoms with different amounts of neutrons and therefore different masses |
|
|
Average atomic mass |
the average of all isotopes based on percent abundance; number on periodic table |
|
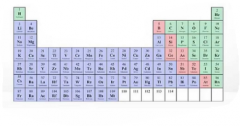
|
green - nonmetals blue - metals pink - metalloids |
|
|
Ions |
atoms that have lost or gained electrons |
|
|
Cation |
ions that have lost electrons; positive charge |
|
|
Anion |
ions that have gained electrons; negative charge |

