![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atomic Weight |
The weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, in AMU per atom.
- A mole is a unit used to count particles and is represented by Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23 particles). |
|
|
Isotopes |
For a given element, multiple species of atoms with the same number of protons (same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons (different mass numbers).
|
|
|
Planck's Quantum Theory |
Energy emitted as electromagnetic radiation from matter exists in discrete bundles called quanta.
|
|
|
Energy of Electron |
E = (-RH/n^2) |
|
|
Electromagnetic Energy of Photons |
E = (hc) / (gamma) |
|
|
Bohr's Model of the Hydrogen Atom |
The group of hydrogen emission lines corresponding to transitions from upper levels n>2 to n=2 is known as the blamer series, while the group corresponding to transitions between upper levels n>1 to n=1 is known as the Lyman series. |
|
|
Absorption Spectrum |
Characteristics energy bands where electrons absorb energy. |
|
|
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle |
It is impossible to determine with perfect accuracy the momentum and the position of an electron simultaneously.
|
|
|
Quantum Numbers |

|
|
|
Principal Quantum Number (n) |
The larger the integer value of n, the higher the energy level and radius of the electron's orbit. The maximum number of electrons in energy level n is 2n^2.
|
|
|
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l) |
Refers to sub-shells. The four sub-shells corresponding to l = 0, 1, 2, and 3 are known as s, p, d, and f; respectively. The maximum number of electrons that can exist within a sub-shell is given by the equation 4l + 2. |
|
|
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) |
This specifies the particular orbital within a sub-shell where an electron is highly likely to be found at a given point in time.
|
|
|
Spin Quantum Number (ms) |
The spin of a particle is its intrinsic angular momentum and is a characteristic of the particle, like it charge. |
|
|
Electron Configuration |

|
|
|
Hund's Rule |
Within a given sub-shell, orbitals are filled such that there are a maximum number of half-filled orbitals with parallel spins.
|
|
|
Valence Electrons |
Electrons of an atom that are in its outer energy shell and that are available for bonding. |
|
|
Periodic Table |
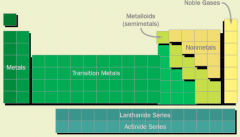
|
|
|
Periodic Table |
Increases Up and to the Right: Effective Charge, Ionization Energy, Electronegativity, Electron Affinity. Increases Down and to the Left: Atomic Radius. |

