![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

STRATOSPHERE |
The region of the uppermost atmosphere where temperature increases along with the altitude due to the absorption of solar ultraviolet radiation by ozone. |
|

CORIOLIS EFFECT |
causes objects including air and water to move to the east in the Northern Hemisphere and to the west in the Southern Hemisphere |
|

ATMOSPHERE |
the layer of gases that surround the Earth
|
|

CONVECTION |
heat transfer through the atmosphere where warm air rises and cold air sinks |
|
AIR PRESSURE
|
the force of air molecules pushing on a surface that can change due to unequal heating of the planet
|
|
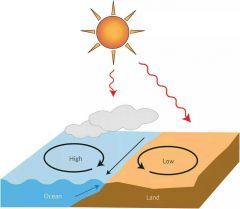
HIGH PRESSURE
|
Air molecules are lowering (more pressure on ground); system moves clockwise; produces clear skies |
|
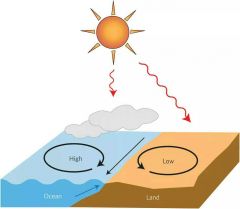
LOW PRESSURE
|
Air molecules are rising (very little pressure on ground); system moves counterclockwise; produces clouds/storms
|
|

BAROMETER
|
measures air pressure
|
|

WIND
|
movement of air caused by differences in air pressure
|
|

ANEMOMETER
|
measures wind speed
|
|

PSYCHROMETER
|
measures relative humidity |
|

JET STREAM |
narrow bands of strong winds in the upper levels of the troposphere |
|

LAND BREEZE |
Breeze flowing from land to the sea (night time) |
|

SEA BREEZE |
Breeze flowing from sea to land (day time) |
|

WINDWARD |
wind moves up this side of the mountain, drawing moisture out of the air. Produces a wet, moist climate |
|

AIR MASS |
large body of air where temperature and moisture are similar throughout |
|

CONTINENTAL (CLIMATE) |
dry air mass that forms over land |
|

MARITIME (CLIMATE) |
moist air mass that form over the ocean |
|

TROPICAL (CLIMATE) |
warm air mass that forms over the Tropics |
|

POLAR (CLIMATE) |
cold air mass that forms over the polar regions |
|

WARM FRONT |
forms when warm air moves over cold, denser air |
|

COLD FRONT |
forms when cold air moves under warm air |
|

STATIONARY FRONT |
a cold air mass and a warm air mass meet, and there is very little movement |
|

OCCLUDED FRONT |
a composite front formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front and forces it aloft |
|
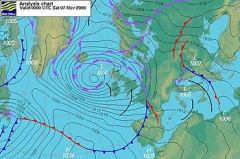
ISOBARS |
line drawn on a weather map or chart that connects points at which the barometric pressure is the same |
|

HURRICANE |
severe storm formed over tropical oceans with winders greater than 74 mph |
|

STORM SURGE |
Abnormal rise of water levels caused by the strong winds of a hurricane or tropical storm |
|

EYE OF THE HURRICANE |
area of warm , calm air in the center of strong tropical storms or hurricanes |
|

TORNADO |
can have stronger winds than a hurricane; forms when a cold, dry air mass meets with a warm, moist air mass |
|

LIGHTNING |
electrical discharge between a negatively and positively charged area |
|
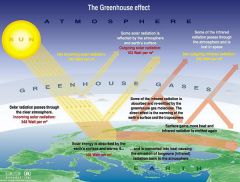
GREENHOUSE EFFECT |
gases in the atmosphere that absorb thermal energy and radiate it back to Earth (ex: water vapor and carbon dioxide) |
|

CUMULONIMBUS (LOW BASE) |
dense, towering vertical cloud associated with thunderstorms; produced at cold front and may also contain hail |
|

STRATUS (LOW BASE) |
Thin, gray, sheetlike clouds with low bases; may bring drizzle or snow. If low enough, can be called fog |
|

ALTOCUMULUS (MID BASE) |
Gray or white layer or patches of solid clouds with rounded shapes |
|

STRATOCUMULUS |
Rounded cloud masses that form in a layer |
|
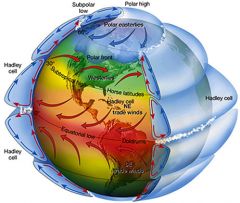
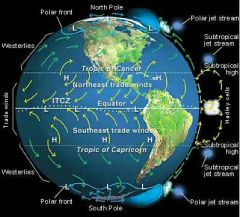
GLOBAL WINDS |
Predictable air mass movement at every 30 degrees of latitude |
|

NIMBOSTRATUS (LOW/MID BASE)
|
Dark, gray, shapeless cloud layers containing rain, snow, or ice pellets |
|

CIRROCUMULUS (HIGH BASE) |
Thin clouds that appear as small cotton patches |
|

CIRRUS (HIGH BASE) |
Thin, featherlike, crystal clouds |
|

CIRROSTRATUS |
Thin white clouds that resemble veils |
|

ALTOSTRATUS |
Grayish or bluish layer of clouds that can obscure (hide) the Sun |
|
TRADE WINDS |
prevailing winds that blow from east to west from 30 degrees latitude to the equator in both hemispheres. |
|
WESTERLIES |
prevailing winds blowing from west to east from 30 - 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres. |
|
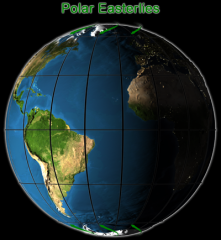
POLAR EASTERLIES |
east blowing wind that blow from the poles (north and south poles) |
|

CONTINENTAL POLAR |
cold and dry |
|

CONTINENTAL TROPICAL |
warm and dry |
|

MARITIME POLAR |
cold and moist |
|

MARITIME TROPICAL |
warm and moist |
|
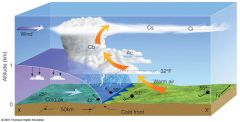
FRONT |
The boundary between air masses |
|

THERMOSPHERE |
the thermal classification of the atmosphere. In this layer temperature increases with altitude. It includes the exosphere and the ionosphere. |
|

TROPOSPHERE |
lowest region in earths atmosphere. It goes from sea level to about 11m high. Weather and clouds occur in this layer. |
|
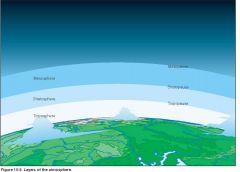
TROPOPAUSE |
boundary zone between troposphere and stratosphere. It is characterized by little to no temperature change as altitude increases. |
|

EXOSPHERE |
outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere. It is about 400-800 m highThe lowest level of this layer is called the critical level of escape, where atmospheric pressure and temperature is very low. |
|

IONOSPHERE |
the layer is about 43-400 m high. Contains many ions and free electrons. The ions are created by the sunlight when it tears off electrons. This is the layer of the auroras (northern lights) |
|
|
MESOSPHERE |
characterized by temperature that rapidly decrease as altitude increases. It extends about 50 m above the earth's surface. METEORS |

