![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the earliest intervention for "A" in trauma patients?
|
All trauma patients must receive supplemental O2
|
|
|
What are 2 key reasons to assure a trauma patient has a patent airway?
|
1. Prevent hypercarbia
2. Maintain oxygenation |
|
|
What are the objective signs of airway obstruction? (4)
|
1. Observe patient: agitation (hypoxemia) vs obtunded (hypercarbia); cyanosis? (hypoxemia); retractions/acc. muscle use? (airway compromise)
2. Abnormal breath sounds: snoring, gurgling, stridor are all abnormal 3. Position of trachea: midline? 4. Patient's behavior: abusive/belligerent may be HYPOXIC and not intoxicated |
|
|
3 signs of laryngeal trauma?
|
1. Hoarseness
2. SubQ emphysema 3. palpable fracture |
|
|
High concentrations of O2 can mask breathing problems, what are 2 ways to more accurately measure ventilatory efforts?
|
1. Arterial CO2
2. End tidal CO2 |
|
|
Name 3 objective signs of inadequate ventilation.
|
1. Asymmetric chest rise/chest wall excursion - splinting of rib cage or flail chest
2. Asymmetric breath sounds - presence of thoracic injury 3. Pulse oximeter - O2 saturation (NOT adequacy of vent) |
|
|
During "B" in the ABCDEs, what precaution is of utmost importance?
|
Maintaining C-spine protection
|
|
|
What is a contraindication to a nasopharyngeal airway?
|
Suspected cribiform plate fracture
|
|
|
A patient arrives with a LMA in place, what must be done?
|
Plan for a definitive airway -- LMAs are NOT definitive airway options
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of definitive airways?
|
1. Orotracheal
2. Nasotracheal 3. Surgical airways (cricothyroidotomy/tracheostomy) |
|
|
When is an orotracheal intubation indicated over a nasotracheal route?
|
If the patient has apnea
|
|
|
What are 3 contraindications to use of succinylcholine?
|
Can precipitate severe hyperkalemia in:
1. Burn victims 2. Crush injuries 3. electrical injuries |
|
|
What is the normal RSI dose of etomidate?
|
0.3mg/kg for induction, typically 30mg
|
|
|
What is the normal RSI dose of succinylcholine?
|
1-2mg/kg for paralysis, typically 100mg
|
|
|
What is the DOC to reverse benzo action in trauma patients?
|
Flumazenil
|
|
|
Why are some induction agents (e.g. thiopental) and sedatives particularly dangerous in trauma patients?
|
If hypovolemia is present, can exacerbate
|
|
|
What is preferred in the ED for a surgical airway?
|
cricothyroidotomy (over a tracheostomy)
|
|
|
What does the pulse oximetry NOT measure?
|
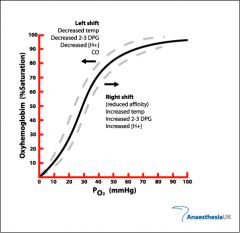
PaO2 levels -- which can vary greatly based upon the position of the oxyhemoglobin curve
|
|
|
What O2 sat typically signifies adequate periph arterial oxygenation?
|
O2 Sat > 95% (usually indicates PaO2 > 70mmHg)
|
|
|
What scenario limits the usefulness of pulse oximetry?
|
CO poisoning -- the pulse oximeter cannot distinguish between oxyhemoglobin and carboxy-/met-hemoglobin
|
|
|
Bag-mask ventilation can result in gastric distention, what are 2 complications associated with this?
|
1. Vomiting and aspiration
2. Stomach distention placing pressure on the IVC resulting in hypotension and bradycardia |

