![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
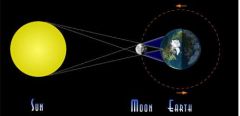
What type of eclipse is shown?
|
Solar Eclipse
|
|
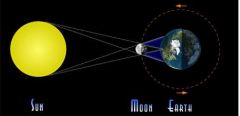
What phase of the moon is shown? How much light will we see on the moon?
|
New moon, we will see no light reflecting on the moon-the sky will be dark.
|
|
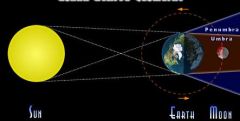
What type of eclipse is pictured?
|
Lunar Eclipse-Earth is casting a shadow on the moon. This is the most frequently seen type of eclipse, because the Earth casts a bigger shadow.
|
|
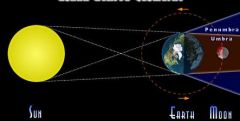
What phase of the moon is pictured? How much light would you see reflected by the moon?
|
This is the full moon orientation. You would see the whole face of the moon illuminated.
|
|

What is the ring of rocks shown called? Between which two planets is it located?
|
Asteroid Belt, found between Mars and Jupiter.
|
|
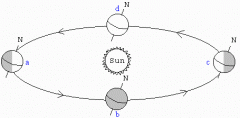
What events are pictured at a and c?
What events are pictured at b and d? |
A + C Winter and Summer Solstice
B + D Spring and Fall Equinox |
|
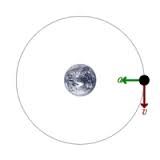
What two forces combine to form an orbit?
|
Gravity pulling in-ward and inertia going in a straight line.
|
|
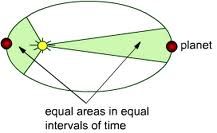
Explain what they mean by equal areas in equal intervals of time. How are those two areas equal? Where does the planet move the fastest? The slowest?
|
The size of the shaded area is equal, the planet travels a much larger distance when its closer to the Sun in the same amount of time as it takes to go a shorter distance when the planet is farther away from the Sun.
It does this because it is moving faster closer to the Sun as it experiences a stronger force of gravity due to the decreased distance to the Sun. Kepler's 2nd Law |
|
What is the Period of Revolution? Which planet will have the shortest Period of Revolution? Which will have the longest? What's Earth's Period of Revolution?
What causes all of this? |
Period of Revolution-the time it takes to complete one orbit of the Sun. Mercury has the shortest, Neptune has the longest. Earth's is 365.25 days which explains why we have a leap year every 4 years to take into account the .25 of a day. The calendar mistake was fixed by Pope Gregory XIII (13th) and it's the reason the calendar is called a Gregorian Calendar.
Objects have shorter periods of revolution (they orbit faster) when they are closer to the Sun because the are pulled on more by the Sun's gravity as the distance is decreased between the high mass object (the Sun) and the lower mass satellite (the planet). |
|
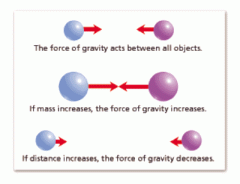
Explain how Gravity works-what are the two factors that influence it and how do they work?
Explain why you experience more gravity on the Earth than you do on the Moon talking about Mass. Explain why you experience less gravity on top of a mountain than you do at the beach. |
Gravity is based on mass the mass of the objects in question and the distance between them. As the mass of the objects increases (there is more of them) and the distance between them decreases (they get closer) gravity will increase.
You are more attracted to the Earth than the moon because the Earth has much more mass. But, the moon does pull on the Earth causing the tides in the oceans of the world. You experience less gravity on top of a mountain because you are farther from the core of the Earth. |
|
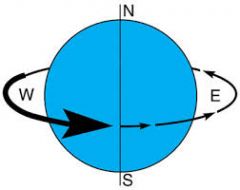
What's shown? How long would it take Earth to do this? What affect does this have on Earth? What tilt should be shown if this object were Earth?
|
Rotation-it takes Earth 24 hours, this causes our day. The Sun doesn't actually come up or go down, we spin and see it more or less throughout our day. The Earth is tilted at 23.5 degrees which the Sun to travel across our horizon.
|
|
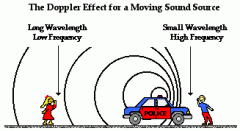
Explain the Doppler Effect and Red and Blue Shifts
|
As an energy source gets closer to the observer, it will appear to become louder-a Blue Shift. It's not really louder, it just seems like it because of the decrease in wavelength.
As the energy source gets farther away, the wavelength will lengthen and it will appear to get quieter-Red Shift |
|

What are the outer planets called? What are they mostly composed of? Why are they made up of this stuff?
|
Gas Giants-they are farther from the Sun and cooler so they have thick atmospheres of gas.
|
|
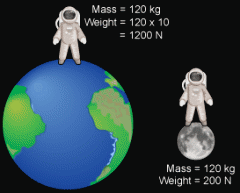
Explain the difference between mass and weight.
|
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Weight is a measurement of gravity's pull on that mass. Mass will not change with location, weight will.
|
|

What do you call a big cloud of gas and dust?
What two forces need to be equalized in order for it to be stable? |
Nebula-Gravity and Pressure
|
|

Why does Venus look like a big fiery ball to observers?
|
It has a atmosphere made out of CO2 gas which is reflective and it reflects Sun Light. It is the planet that is closest in size to the Earth.
|
|
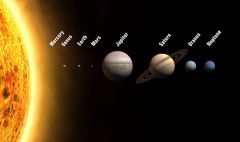
What do you call a Star and Everything that orbits it?
|
Solar System
|
|
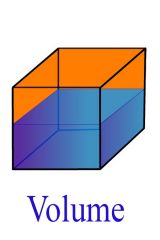
Explain what Volume is
|
The amount of space something takes up or the amount of space within the object
|
|
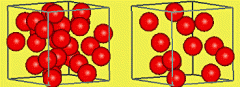
Explain what Density is
|
The amount of matter in a volume (space)
|
|
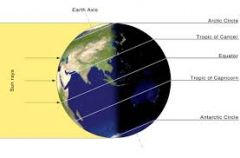
What season would it be in North America and why?
|
Summer-NA is tilted towards the sun
|
|
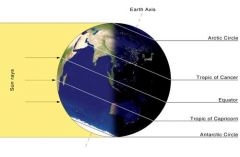
What season would it be in North America and why?
|
Winter, NA is tilted away from the Sun.
|
|

What do you call the process of building by smashing into things?
|
Accretion
|
|
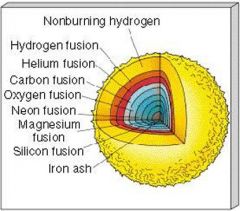
Explain why Iron forms the cores of stars and planets
|
Iron is the densest element that Stars can make by splitting the nucleus and recombining protons. The nucleus of Iron is too dense for stars to burn so the Iron sinks to the core of the star because of its large density. When stars explode they eject Iron into the Universe and this Iron collects because of gravity and forms the cores of planets.
|
|

Explain what the Universe is
|
Everything that exists
|
|
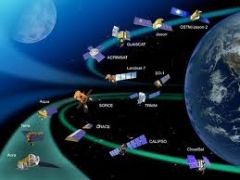
Explain what a satellite is
|
Anything that orbits-the low mass body will orbit the high mass body. The Earth is a satellite of the Sun, the moon is a satellite of Earth.
|
|

Explain what Inertia is and how both the ball moving and the other balls sitting still both have it.
|
Inertia-the resistance of an object to a change in motion. An object sitting still will sit still and an object in motion will remain in motion until a big enough force is applied to change that sitting still or motion.
|
|

Explain what a planetismal is
|
A young planet that is growing through accretion in an immature solar system. Aka a baby planet.
|
|

Explain the differences between and immature and mature solar system
|
Immature-orbits not yet defined, lots of planetismals smashing into each other and acreting (growing by smashing)
Mature-defined orbits, little accretion, full size planets |
|

Which planet is the largest with a giant Red Spot that actually a storm that's bigger than Earth? It also has the most moons as it produces the most gravity...
|
Jupiter
|
|

Which planet has all the rings?
|
Saturn
|
|

Why is Pluto no longer considered a planet?
|
It's not big enough-it turns out that it's actually a hunk of ice that orbits with a lot of other big chunks of ice in a system trans Neptune objects.
|
|
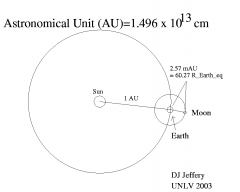
Explain what an Astronomical Unit is and where we use it to measure.
|
It's the average distance from the Earth to the Sun and we use it to measure inside of our Solar System.
|
|

Explain what a light year is and where we use it to measure.
|
It's a really big measurement-the distance that light will travel one year in space. We use it to measure large distances outside of our solar system, like the distance to stars other than our Sun or across Galaxies.
|
|

Why is Mars red?
|
It's made of Iron and rusted.
|
|

Why can we see the light of the moon?
|
It reflects light from the Sun.
|
|
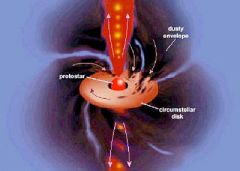
What are protostars and where do you find them?
|
The early stages of star formation inside of a nebula before the star has ignited.
|
|

What do you call a star once its started fusion? What fuel is it fusing (burning)?
|
Main sequence-fusing Hydrogen to make Helium.
Our sun is a middle age main sequence star. |
|

Explain the process that causes main sequence stars to expand. What do you call the next phase of their life? What fuel are they fusing?
|
The main sequence star fuses all of its Hydrogen. When it runs out of fuel, there is no more outward pressure. This causes the star to collapse which causes a lot of friction that makes heat. The heat reaches a temperature that causes the Hellium created by the Main Sequence star to start fusion. Since the Hellium is 4x's denser than the Hydrogen, the volume of the star expands exponentially.
This phase of life is called The Red Giant-the stars in this stage are fusing Helium into Carbon and Oxygen. |
|

After a Main Sequence Star leaves the RED GIANT phase, what happens? What is the density of the star said to be?
|
The super dense core of the star collapses into a very hot but very dim star called a White Dwarf. A planetary Nebula is also produced that will drift into the galaxy.
The density of the star is said to be "a ton per teaspoon" |
|

Explain the mass, volume, and density of a white dwarf star. What was the mass of the star it started out as?
|
The white dwarf star started life as a Low/Med mass Main sequence star. Now it has a mass comparable to that of the Sun but a size comparable to Earth. That makes the star unbelievably dense.
|
|

What happens to White Dwarfs in their final stage of life?
|
They cool off and become Black Dwarfs.
|
|
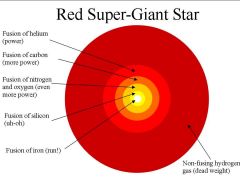
What makes a Red Super Giant instead of a Red Giant Star?
|
High Mass stars turn into Red Super Giants as they are burning much more fuel much more quickly, they expand in volume a lot more.
|
|
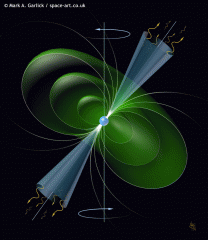
After the SuperNova stage for a high mass star, what happens to the not so big ones? What do we call this stage of life?
|
The Red Super Giants explode in SuperNova's. The not so big Super Giant stars, eject their cores which spin so fast that we can actually hear the radio waves they give off. We call this stage of life the Pulsar or Neutron star.
|
|
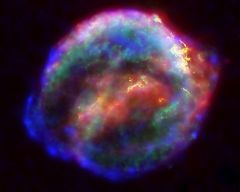
What do you call the huge explosion that marks the end of the life of a high mass star?
|
Super Nova
|
|
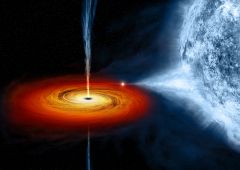
What is the final stage of life for the highest mass stars? What causes it?
|
Black Hole-when these stars explode, they push out with so much pressure that their cores contract to counteract the pressure to the point where not even light can escape their gravitational pull.
|
|

What kind of galaxy is the Milky Way? What kind of stars do you find in the center? What kind of stars do you find in the arms? How much dust and gas is there?
|
Milky Way is a Bar Spiral Galaxy. There are old red stars in the center and young blue stars in the arms. There is a lot of dust and gas which is why there are so many young blue stars.
|
|

What type of galaxy is this? What kind of stars is it made of? How much dust and gas?
|
Elliptical galaxy-old red stars-not much dust and gas.
|
|

What kind of star is the sun? How old is it? What's it fusing? What will it turn into?
|
Main Sequence red/yellow -middle age-fusing hydrogen-turning into a white dwarf someday.
|
|

Where are we located in the Milky Way?
|
2/3 of the way down one of the arms.
|
|

How many stars are in a Galaxy?
|
Billions
|
|

Explain what a Comet is, where it comes from, how it travels (orbit, no orbit, etc.), and which way its tail points.
|
A Comet is basically a big hunk of ice and rock (dirty snowball) that orbits our star (the Sun). It comes from somewhere out beyond the Kuiper Belt that contains Pluto. We think they come from the Oort cloud, the farthest part of our Solar System. They may orbit multiple stars, but they do have defined orbits. Haley's Comet is probably the most famous example, it's orbital period is 75-76 years.
The tail of comets always point away from stars as the tail is produced by melting the ice and rock on the face of the comet which then blows off the back-kind of like your hair with a blow dryer. |
|

These rocks enter Earth's atmosphere. What are they? Which way does their tail point? What are they usually made of?
|
These are meteors. They usually burn up because of friction with the atmosphere before they hit the ground. If they do hit the ground, we then call them meteorites.
Their tail points in the direction they are coming from. About 99% of them are Iron as they are part of a star that supernova'd. You'll know if you find one if it has a black crust like burnt toast (fusion crust) and a magnet sticks to it as it's iron. It won't be perfectly round though! |
|
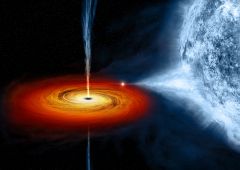
Explain what causes a Black Hole. What you call the edge of it and what would happen if you fall over the edge.
|
Black Holes are created by the collapse of Very High Mass Stars. They are proposed to be found at the center of most galaxies.
The edge of the black hole is called the Event Horizon and if you went inside, time would slow down drastically around you but not for you. Think of it like this-every one of the minutes you experienced inside of it would be equal to 1000 Earth years. That is until you get "spaghettified" and gravity rips you to shreds. |

