![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Suppose you drop a 10-pound weight and a 5-pound weight on the Moon, both from the same height at the same time. What will happen?
|
Both will hit the ground at the same time.
|
|
|
Newton showed that Kepler's laws are
|
natural consequences of the law of universal gravitation.
|
|
|
Suppose the Sun shrunk in size but its mass remained the same. What would happen to the orbit of the Earth?
|
Earth's orbit would be unaffected.
|
|
|
An asteroid moving in an elliptical orbit about the Sun will be travelling fastest when it is
|
closest to the Sun.
|
|
|
An asteroid orbiting the Sun in a circular orbit with a radius that is twice that of Earth's orbit would have an orbital period of
|
2.8 years
square root of x^3 |
|
|
Consider an astronaut in the Space Shuttle as the Space Shuttle orbits Earth. Is there a gravitational force exerted by Earth on the astronaut?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What is a CCD?
|
It is an electronic detector that can be used in place of photographic film for recording images.
|
|
|
what causes the twinkling of stars?
|
atmospheric turbulence
|
|
|
What is the SINGLE most important feature of an astronomical telescope?
Choose one answer. a. Greater Magnification. b. Greater Light Gathering Power. c. Greater Resolving Power. d. Greater Color Contrasting Power |
Greater Light Gathering Power
|
|
|
The strength of the gravitational force between two masses, M1 and M2, can be written as F = GM1M2/r2. where r is the distance between the two masses. Accordingly, the strength of the gravitational force depends _____ on M1
|
directly
|
|
|
The strength of the gravitational force between two masses, M1 and M2, can be written as F = GM1M2/r2. where r is the distance between the two masses. Which of the following changes would most effect the strength of the gravitational force?
Choose one answer. a. Changing M2 a little while leaving M1 and r unchanged. b. changing r a little while leaving M1 and M2 unchanged. |
b. changing r a little while leaving M1 and M2 unchanged.
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes why radio telescopes are generally much larger in size than telescopes designed to collect visible light?
|
Getting an image of the same angular resolution requires a much larger telescope for radio waves than for visible light.
|
|
|
Suppose that the angular separation of two stars is 0.1 arcseconds, and you photograph them with a telescope that has an angular resolution of 1 arcsecond. How will the stars appear in the photograph?
|
Since their angular separation is smaller than the telescope's angular resolution, your photograph will seem to show only one star rather than two.
|
|
|
Suppose you point your telescope at a distant object. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of taking a photograph of the object through the telescope as compared to just looking at the object through the telescope?
a. By using a long exposure time, the photograph can allow you to see objects that would be too dim to see with your eye. b. The photograph provides a more reliable record of what is seen through the telescope than can a drawing made by eye. c. If taken with a camera with a sensitive detector such as a CCD, the photograph can capture a much larger percentage of the incoming photons than can your eye. d. The photograph will have far better angular resolution than you can see with your eye. |
The photograph will have far better angular resolution than you can see with your eye.
|
|
|
The stars in our sky twinkle in brightness and color because of
|
turbulence in the Earth's atmosphere.
|
|
|
The strength of the gravitational force between two masses, M1 and M2, can be written as F = GM1M2/r2. where r is the distance between the two masses. Accordingly, the strength of the gravitational force depends
directly/inversly on distance r. |
inversely
|
|
|
What do we mean by the diffraction limit of a telescope?
|
It is the angular resolution the telescope could achieve if nothing besides the size of its light-collecting area affected the quality of its images.
|
|
|
The Chandra X-ray Observatory must operate in space because:
|
X rays do not penetrate Earth's atmosphere.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of interferometry?
|
two or more small telescopes to achieve the angular resolution of a MUCH larger telescope
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the principle advantage of CCDs over photographic film?
Choose one answer. a. CCDs allow long exposures (e.g., minutes or hours) and film does not. b. CCDs capture a much higher percentage of the incoming photons than film. c. CCDs can record the colors of astronomical objects accurately while film cannot. d. CCDs can be attached to modern telescopes more easily than can photographic film. |
b. CCDs capture a much higher percentage of the incoming photons than film.
|
|
|
How does the light-gathering power of an 8-meter telescope compare to that of a 2-meter telescope?
|
The 8-meter telescope has 16 times the light-gathering power of the 2-meter telescope.
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of the Hubble Space Telescope over ground-based telescopes?
Choose one answer. a. It is closer to the stars. b. It never has to close because of cloudy skies. c. It can observe infrared and ultraviolet light, as well as visible light. d. Stars do not twinkle when observed from space. |
a. It is closer to the stars is not an advantage because it's barely closer at all
|
|
|
Suppose you heat up an oven to 400 degrees F and boil a pot of water. Which of the following explains why you would be burned by sticking your hand briefly in the pot but not by sticking your hand briefly in the oven?
|
The water can transfer heat to your arm more quickly than the air.
|
|
|
The star Sirius has a surface temperature about twice that of the Sun (12,000 Kelvin for Sirius versus 6,000 Kelvin for the Sun). Per unit surface area, how much more energy does Sirius radiate than the Sun?
|
16 times as much energy.
|
|
|
T/F: X-rays have shorter wavelengths than radio waves.
|
True
|
|
|
Absolute zero is
|
0 degrees Kelvin
|
|
|
Which of the following scenarios involves energy that we would typically calculate with Einstein's formula E=mc2?
|
When hydrogen is fused into helium, whether in the Sun or a nuclear bomb, some of the mass disappears and becomes energy.
|
|
|
In the formula E=mc2, what does E represent?
|
The mass-energy, or potential energy stored in an object's mass.
|
|
|
Suppose a light source is emitting red light at a wavelength of 700 nm and another light source is emitting ultraviolet light at a wavelength of 350 nm. Each photon of the ultraviolet light has _______ the energy of each photon of the red light.
|
twice the energy of each photon of the red light.
|
|
|
Radiative energy is
|
energy carried by light
|
|
|
What does temperature measure?
|
The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
|
|
|
What is a joule?
|
It is the standard unit of energy used in science.
|
|
|
Suppose you have a 100-watt light bulb that you leave turned on for one minute. How much energy does it use?
|
6,000 joules
1 joule per watt per second |
|
|
Suppose you kick a soccer ball straight up to a height of 10 meters. Which of the following is true about the gravitational potential energy of the ball during its flight?
|
The ball's gravitational potential energy is greatest at the instant when the ball is at its highest point.
|
|
|
The energy emitted per second by the Sun is greatest at a wavelength of about 500 nm. The energy emitted per second by a star that is three times hotter than the Sun would be greatest at a wavelength of about
|
170 nm (1/3 of 500 nm)
|
|
|
The energy attributed to an object by virtue of its motion is known as
|
kinetic energy
|
|
|
Suppose the Sun was 4 times hotter than it actually is, but staid the same size. How much more energy per second would the Sun emit?
|
256 times more.
|
|
|
If star Zeta emits electromagnetic radiation most intensely at a wavelength of 500 nanometers, what is the surface temperature (in Kelvin) of this star?
|
5,800
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes why we say that light is an electromagnetic wave?
|
The passage of a light wave can cause electrically charged particles to move up and down.
|
|
|
Gamma rays have a very small
|
wavelength.
|
|

The graph shows the intensity versus wavelength plots for two different stars, A and B. Which star is emits more blue light?
|
Star A
|
|

The graph shows the intensity versus wavelength plots for two different stars, A and B. Which star emits more red light?
|
Star A
|
|
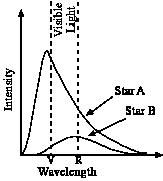
The graph shows the intensity versus wavelength plots for two different stars, A and B. Which star appears red?
|
Star B
|
|
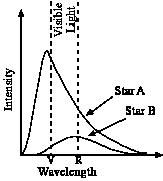
The graph shows the intensity versus wavelength plots for two different stars, A and B. Which star is hotter?
|
Star A
|
|
|
T/F: At the equator, over the course of the year, all 88 constellations will at some point be visible in the evening sky.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T/F: At the equator, there are no circumpolar stars in the equatorial sky.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T/F: At the Earth's equator, the north celestial pole is directly on your horizon, due north (with Polaris quite nearby).
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T/F: At the equator, the Sun will pass directly overhead around noon each day.
|
FALSE: at the equator the sun will pass directly overhead on the Vernal and Autmnal Equinoxes
|
|
|
how far away is the andromeda galaxy?
|
2.5 million light-years
|
|
|
how many AU's in a light year?
|
~63,000
|
|
|
arrange in order: solar system, local supercluster, local group, galaxy,
|
solar system
galaxy local group local supercluster |
|
|
T/F: X-rays have higher frequency than radio waves.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
3 objections to heliocentricism?
|
1.Aristotle: Earth is not moving, or things would fall off
2. Aristotle: heavens are perect, so orbits are perfect circles 3. no stellar parallax |
|
|
Ptolemy? (3)
|
1. geocentric
2. small circles on big circles 3. accurate predictions |
|
|
Copernicus? (3)
|
1. heliocentric
2. heavenly bodies move in perfect circles 3. no more accurate than Ptolemy |
|
|
Tycho Brahe?
|
no model
made observations that kepler would use |
|
|
Kepler?
|
1. orbits are not circles, but elipses
2. equl areas in equal times 3. more distant orbits have slower periods |
|
|
Galileo? (5)
|
Galileo? (5)
1. heliocentric 2. earth can move without things falling off because objects remain in motion until a froce stops them 3. heavens are not perfect: sun spots and moon mountains: so orbits don't have to be circles 4. moons orbit jupiter, so not everything orbits earth 5. venus phases only work if it orbits sun |
|
|
emitted power per square meter of surface =
|
sigma * (T ^ 4)
|
|
|
wavelength of max intensity =
|
2,900,000 / T
|
|
|
telescope light-collecting area =
|
diameter ^ 2
|
|
|
orbital period =
|
square root of (a ^ 3)
|

