![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In this model everything revolves around a stationary earth |
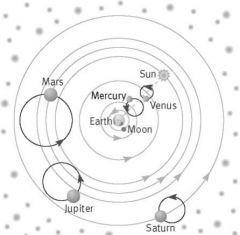
Geocentric |
|
|
What is the name for the Sun centered model of the solar system |
Heliocentric |
|
|
How do we explain night and day in a heliocentric model of the solar system?
|
Earth rotates |
|
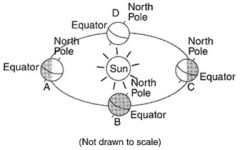
What are the two pieces of evidence that prove that the Earth revolves around the Sun? |
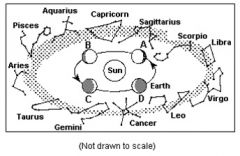
Seasons change and constellation change |
|

What are the two things that prove the Earth rotates? |
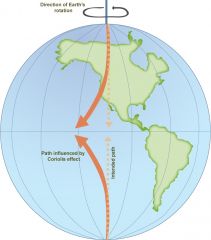
Focault's Pedulum and the Coriolis Effect |
|
|
What Earth motion causes winds, ocean currents, rockets and anything else moving across Earth to be deflected or (curved) |
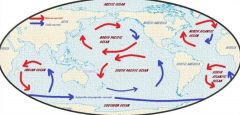
rotation |
|
|
Which direction are winds and ocean currents deflected to in the Northern Hemisohere due to the corilis effect? |
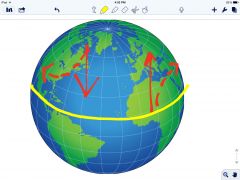
Right |
|
|
Foucault’s pendulum and Coriolis effect prove the earth ________________________
|
Earth rotates on its axis |
|
|
Changing seasons and constellations prove the Earth_________ |
Revolves around the sun
|
|
|
Why do stars like the sun appear to move in the sky?
|
Earth rotates on its axis |
|
|
Stars like the Sun and all other celestial objects appear to move at a rate of ______ degrees per hour
|
15
|
|
|
Which is the only star that does not appear to move due to Eaerth's rotation? |

Polaris |
|
|
All celestial objects like the Sun and moon appear to rise in the ____ and set in the _____ |
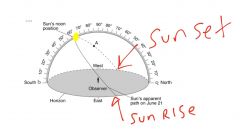
East West |
|
|
The earth ________________ counterclockwise (in 24 hours) at a rate of _______degrees per hour |
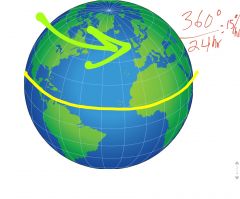
rotates |
|
|
The earth _____________ around the sun (in 365 1/4 days) at rate of ____degree per day. |
revolves |
|
|
What does the term zenith mean?
|
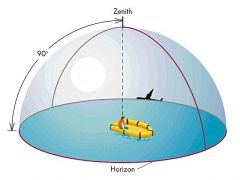
spot directly above your head at a 90 degree angle |
|
|
Polaris is located directly above |
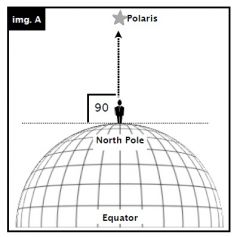
The Earth's axis of rotation |
|
|
The Altitude of star is the measurement of its angle above the _________ |
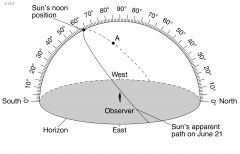
horizon |
|
|
You can only see Polaris in the _________hemisphere |
Northern
|
|
|
you always have to look _________ to see polaris |
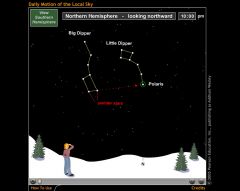
North |
|
|
Polaris is the last star in the handle of the ________ ________ (constellation) |
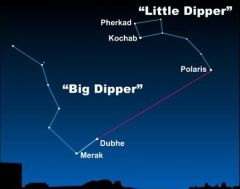
Little Dipper |
|

What direction are you |
north |
|
|
The altitude of Polaris (north star) above the horizon is the same as the observer’s ________________ |
latitude
|
|
|
As a person’s latitude increases, the altitude of Polaris ______________ |
increases
|
|
|
Plot the apparent position for Polaris as seen from an observer at 41N |
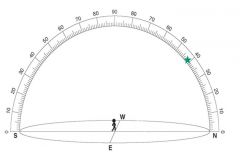
|
|
|
If you’re at 90°N, then Polaris is _______° above the horizon- If you are at the equator then Polaris is at ______° |
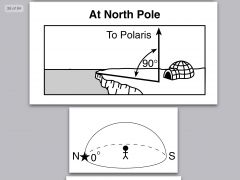
90 |
|
|
the latitude of the North pole is_____ |
90N |
|
|
The latitude of the Equator is |
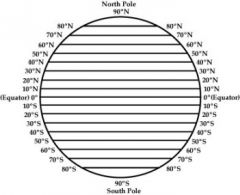
0 |
|
|
The longitude of the Primer meridian is |
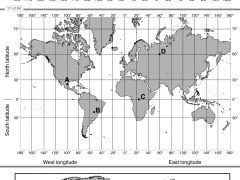
0 |
|

What direction are you looking? indicate which star is polaris. |

North |
|
|
the altitude of Polaris is always the same as the observer's |
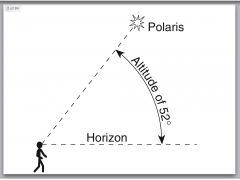
latitude
this person is at 52N |
|
|
As a person's latitude increases, Polaris's angle.................. |
Increases |
|
|
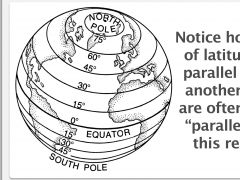
latitude lines measure distances__________ or ___________ of the equator |
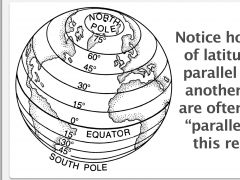
north or south |
|
|
Longiude lines measure disdtance ________and ______of the Prime Meridian |
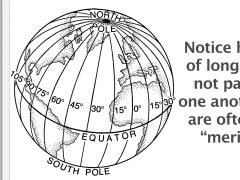
East and west |
|
|
Every 15 degrees of longitude equals a ___________ hour time difference |
1 |
|
|
Two location 60 degrees apart will have a _______ time difference |
4 |
|
|
As you travel west, what happens to your local time? |
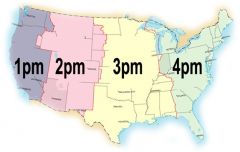
Gets earlier |
|
|
Altitude is the angle of a star above the _________ |
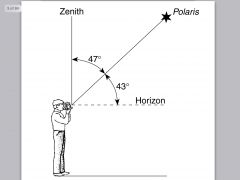
Horizon |
|
|
The degrees measured from North along the horizon is called the |
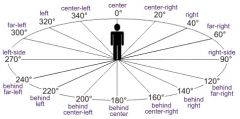
Azimuth |
|
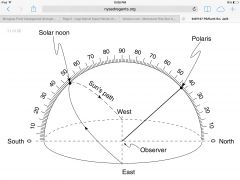
What is the observer's latitude? |
42 since Polaris is at an angle of 42 |

