![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
207 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What problem do refractor telescopes have the reflectors don't? |
chromatic aberration-- tendancy to focus red and blue light differently |
|
|
Why are most large telescopes reflectors, not refractors? (4 reasons) |
1. large lenses deform under their own weight, but mirrors can be supported. 2. large, very clear lenses are harder to cast than more tolerant mirror breaks. 3. reflectors do not suffer from chromatic aberration like refractors do. 4. large mirrors need only one optical surface, achromats 4 surfaces to grind. |
|
|
What is the resolution of a telescope? |
its ability to distinguish 2 adjacent objects close together in the sky. |
|
|
What is the resolving power of the telescope? |
its ability to distinguish 2 adjacent objects close together in the sky. |
|
|
What type of telescope is the Hubble Space Telescope? |
Cassegrain (reflector telescope) |
|
|
A mountain top is an especially good site for infared telescopes since: (4 reasons) |
1. you are above most of the carbon dioxide and water vapor in the atmosphere. 2. closer to celestial objects 3. less air above means better seeing in many cases 4. the cold weather helps the sensitivity of infrared detectors. |
|
|
In astronomy, an interferometer can be used to |
improve the angular resolution of radio telescopes *higher than optical telescopes |
|
|
Which planet by itself contains the majority of mass of all the planets? |
Jupiter |
|
|
What is true about solar system densities? |
The denser planets lie closer to the Sun. |
|
|
The planet's orbital period is |
the time it takes to return to the same location in the sky, relative to the Sun. |
|
|
How do the densities of the jovian and terrestrial planets compare? |
All terrestrials are more dense than any of the jovians. |
|
|
Which of the following are the Jovian planets? |
Juipter, Saturn, Uranus, & Neptune |
|
|
What are the 3 terrestrial planets? |
Mercury, Venus & Mars |
|
|
5 characteristics of Jovian Planets: |
1. all orbit far from the Sun 2. much larger than inner planets 3. no solid surfaces 4. mainly composed of hydrogen & helium 5. low density |
|
|
Modern telescopes |
are all reflectors |
|
|
4 Types of reflecting telescopes |
1. Prime focus 2. Newtonian focus 3. Cassegrain focus 4. Nasmyth/coude focus |
|
|
Main Mirror of Hubble Space telescope (3 types of radiation/light) |
1. visible 2. infrared 3. ultraviolet |
|
|
Brightness is proportional to |
square of radius of mirror |
|
|
Resolving power |
when better, can distinguish objects that are closer together |
|
|
1. Resolution is proportional to 2. Inversely proportional to |
1. wavelength 2. to telescope size |
|
|
Charge-coupled devices (CCDs) |
electronic devices, which can be quickly read out and reset consists of hundreds, thousands, or even millions pixels, usually arranged in square array. --> computer can reconstruct the pattern of light (image) falling on the chip. |
|
|
What happens when light strikes a pixel? |
electronic charge builds up on it |
|
|
Active Optics |
control mirrors based on temperature & orientation |
|
|
Adaptive Optics |
track atmospheric changes with laser adjust mirrors in real time |
|
|
Radio telescopes (3 characteristics) |
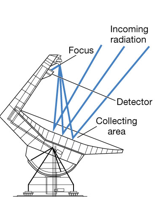
1. similar to optical reflecting telescopes 2. prime focus 3. less sensitive to imperfections-- longer wavelength |
|
|
Largest Radio telescope |
-300-m diameter of dish -Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico |
|
|
1 Disadvantage of Radio Astronomy 3 Advantages |
1. longer wavelength= poor angular resolution
1. observe 24 hours/day clouds 2. weather doesn't interefere 3. different frequency= different info |
|
|
1. Interferometry 2. resolution? 3. *also done with?*
|
1. combines info from several widely spread radio telescopes as from a single dish 2. = to largest separation between dishes-- can be close to optical 3. *can be done with visible light (more difficult b/c of shorter wavelengths* |
|
|
Infrared radiation |
1. can produce image where visible radiation is blocked (b/c of longer wavelength) 2. generally can use optical telescope mirrors & lenses 3. can be used in space |
|
|
Ultraviolet observing must be done __1___ because __2___ |
1. in space 2. the atmosphere absorbs almost all UV rays |
|
|
_______ and ______ will not reflect off mirrors as other wavelength do |
xrays gamma rays |
|
|
Xrays reflect at a ______ and can therefore be focused |
very shallow angle |
|
|
gamma rays ___1___, images are therefore ___2___ |
1. cannot be focused at all 2. coarse |
|

Modern telescopes use mirrors rather than lenses for all of these reasons EXCEPT:
|
E |
|
|
Resolution is improved by using |
larger telescopes shorter wavelengths |
|
|
Diffraction is the tendency of light to |
bend around |
|

An advantage of CCDs over photographic film is: |
E) all of the above. |
|
|
"Good/ poor Seeing" in astronomy is a measurement of |
the image quality due to their air stability. |
|
|
"Adaptive optics" refers to |
reducing atmospheric blurring using computer control |
|

Radio telescopes are useful because |
E) all of the above. |
|

|
A |
|

|
E |
|

|
D |
|
|
Where are most asteroids found? |
between the orbits of Mars & Jupiter |
|
|
The Kuiper Belt is found where in the solar system? |
Beyond the orbit of Neptune |
|
|
What is the difference between a meteoroid & an asteroid? |
the size meteoroids are typically smaller. |
|
|
A meteorite is |
a chunk of a meteoroid or asteroid that comes through the Earth's surface & hits the ground |
|
|
The tail of a comet always points When is it longest & brightest? |
away from the sun at perihelion |
|

|
Marnier 10 is now dead, but still in orbit around Mercury. |
|
|
Average density of a planet formula: |
mass/ volume |
|
|
Which of these bodies has the lowest density? a. Jupiter b. Saturn c. a comet d. Kuiper Belt objects e. an asteroid |
C. a comet |
|
|
The plane in which almost all planets orbit the sun is called the |
ecliptic |
|
|
Mecury's most unusual orbital feature, as compared to the other planets, is |
the shape of its orbit |
|
|
Which of the following is not icy in composition? |
asteroids |
|

|
Kuiper Belt objects |
|
|
Which measurement is the precise measurement of brightness? |
photometry |
|
|
Diffraction is the tendency of light to |
spread/bend around corners |
|
|
What are 2 advantages of large scopes over smaller ones? |
1. more light-gathering power 2. resolving power (better resolution) |
|
|
One advantage of the Hubble Space telescope over ground based ones is that |
in orbit, it can operate close to its diffraction limit at visible wavelengths |
|
|
What are the main consistuents of Venus' atmosphere? (2) |
1. carbon dioxide 2. clouds-- sulfuric acid |
|
|
What is the evidence for active volcanoes on Venus? (2) |
many regions look like lava flows changing chemical composition in the atomosphere |
|
|
Why is Mars red? |
Iron oxide on the surface |
|
|
What is the evidence that water once flowed on Mars? |
dry river beds & runoffs |
|
|
How were the masses of Mars' moons measured? |
Measured by the viking orbits |
|
|
What did the masses of Mars' moons tell us about their origin? |
Thought to be captured asteroids |
|

|
C- Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars |
|
|
The major differences between the terrestrial & jovian planets are: (2) |
1. Jovian planets are more massive 2. Terrestrial planets are more dense |
|

|
E-slower rotation |
|
|
Asteroids are evidence of |
ancient material from the formation of the solar system |
|
|
___, _____, and _____ may have not changed at all since the formation of the solar system |
Asteroids, comets & meteoroids |
|
|
The condensation theory explains why |
terrestrial planets are different from joivan planets |
|

|
B-the direction that planets orbit the sun is opposite to the sun's spin. |
|
|
Early astronomers knew about these 9 things in space |
1. moon 2. stars 3. Mercury 4. Venus 5. Mars 6. Jupiter 7. Saturn 8. comets 9. meteors |
|
|
How many moons does the solar system have? |
166 moons |
|
|
How many asteroids does our solar system have? |
8 asteroids |
|
|
How many extrasolar planets are there? |
400+ |
|
|
All orbits except _______ are close to the same plane |
Mercury's |
|
|
Terrestrial planets (7 characteristics) |
1. small 2. rocky 3. close to sun 4. rotate slowly 5. have weak magnetic fields 6. few moons 7. no rings |
|
|
Jovian planets |
1. large 2. gaseous 3. far from sun 4. rotate quickly 5. strong magnetic fields 6. many moons 7. rings |
|
|
Out of the terrestrial planets, which 2 spin at about the same rate? |
Earth & Mars |
|
|
Out of the terrestrial planets, which 2 have moons? |
Earth & Mars |
|
|
Out of the terrestrial planets, which 2 have magnetic fields? |
Earth & Mercury |
|
|
_____ are icy with some rocky parts |
Comets |
|
|
_______ is the closest Kuiper Belt object to the Sun |
Pluto |
|
|
________ probes landed on Venus from 1970-1978 (Soviet Union) |
Venera |
|
|
The most recent expedition from the U.S. was the _______ orbiter (1990-1994) |
Magellan |
|
|
______ landers arrived at Mars in 1976 |
Viking |
|
|
______ was deployed on Mars in 1997 (small self-propelled vehicle) |
Sojourner |
|
|
Gravitational Slingshots |
can change the direction of spacecraft can also accelerate it |
|
|
The 2 identical spacecrafts that flew through the outer solar system: |
Voyager & Pioneer |
|
|
________ mission arrived at Saturn in 2004. |
Cassini |
|
|
Nebular Contraction |
cloud of gas & dust contracts due to gravity conservation of angular momentum means it spins faster & faster as it contracts |
|
|
Conservation of Angular Momentum |
the product of radius & rotation must be constant |
|
|
How did the solar system form? |
1. Nebular contraction 2. condensation around dust grains 3. larger & larger clumps 4. gravitational attraction takes over & planets form |
|

|
Ultraviolet radiation |
|
|
The principal greenhouse gases in our present atmosphere are (2) |
water vapor carbon dioxide |
|
|
A greenhouse gas lets ______wavelength light pass through, but absorbs ______ wavelength light. |
shorter longer |
|

|
B-the Earth's oceans would be frozen |
|
|
Earth's greenhouse effect makes the planet about ______ degrees C ____ than it would be otherwise |
40 hotter |
|

|
C-Van Allen radiation belts |
|
|
The Earth's magnetosphere |
influences the charged particles of the solar wind. |
|
|
Some particles of the solar wind are channeled toward the poles, creating the _____ |
aurora |
|

|
D-volcanic eruptions |
|
|
Our planets magnetosphere is generated by the Earth's ______ and its ______ |
rotation liquid metal core |
|

|
E- Both new & full moon |
|

|
About 5 times denser, like Mercury & Venus |
|

|
C |
|
|
Without the greenhouse effect operating in our atmosphere, |
Earth would have an average temperature of -23 degrees C |
|
|
What gas is the primary constituent of our atmosphere? |
Nitrogen |
|

|
Oxygen |
|

|
Ozone layer |
|

|
troposphere |
|
|
What is the hole in the ozone layer thought to be caused by? |
CFCs |
|
|
Within Earth's atmosphere, the ozone layer is located |
in the stratosphere |
|
|
Why is the sky blue? |
the atmosphere scatters the light from the Sun. |
|

|
A |
|

|
A |
|
|
The oldest rocks on our crust are radioactively dated at about |
4 billion years old |
|
|
The region around Earth where the magnetic field traps charged particles is the |
Van Allen Radiation Belts |
|
|
At what phase are the tides least noticeable? |
third quarter |
|
|
Why can't Mercury usually be seen from Earth? |
always very close to the Sun |
|

|
Neither body has a permanent atmosphere |
|

|
rotation rate |
|
|
The lunar mare are radioactively dated at |
3.9-3.2 billion years old formed after most of the bombardment was over |
|
|
The youngest features visible with telescopes on the Moon are |
the craters sitting atop the mare. |
|

What causes Mercury's 3:2 spin-orbit resonance? |
All of the above |
|

Which is true of the Moon's orbital & rotational periods? |
C-They are equal |
|

The rate of cratering in the lunar highlands shows us that |
B |
|
|
What type of feature is the best evidence of lunar volcanism? |
rilles associated with lava flows accompanying the mare foundation |
|
|
Mercury's surface most resembles that of which other body? |
Moon |
|
|
The scarps on Mercury were probably caused by |
the interior cooling & shrinking |
|
|
What do moonquakes reveal about the moon? |
Its small, partially molten core has been pulled toward us by tidal forces |
|
|
What are the main (2) factors that rule out the co-formulation theory for the Moon-Earth system? |
Each body has a different density & different chemical composition |
|
|
The cratering of the lunar highlands shows us |
they are older than the smoother maria |
|
|
Comparing the densities of the Moon & Mercury, we find |
the moon is similar to earth's crust, while Mercury's is similar to the entire Earth |
|
|
Convection |
occurs whenever cool matter over lies warm matter. depends on warming of ground by the Sun |
|
|
Ionosphere |
-ionized by solar radiation & a good conductor -reflects radio waves in the AM range, but is transparent to FM & TV |
|
|
Ozone Layer |
between ionosphere & mesosphere absorbs UV radiation |
|
|
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) _____ is located over ______ |
have been damaging the ozone layer = ozone hole Hole, over the Antarctic |
|
|
Sunlight that is not reflected is _____________ |
absorbed by Earth's surface= warming it |
|
|
Surface re-radiates as ____________ |
infrared thermal radiation |
|
|
Greenhouse Effect |
sunlight that is not reflected by clouds reaches Earth's surface & warms it up. |
|
|
What color light it scattered most strongly, and why? |
Blue because the wavelength is closer to the size of air molecules |
|
|
Amount of molecular scattering is proportional to the inverse of the ______ |
fourth power of the wavelength of the light |
|
|
Why is the sky sometimes red? |
more dust is in the sky, which creates more light scattering = less blue in the sky. |
|
|
Earth's Primary Atmosphere |
hydrogen, helium escaped Earth's gravity |
|
|
Earth's Secondary Atmosphere |
from volcanic avtivity mostly nitrogen |
|
|
Life appeared, creating ___________ |
atmospheric oxygen |
|
|
5 possible consequences of global warming |
1. rise in sea level 2. more severe weather 3. crop failures 4. expansion of deserts 5. spread of tropical diseases (away from tropics) |
|
|
Earthquakes produce both _______ and _____ waves. |
pressure shear |
|
|
1. Pressure waves are 2. Where are they seen in relation to the Earthquake? |
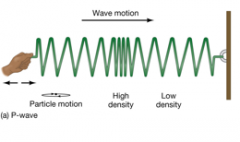
1. longitudinal & will travel through both liquids & solids 2. to the opposite side of Earthquake |
|
|
1. Shear waves are 2. Where are they seen in relation to the Earthquake? |
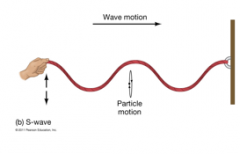
1. transverse & will not travel through liquid, as liquids do not resist shear forces. 2. do not reach opposite side |
|
|
Wave speed depends on ______ |
the density of the material |
|
|
We can use the pattern of reflections during Earthquakes to ____________ |
deduce the interior structure of the Earth. |
|
|
Inner Core of Earth is about _____ km in diameter. |
2600 km |
|
|
Liquid inner core is about _____ km across |
7000 km |
|
|
Mantle: 1. much less dense than _____ 2. is _____ |
1. core 2. rocky |
|
|
Core: 1. is _____ (_____ and _______) 2. outer is _____ 3. inner is ______-- why are they different? |
1. metallic (iron & nickel) 2. liquid 3. solid--due to pressure |
|
|
Where does volcanic lava come from? What does it allow for? |
Mantle analysis of composition |
|
|
Earth was probably __1____ when formed & melted due to bombardment by __2__ 3. Heavier materials sank where? |
1. molten 2. space debris 3. to the center |
|
|
Radioactive Decay Formula (remaining material= ) |
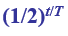
t= time T= half-life |
|
|
Uranium-238's half-life |
4.5 billion years |
|
|
The dating process involves measuring the ratio between the _____ _______ and the ______ ________ |
parent nucleus daughter nucleus |
|
|
Continental drift |
Earth's surface is covered with crustal plates, which can move independently. |
|
|
At plate boundaries, 2 things occur |
earthquakes volcanoes |
|
|
Subduction zone |
where one plate slide below another |
|
|
1. A plate colliding with another can also raise it, resulting in ________ 2. Plates can also slide along each other, creating _____, where _____ occur 3. Plates can move away from each other, creating |
1. very high mountains 2. faults, many Earthquakes 3. rifts |
|
|
Field reversals |
occur about every 500,000 years |
|
|
What drives plate motion? |
convection in the Earth's upper mantle (probably) |
|
|
Magnetosphere |
the region around the Earth where charged particles from the solar wind are trapped |
|
|
Magnetopause |
the boundary of the magnetosphere in the sunward direction |
|
|
Van Allen belts |
where charged particles are trapped in areas they spiral around the magnetic field lines |
|
|
Aurorae lights |
when the charged particles escape from the Van Allen Belts |
|
|
Tides are due to the ______ |
gravitational force on Earth from Moon |
|
|
Tides are biggest in which 2 moon phases? why? |
Full & New because the Sun, Moon & Earth are aligned, and the tidal buldges reinforce one another. |
|
|
Tides are smallest in which 2 moon phases? why? |
First & Third-quarter the buldges partially cancel each other out (Moon is closer, therefore stronger than Sun's influence) |
|

why? |
A having no permanent atmosphere contributes to the craters. |
|

|
B |
|

|
E |
|

|
E |
|
|
What force rivets the Moon's near-side to constantly face Earth? |
Earth's tidal force |
|

Which statement about the rotations of Mercury & the Moon is FALSE? |
C |
|
|
Where are Lunar Maria found? why? |
mostly on the side facing the Earth because that side has a thinner crust, and is also less cratered. |
|

The moon's internal structure is similar to Earth's, but the moon lacks |
D |
|

Today, which of these theories best explains the Moon's origin? |
B |
|
|
Distance between Earth & Moon has been measured to accuracy of a few centimeters using _____ |
lasers |
|
|
When can phases of Mercury be seen best? |
when at its maximum elongation |
|
|
maximum elongation |
at greatest distance from the Sun |
|
|
Marks on the Moon: 1. Maria (large, dark, flat areas) are from 2. craters are from |
1. lava flow 2. meteorite impacts |
|
|
Far side of the moon has ___(craters) and ____(maria) |
some no |
|
|
Mercury was long thought to be tidally locked to ____, but measurements in 1965 proved this false. |
the Sun |
|
|
Mercury's ratio of day to a year |
3:2 -rotates 3 times, while going around the Sun twice. |
|
|
Who had first contact with the Moon? |
Soviets |
|
|
When does escape become more probable (3)? |
1. for lighter molecules 2. higher temperatures 3. smaller planets (escape speed is less) |
|
|
4 stages in the formation of a crater by meteoroid impact |
1. meteoroid strikes Moon 2. ejects material 3. explosion ejects more material 4. leaving crater |
|
|
How much bigger is the crater usually than what created them? |
10 times wider twice as deep |
|
|
Most lunar craters date to at least ____ years ago |
3.9 billion |
|
|
Regolith |
thick layer of dust left by meteorite impacts depth of roughly 20 m |
|
|
Barringer Crater |
near Windlow, Arizona 1.2 km in diameter, 0.2 km deep--meteoroid was probably 50 m across, and weighed 200,000 tons thought to be about 25,000 years old |
|
|
scarp |
cliff, several hundred kilometers long & up to 3 km high thought to have been formed when the planet's crust cooled & shrank seen on Mercury |
|
|
Caloris Basin |
very large impact feature on opposite side of Mercury--most prominent geological feature about 1400 km across--spans more than half of Mercury's radius ringed by concentric mountain |
|
|
"Weird terrain" (on Mercury) is thought to result from focusing of _____ |
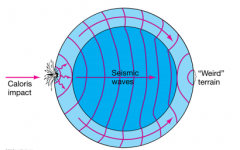
seismic waves |
|
|
Moon's density is relatively _____ and has ____ magnetic field Crust is _____ than Earth's |
low, no much thicker |
|
|
3 Parts of the moons center |
1/ Lithosphere 2. Inner mantle/Lunar Asthenosphere 3. core--may be partially molten |
|
|
Mercury is ______ than the Moon and has a weak ____ |
much denser magnetic field |
|
|
Current theory of Moon's orgin (3 steps) |
1. glancing impact of Mars-sized body on the still liquid Earth 2. enough material--mostly from mantle, to be ejected 3. formed the Moon |
|
|
Timeline |

|

