![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Definition |
chronic inflammatory disorder of airways |
|
|
|
Asthma associated with..? |
airway hyperresponsiveness wheezing 🐦 breathlessness🤐 chest tightness coughing🤧 |
|
|
|
Patient came with Recurrent wheezing ,cough at night ,after exercise and after exposure to allergens or pollutants . After that he came with Colds which take more than 10 days to clear What’s your diagnosis |
Asthma |
|
|
|
What will u see in asthmatic airway??? |
Smooth muscle dysfunction Inflam (edema/mucus) Remodel |
|
|
|
What are the airway structural cells |
epithelial cells Smooth muscle cells Endothelial cells Fibroblasts Airway nerves |
|
|
|
Cell that sense mechanical environment |
epithelial cells |
|
|
|
Rule of fibroblast |
Airway remodel |
|
|
|
Cell that release inflam protein |
Smooth muscle cells |
|
|
|
Cell that recruits inflammatory cells |
Endothelial cells |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic action |
Brochioconstrictor Smooth muscle contaction Mucus secretion
|
|
|
|
Ipratropium is anticholinergic What’s its action ?? |
bronchodilatation decreased secretions |
|
|
|
Sympathetic action ? |
relaxation of airway smooth muscles |
|
|
|
Salbutamol is β 2 adrenergic agonists What is the action ?? |
Brochiodilator
For asthma |
|
|
|
Mediator of |
Symp—— cateocholamine Parasymp—-Ach Non—-NO |
|
|
|
Action of Non adrenergic Non Cholinergic inhibitory system. |
run in the vagal trunk , but cause bronchial smooth muscle to relax.🤷🏻♂️🤷🏻♂️ |
|
|
|
What are the inflam cell in asthma |
• Mast Cells • Eosinophills • T lymphocytes • Dendritic cells • Macrophages • Neutrophils |
|
|
|
Cell prod brochioconstrictor subs like —(histamine,leukotrien,prosta) |
Mast cell |
|
|
|
Cell that release proteins that damage airway cells |
Eosinophils |
|
|
|
Brochconstrictor mediator |
Leukotrien Histamine Prostaglandin |
|
|
|
What occurs in early phase of asthma |
Allergen stimulate Mast cell to release histamin/ prosta/leukotrien Which lead to brochioconstrictor and infiltration of inflam cell |
|
|
|
What occurs in late phase of asthma |
Airways inflam cause edema and tissue injury |
|
|
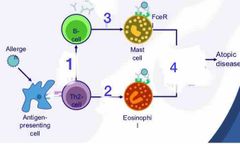
What’s (1,2,3,4) |
1) IL4,13 2) IL5 3) IgE 4) histamine,leukotrien, prosta |
|
|
|
How airway resistance increase in asthma |
IgE mediate release of IL5 ,IL-b4 which bind to eosinophil to release Leukotrien ,MBP ,ROS ** The results in....... 1) ⬆️ airway inflam —damage airway epith— stop cillia function — +sensory nerve—narrow airway 2) ⬆️ edema —airway narrow |
|
|
|
Complication of increase airway resistance |
⬆️ WOB—- fatigue V/Q mismatch Hypoxia |
|
|
|
Complication of increase airway resistance |
⬆️ WOB—- fatigue V/Q mismatch Hypoxia |
|
|
|
Both O2 and CO2 will decrease in case of ..... but CO2 is high in case of ...... |
Hypoxia V/Q mismatch (cyanosis) |
|
|
|
Asthma started with hypoxia and hypocarbia If uncontrolled,CO2 amount will increase. Why??? |
accessory muscle get tired 😓 because of less O2 So ventilation will decrease and CO2 will build in body |
Acidosis cause increase of bicarbonate ( compensation) |
|
|
What will U give in sever asthma symptoms?? |
O2 Salbutamol Ipratropium Hydrocortisone Mg sulphate (IV) |
|
|
|
What will U give in sever asthma symptoms?? |
O2 Salbutamol Ipratropium Steroids Mg sulphate (IV) |
|
|
|
Complication of asthma |
Resp failure Acidosis Pneumothorax Lung collapse |
|
|
|
Complications of COPD |
Pulmonary hypertension Resp failure Pneumothorax |
|
|
|
Complications of COPD |
Pulmonary hypertension Resp failure Pneumothorax |
|
|
|
Type of resp failure |
Type 1–hypoxemic (pneumonia) Type 2–hypoxia /hypercapnia (COPD) |
|
|
|
Complications of COPD |
Pulmonary hypertension Resp failure Pneumothorax |
Resp failure who PaO2<60 |

