![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
291 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lecture 1 |
2/8/2016 - Monday |
|
|
What are the 3 parts of a basic cardiac exam? |
Inspection Palpation Auscultation |
|
|
What do you do during inspection? |
Give a general visual survey and look for RIJ distention to see if there is JVD. |
|
|
What is the purpose of looking for Jugular vein distention? |
For pts with a hx of heart failure, you want to make sure they are optimized, which means that they do not have too much fluid. |
|
|
How often do we do palpation? How do we do it, and what are we looking for? |
Rarely If you've got extra time and you suspect that a pt has really bad CAD. Locate the point of maximum impulse at the left 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line. |
|
|
How do we do auscultation? |
On the skin! Skin to diaphragm. |
|
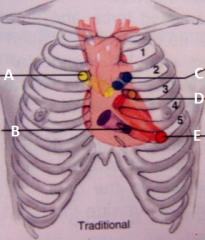
Names these auscultation sites. |
A- Aortic B- Tricuspid C- Pulmonic D- Erb's point E- Mitral area |
|
|
What is CO? |
Amount of blood that is being ejected in 1 min SV x HR |
|
|
How much CO is due to atrial kick? |
20-30% |
|
|
What is EF? |
EDV-ESV/EDV SV/EDV |
|
|
If you have a very low EF, what anesthetic are you expecting to use? |
Hand holding, regional, etomidate |
|
|
What is our goal with supply and demand of the heart? |
Increase supply and decrease demand |
|
|
What contributes to demand? |
HR Preload Afterload Contractility |
|
|
What contributes to Supply? |
Coronary artery Anatomy Diastolic pressure Diastolic time O2 extraction Hb SaO2 |
|
|
If your heart rate is up, what does it mean for the diastolic time? |
It is shorter |
|
|
What is the common factor between supply and demand? |
HR |
|
|
How to treat tachycardia in the OR? |
Fluids Beta blockers Pain medications |
|
|
What have the most impact on O2 supply and demand? |
HR and Pressure work. |
|
|
What are the concerns when it comes to the conducting system? |
heart blocks Use epi if you need to |
|
|
What does the ventricular filling pressure refer to? |
How much filling pressure will result in what amount of CO |
|
|
What are examples of filling pressures? |
LAP PCWP |
|
|
What are examples of the ventricular output? |
CO SV |
|
|
Increase in afterload does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
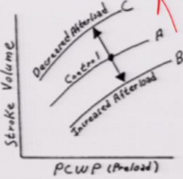
It goes down Dopamine Levophed |
|
|
Decrease in afterload does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
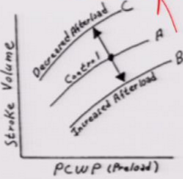
Goes up Anti-hypertensive Nipride Nitroglycerine |
|
|
Decrease in preload does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
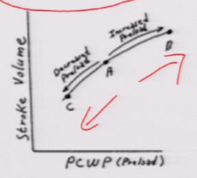
Goes to the left Lasix |
|
|
Increase in preload does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
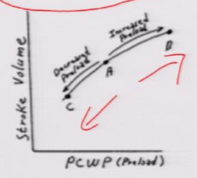
Goes to the right |
|
|
Increase in contractility does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
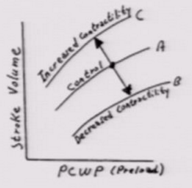
Goes up Milrinone Dobutamine |
|
|
Decrease in preload does what to the ventricular fill pressure curve? |
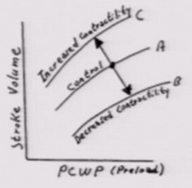
Goes down |
|
|
What are the easiest cardiac surgeries you can do? |
On pump cardiac surgeries. |
|
|
What makes off pump so hard? |
Every time the MD touches the heart the BP goes down. |
|
|
What's a great gas for an open heart surgery and why? |
Civoflurane Easy and quick to adjust |
|
|
What are the common cardiac reflexes that you will encounter in the OR? |
Baroreceptor Valsalva Cushing Chemoreceptor Bainbridge Oculocardiac Celiac Bezolh-Jarish |
|
|
Baroreceptor |
Located in the aortic arch and the carotid bodies Activated by HTN -Afferent X from Aorta & IX(Herring) from the Carotid sinus to the Medulla -Efferent X increases the action potentials and drop the BP |
|
|
Valsalva Maneuver |
It effects baroreceptors and thus CN IX and X Done via force expiration against the closed glottis Inhibits SNS and Stimulates the PNS (Decreases HR) |
|
|
How do you do a valsalva maneuver in the OR? |
Take the pt off the vent and close the APL valve all the way and then blow up the ballon to 5-6 L and put positive pressure in to increase intrathoracic pressure. This is to make sure they weren't leaking. |
|
|
Cushing reflex |
Physiologic response to CNS ischemia caused by increased ICP. Increased BP with wide pulse pressure(early) Bradycardia Respiratory instability |
|
|
When can cushing happen in the OR? |
Pt on plavix and bleeding and occluding. You will have this issue. |
|
|
Bainbridge |
Done via the R atrial stretch Afferent is vagus to the medulla, which sends a decrease in parasympathetic efferent firing. This increases the HR and the BP |
|
|
Oculocardiac reflex |
5 and dime reflex. It's in the eye. When you tug or put pressure on the eye(V1-opthalmic), or sphenoidal approach to brain sx your HR(20s) and BP drops. Treat by stop what you are doing or you can pre-medicate with robinol. |
|
|
Celiac |
Causes bradycardia and hypotension(apnea will not be seen due to vent) from the insufflation of the abdomen from laprascopic surgeries or the surgeon is tugging on pt abdomena and the pt is light. Premedicate with robinol. You want the 15 mm Hg or less for insufflation to also allow for ventilation. |
|
|
Chemoreceptor |
Triggered by high (acidotic)pCO2 or low (< 50-60)pO2. Improve ventilation to normalize it. Problem would occur if pt was septic coming in. |
|
|
Hyperventilation |
Lowers pCO2, but increases oxygenation |
|
|
How do you increase your FiO2? |
Turn off air and nitrous. |
|
|
Bezold - Jarisch Reflex |
Protective and inhibitory reflex Stimulates the LV via chemoreceptor or mechanoreceptors or Zofran. Causes Hypotension, bradycardia, and coronary dilation Good for pt with CAD. |
|
|
How does bradycardia help the heart? |
Increased time for oxygen exchange and decreases demand for O2. |
|
|
What are some preop eval? |
EKG and monitoring. |
|
|
What are the two types of EKG in the OR? |
3 lead and 5 lead |
|
|
What lead do we typically look at? |
Lead II because it has the best visibility of the P wave. If you have a 5 lead, then you can change the view to the 5th lead. |
|
|
What's the pre-op assessment for cardiac? |
Assess EKG, pulse ox Review recent events Check electrolytes |
|
|
What's the important about reviewing recent events? |
It's that we can see if they have stents and when they were placed. |
|
|
Why is it called bi polar leads? How many are there? |
Need both sides to connect to give reading. 3 |
|
|
How many augmented Unipolar limb leads? |
3 aVL - Left arm aVR - Right arm aVF - Left leg |
|
|
What are the precordial leads? |
The remaining 6 leads to the 12 lead EKG |
|
|
How can you tell if a pt has an old MI? |
The Q wave is 1/3 the depth of the R wave. |
|
|
What leads should you look at for inferior MI of the heart? |
Leads II, III, and aVF MI: Q, ST elevation, and T wave elevation Looks at the Right Coronary Artery -SA node and a possibility for bradycardia |
|
|
What leads should you look at for anterior MI of the heart? |
Leads: I, aVL, V1-V4 MI: Q, ST elevation, and T wave elevation Looks at the left anterior descending artery |
|
|
What leads should you look at for Posterior MI of the heart? |
Leads: V1-V2 MI: R wave elevation, ST depression, and T wave depression Looks at the left circumflex |
|
|
What leads should you look at for Lateral MI of the heart? |
Leads: I, aVL, V5-V6 MI: Q, ST elevation, and T wave elevation Looks at the left circumflex |
|
|
What leads should you look at for antereoseptal MI of the heart? |
Leads: V1-V4 MI:Q, ST elevation, and T wave elevation Looks at the left anterior descending |
|
|
If we were to check for the a-line, then what would we need to do? |
The allen's test Occlude ulnar and radial artery, release ulnar artery to see if there is collateral circulation. |
|
|
Phlebostatic axis |
reference to zero homedynamic monitoring devices. |
|
|
What can effect BP? |
Position More for the NIBP not the direct arterial line. |
|
|
So if I was up 20 cm from the zero point, how would my NIBP change? |
15 mm Hg lower htan what it is. |
|
|
Distal Pulse amplification |
It is higher the further away you take it from the center. |
|
|
Aortic stenosis has what two wave forms? |
Pulsus parvus (narrow pulse pressure) Pulsus tardus (delayed upstroke) |
|
|
What kind of waveform does aortic regurgitation have? |
Bisferiens pulse (double peak) |
|
|
Cardiac tamponade |
Pulsus paradoxus (exaggerated decreased in systolic BP during spontaneus inspiration) |
|
|
Systolic Left Ventricular failure |
Pulsus alternans (alternating pulse pressure amplitude) |
|
|
Can you stick a non-collapsible structure? |
Nope, that's an artery |
|
|
What does CVP monitor? |
Fluid status |
|
|
What's the easier side to hit for a CVP line? What position makes it easier for the placement of the CVP? |
The left side is easier. Trendelenburg |
|
|
What is the most likely problem that can occur with placing a CVP? |
Pneumothorax |
|
|
Are PA catheters used often? |
Nope, only when the pt is really really sick |
|
|
What is a complication of PA catheter? |
Pulmonary rupture with symptoms of coughing blood |
|
|
Where do you wedge for a PA? |
Zone 3 |
|
|
Milrinone |
increases contractility |
|
|
Nipride |
Vasodilator decrease SVR |
|
|
Lasix |
Lower preload |
|
|
Digitalis |
increase contractility |
|
|
Nitroglycerin |
vasodilator decrease SVR |
|
|
Neo |
Increases BP and SVR |
|
|
Lecture 2 |
2/12/2016 - Friday |
|
|
What is an epidural needle size? |
19 G |
|
|
What are the 5 things we need to take into consideration for the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association? |
1) Consider Urgency 2)Consider Active Cardiac Condition 3) Consider risks of the surgical procedure 4) Assess the pt's functionality 5) Consider pts w/ poor or indeterminate functional capacity scheduled for vascular, intermediate, or high procedure risks. |
|
|
What's the first step? |
See if the surgery is emergent. If it is, we need to continue with the surgery, get a 12 lead EKG, all labs associated with cornary artery disease, and anti-arrhythmic drugs and monitor the pt |
|
|
What are emergency cases? |
Appendectomy, accidents, bowel perforation |
|
|
What can you get your monitor to look at for the heart? |
ST changes, BP |
|
|
What can hypotension do? |
Decreased blood supply to the coronary arteries, which can cause an MI. |
|
|
Now let's say that the surgery is not an emergency, what do you do next? |
Check the pt's active cardiac conditions |
|
|
What are some active cardiac conditions that we need to look at? |
Unstable coronary syndrome Decompensated Heart failure Significant arrhythmia Severe valvular disease |
|
|
What do we need to look at for unstable coronary syndrome? |
Acute MI and Recent MI |
|
|
Acute MI What surgery gets cancelled? |
Occuring within the past 7 days, elective surgery is postponed Elective surgery |
|
|
Recent MI |
Within 30 days(longer than 7 days) w/ myocardium at risk (+stress test and persistent symptoms) |
|
|
How do you know thre is myocardium at risk? |
+ stress test Cath without stents |
|
|
What should you look at for decompensated heart failure? |
If it is NY heart association class IV: Any physical activity that brings discomfort and symptoms occur at rest. |
|
|
What's happens to heart failure pts that bring them back to the ICU? |
Non-compliance |
|
|
Do we classify heart failure? |
No, we look at the history from the cardiac consult to see what it is. |
|
|
What do we look for in the significant arrhythmias? |
Mobitz II 3rd degree heart block SVT or A-fib with rapid ventricular rate or new onset Symptomatic ventricular arrhythmia or bradycardia New ventricular tachycardia |
|
|
What's an okay rate for A-fib to run at? |
70-80 bpm |
|
|
If we go from the ICU to surgery, what kind of surgery is that? |
Emergency surgery, so it fulfills the first question. |
|
|
What's vital sign is super important to watch for MI? |
BP |
|
|
What do you look at for severe valvular diseases? |
Severe Aortic Stenosis Severe Mitral Stenosis |
|
|
What should you consider especially for aortic stenosis when it comes to anesthesia? |
Spinal anesthesia |
|
|
What age population tend to have knee and hip surgery? |
Older people |
|
|
What is the best anesthesia for older pts? |
Regional anesthesia |
|
|
So, if the pts have any of these cardiac conditions, what do we want to check? |
We want to check if the pt has had treatments, and if the treatments are working |
|
|
If they don't pass this stage, what's the next thing that we look at? |
Step 3: Is it a low risk surgery? |
|
|
What are low risk surgeries? |
Endoscopic procedures Breast Cataract |
|
|
What are intermediate risks? |
Ortho Head and neck Prostate |
|
|
What are High risk surgeries? |
Aortic Vascular Intraperitoneal Intrathoracic |
|
|
Can pt still have an MI in a low risk surgery? |
Yes |
|
|
What should you use for a low EF? |
etomidate |
|
|
So, if the surgery is not low risk, what do we move on to? |
Step: What is functional capacity? We want at least 4 METs, then we can proceed with surgery. |
|
|
What is a MET? |
Metabolic equivalent of the task Functional capacity or exercise capacity. O2 consumption in a resting state is 3.5 mL/kg/min or 1 MET |
|
|
What is 4 METs? |
can go to the mailbox without SOB Can you go to the 2nd floor in your house w/o SOB |
|
|
How do you ask pt if they ate? |
Ask how was their breakfast this morning? |
|
|
So, what if they have crappy cardiac functionality? |
You look at the clinical risk factors |
|
|
What are the clinical risk factors |
Lee Revised Cardiac risk index (Modified Goldman Index) |
|
|
What do you do for 0 clinical risk factors? |
Proceed with surgery |
|
|
What do you do for 1-2 clinical risk factors? |
Make sure there is heart rate control, but you can proceed with intermediate risk and vascular surgery. |
|
|
What do you do for 3 or more clinical factors? |
Intermediate risk surgery: proceed, but have heart rate control Vascular surgery: Do further stress tests and echo to determine if the treatment is working. |
|
|
What do you you want if you're gonna watch your pt like a hawk? |
Get an A-line |
|
|
What do we look for in the Modified Goldman Index? (There are 6) |
What type to surgical procedures. Hx of ischemic heart disease Hx of congestive heart failure Hx of cerebrovascular disease Pre-op tx w/ insulin Pre-op serum creatinine > 2.0 mg/dL |
|
|
What kind of procedures do we count? |
High risk procedures: Intraperitoneal, intrathoracic, and suprainguinal |
|
|
What kind of ischemic heart hx would we count? |
hx of MI kx of positive exercise test Current complain of chest pain, secondary to myocardial ischemia Use of nitrate therapy ECG w/ pathological Q waves |
|
|
What kind of congestive heart failure hx would we count? |
hx of CHF Pulmonry edema Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Bilateral rales or S3 gallop Chest radiograph show pulmonary vascular redistribution |
|
|
What kind of cerebrovascular hx would we count? |
hx of TIA or CVA |
|
|
What kind of DM hx would we count? |
needed pre-op tx with insulin |
|
|
What kind of renal hx would we count? |
Preop serum creatinine > 2.0 mg/dL |
|
|
What is the risk for major cardiac complications for all the scores? |
0 = 0.4% 1 = 0.9% 2 = 6.6% 3 or more = 11% |
|
|
Is 11% high? |
It is if it happens to your pt |
|
|
What does cardiology do after we send pts to them for re-evaluation? |
They try 3 therapeutic options: 1) Revascularize by sx 2) Revascularize by PCI w/ or w/o stents 3) Optimal medical management |
|
|
What is PCI? |
Percutaneous intervention |
|
|
What is uncontrolled HTN? |
2 or more readings >140/90 |
|
|
At what BP should elective sx be delayed? |
Severe HTN DBP >115 mmHg SBP >200 mmHg |
|
|
Do you just d/c sx after 1 reading? |
NOOOO!!! Do supportive therapy. Try to give versed and reposition pt and try to calm them. |
|
|
What is the preop evaluation that we should do for HTN? |
Determine adequacy of BP control Review pharm of drugs being admin to control BP Eval for evidence of end-organ dps Continue drugs used for control of BP |
|
|
How do we determine the adequacy of BP control? |
Ask if they take their BP med regularly |
|
|
How many changes can occur in the OR with HTN? |
Alot, so be very vigilant in what you are doing. |
|
|
What can we expect from the pt intraoperatively even if they have HTN preop? |
Hypotension from the gas, opioids, and propofol |
|
|
If they usually have high BP, what should you do with BP intraoperatively? |
You want to keep it up.
|
|
|
What is permissive hypotension? |
Lower BP on purpose to decrease bleeding in shoulder surgeries and head surgeries. |
|
|
So, what if you gave all your meds and the pt is still hypertensive? |
HTN medication |
|
|
What does the BP do in pts, who have HTN? |
The BP fluctuates in the OR |
|
|
When you do an intervention, what should you do? |
Only do one intervention at a time, so you know if it works. |
|
|
At induction what are you giving? |
Propofol Fentanyl Rocuronium Sevo at 1 MAC |
|
|
When BP is dropping after the induction, what should you do? |
Lower gas to 0.8% MAC |
|
|
What do you give during incision? |
Give fentanyl to prevent a hike in the BP |
|
|
If the pt takes an ACE inhibitor the day of sx, what are you expecting? |
You'll be chasing that BP |
|
|
What BP med do you want them to take? |
Beta blockers |
|
|
What are exaggerated drops in BP usually from? |
blood loss, positive pressure ventilation, and changes in body position |
|
|
In what position will BP go down? |
Reverse trendelenburg |
|
|
In what surgeries do MDs use reverse trendelenburg? |
Breast augmentation, laprascopic sx, chest sx |
|
|
What is a good anesthesia adjunct to hypotension? |
vasopressors |
|
|
What are you evaluating for in end organ dps? |
If you can improve the end organ damage before sx, then do it before an elective sx. Still consider the urgency of the surgery. |
|
|
What should you consider for HTN pts during induction and maintenance of anesthesia? |
Anticipate exaggerated BP response to anesthetic drugs Limit duration of direct laryngoscopy Admin a balanced anesthetic to blunt HTN responses Consider placement of invasive cardiac monitoring Monitor for myocardial ischemia |
|
|
How do we induce the pt? |
use propofol or etomidate Since we will take more time, think about fentanyl to blunt the SNS for DL. |
|
|
If the pt took an ACE of ARB, what can you expect during induction? |
hypotension |
|
|
How can you prevent the hypotension? |
Load them with fluids, and if it doesn't work then use the vasopressors. |
|
|
What can DL cause cardiac-wise? |
Significant HTN and tachycardia |
|
|
How do we avoid tachycardia and hypotension? |
deepen anesthesia with more gas |
|
|
What order of meds did he list for induction? |
lidocaine propofol fentanyl(check corneal reflex and make sure you can ventilate) Rocuronium Can turn on gas while ventilating, but make sure you have a good seal. |
|
|
What med is too much for induction? |
Beta blocker This is only if the pt is really really HTN. Use short-acting esmolol. |
|
|
What's the time limit on DL, if we want to minimize BP changes? |
15 seconds |
|
|
What's our goal with BP in the OR? |
minimize fluctuations in BP |
|
|
What kind of anesthesia minimizes blood loss? |
Regional anesthesia because of decrease in BP and can unmask unsuspected hypovolemia |
|
|
What surgery can we not do with regional anesthesia? |
Craniotomy, too high |
|
|
What does light anesthesia do intraoperatively for the HTN pt? |
Pt has HTN |
|
|
What do we want to do for this pt and they are starting to wake up? |
turn gas up, remove from the vent and manually ventilating the pt. If this does not work, then use propofol. Place pt back on the vent once they are asleep |
|
|
When do pts usually get light? |
This is usually at the end of the surgery. |
|
|
If you think a pt will move during a painful surgery like planting seed around the prostate, what shoudl you do? |
Run high gas |
|
|
What is the least soluble gas? |
Des |
|
|
How do we typically admin antihypertensive meds? |
Bolus |
|
|
What neuromuscular blocker do we see an increase BP? Where do we see it? |
Pacuronium Coronary artery bypass and grafting because it is long acting and helps with BP during induction. |
|
|
How do we treat intraoperative hypotension? |
drop depth of anesthesia or increase intravascular volume Admin pressurs |
|
|
Lecture 3 |
2/15/2016 - Monday |
|
|
Pts on which drugs will have a tendency to become hypotensive in the OR? |
ACE inhibitors ARBs |
|
|
How do you solve hypotension with the pt on ACE inhibitors or ARBs? |
You need to prehydrate the pt with crystalloid solutions. This really helps to avoid the use of neo, ephedrine, and vasopressin. During surgery keep your IV open. |
|
|
What sympathomimetics could you possibly use with pts taking ACE inhibitors? What will you probably end up using? |
Ephedrine and neo Vasopressin |
|
|
What rhythms will get rid of your atrial kick? |
Junctional rhythms and afib |
|
|
How much does the loss of atrial kick do to CO? |
drops it by 20% |
|
|
What med can you use to treat a fib? |
Cardizem |
|
|
What should you expect from a hypertensive pt post-operatively? |
HTN Especially if they are hypertensive initially |
|
|
What can HTN be secondary to? |
Pain |
|
|
What is a good long term opioid? |
Dilaudid |
|
|
What should you tell the PACU nurse when you are giving off report? |
Meds that the pt is taking The meds I gave in the OR (opioids) Make sure you have post-op orders. |
|
|
What can happen if you don't treat HTN post-op? |
Myocardial ischemia, cardiac dysrhythmias, CHF, stroke, and bleeding. |
|
|
What's the drug most used for post-op HTN? |
Labetalol/trandate |
|
|
Where should you leave your gas at? |
1 MAC |
|
|
What does neo cause? |
Bradycardia |
|
|
What is the problem that all valvular diseases tend to have? |
CHF, which can lead to sudden death |
|
|
What are the two valvular condition that can cause pressure overload? |
Mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis |
|
|
What are thetwo valvular condition that can cause volume overload? |
Mitral regurgitation and aortic regurgitation |
|
|
What do we need to deteremine pre-op about valvular diseases? |
the severity of the disease degree of impair myocardial contractility Presence of associated major organ system disease. |
|
|
What do we look at to determine the severity of the valvular disease? |
ECHO and the history |
|
|
Will there be organ damage with valvular diseases? |
Yes |
|
|
What things do you look at in the chart on these valvular disease pts? |
Exercise tolerance test? |
|
|
What is class I? |
Asymptomatic |
|
|
What is class II? |
Symptoms with ordinary activity but comfortable at rest |
|
|
What is class III? |
Symptoms with minimal activity but comfortable at rest |
|
|
What is class IV? |
Symptoms at rest |
|
|
What do you hear with a pt with heart failure? |
S3 gallop |
|
|
What happens to surgery? |
Elective surgery can be delayed until the CHF is treated |
|
|
How can a pt have angina without CAD? |
This can occur because the walls of the heart are too thick and squeeze down on the arteries. |
|
|
What rhythm is very common with those pts that have valvular diseases? |
A fib |
|
|
Where does bacterial endocarditis come from? |
Infective thrombus from pacer wire, catheter |
|
|
Which valve is most likely to have bacterial endocarditis? |
MV because it is in an O2 rich environment |
|
|
Which valve is least likely to have bacterial endocarditis? |
PV |
|
|
Which cardiac conditions are the most likely to have adverse outcomes from endocarditis? |
Prosthetic cardiac valve Previous infective endocarditis Congential Heart disease Cardiac transplantation recipients |
|
|
Which procedures do you need the endocarditis prophylaxis for? |
Dental procedures Invasive procedures involving respiratory tract, infected skin, skin structures, or musculoskeletal tissue |
|
|
Which procedures do you not need the endocarditis prophylaxis for? |
GU and GI procedures |
|
|
What is a first generation cefalasporin? |
Cefazolin 1G IV |
|
|
What is the 3rd generation cefalasporin? |
Ceftriaxone 1G IV |
|
|
How much ampicillian do we give? |
2 G IV |
|
|
What are the meds you give if pt is allergic to PCN or ampicillin? |
Cefazolin or ceftriaxone 1 G IV Clindamycin 600 mg IV (this is for endocarditis) |
|
|
What is the typical size of the aortic valve? |
2.5-3.5 cm2 |
|
|
How many cusps does the aortic valve have? |
3 |
|
|
How much of the pressure difference i required for flow to happen? |
2-4 mm Hg |
|
|
What is the most common valve problem in the US? |
Aortic Stenosis |
|
|
How can aortic stenosis occur? |
congenital bicuspid valve calcification of the cusps Infective Endocarditis Rheumatic heart disease |
|
|
At what size cusp, do we start to see symptoms with aortic stenosis? |
1.5 cm2 |
|
|
At what cusp size and pressure gradient is the aortic stenosis considered critical? |
>50 mm Hg mean pressure gradient < 0.7 cm2 aortic valve area >4.5 m/sec velocity of aortic jet |
|
|
At what values is the severe aortic stenosis? |
40-50 mm Hg mean pressure gradient 0.7-1.0 cm2 aortic valve area 4 - 4.5 m/sec velocity of aortic jet |
|
|
At what values is the moderate aortic stenosis? |
25-40 mm Hg mean pressure gradient 1.0-1.5 cm2 aortic valve area 3-4 m/sec velocity of aortic jet |
|
|
At what values is the mild aortic stenosis? |
< 25 mm Hg mean pressure gradient >1.5 cm2 aortic valve area < 3 m/sec velocity of aortic jet |
|
|
How often do they do ECHOs for Severe, Moderate, and Mild aortic stenosis? |
Severe - 1 year Moderate - 2 years Mild - 5 years |
|
|
When do we start to see symptoms in the pt with aortic stenosis? |
Upper 50s and 60s |
|
|
What can the pts with sortic stenosis have sudden death from? |
Arrhythmias, HF, and MI |
|
|
What happens with a stenotic aorta? |
The valve orifice is decreased > LV pressure overload > LV hypertrophy(drop coronary perfusion) > LV ischemia > LV failure > LV output and pulmonary edema |
|
|
What was the expected lifespan for the pts with aortic stenosis that had angina, syncope, and dyspnea. |
Angina - 5 years Syncope - 3 years Dyspnea(CHF) - 2 years |
|
|
Where do you hear the aortic stenosis? |
R 2nd intercostal space on the parasternal line radiates to the neck |
|
|
When do you hear the aortic stenosis? |
Mid systole, between S1 and S2, as a crescendo-decrescendo that radiates to the carotids |
|
|
What can decrease the intensity of the crescendo and decrescendo? |
Sustained hand grip in 10-15 seconds as it increases SVR and valsalva maneuver at 10 seconds, it decreases the venous return. |
|
|
Which side of the stethoscope do we use for the low pitched sounds? |
bell |
|
|
Which side of the stethoscope do we use for the high pitched sounds? |
diaphragm |
|
|
What is concentric hypertrophy? |
thickening of the heart walls from fighting against increase pressure. |
|
|
What does the pressure volume curve look like? |
Looks like an astronaut going into space |
|
|
What is expiratory residual volume? |
No matter how hard you exhale. It does not come out. |
|
|
What is capacity? |
It's made up of two or more volumes |
|
|
What can cause a death spiral in aortic stenosis pts? |
Hypotension |
|
|
What happens in the death spiral? |
hypotension causes myocardial ischemia > ischemic contractile dysfunction > decreased CO > worsening hypotension > Increased ischemia > more ischemic contractile dysfunction |
|
|
What is the best drug for the death spiral? |
Neo because it won't cause tachycardia. Treat BP as fast as you can. |
|
|
What is atrial kick for pts with aortic stenosis? |
40% of CO, so needs to be normal sinus rhythm of 70-90 going to the OR. This allows for adequate CO. |
|
|
What rhythms do you want to avoid for aortic stenosis? |
bradycardia, drops CO Tachycardia, increases demand and reduces supply Arrhythmias, cardiovert as soon as possible. |
|
|
What do you want in terms of cardiac preload? |
Adequate preload for adequate CO |
|
|
What can lower your preload? |
Blood loss and dehydration, so make sure your pt is well hydrated. |
|
|
Would you do permissive hypotension with aortic stenosis? |
Nope |
|
|
What can overloading your pt with volume do to them? |
pulmonary edema |
|
|
What should afterload be in aortic stenosis? |
Maintain or increase |
|
|
When in comes to contractility, when do you give the inotropic support? |
Whenever you need it, like during hypotension. Dobutamine, watch HR |
|
|
When do you place IVs? |
one in pre op and one in OR after the pt is out. |
|
|
If it's a big case, what kind of line would you like to have? |
central line |
|
|
What kind of anesthesia do we use on the aortic stenosis pt? |
General anesthesia |
|
|
What anesthesia is contraindicated in aortic stenosis pts? |
spinal because of possibility of sympathectomy, especially for those with severe and critical aortic stenosis. |
|
|
What is the goal of a spinal? |
To get certain dermatone lvls. |
|
|
If you were to do hip or knee cases, what would you do? |
T10- hip T12- knee |
|
|
Where are the cardio accelerator nerves? |
T1-T4 |
|
|
What happens when you put a spinal in? |
The medication has a tendency to drift upward. |
|
|
What is a sympathectomy? |
Lowers BP and HR |
|
|
Could you do a spinal with mild to moderate aortic stenosis? |
You could do an epi because there is less sympathetic response. |
|
|
What's another way of saying sympathectomy? |
High spinal |
|
|
How do you check to see if it is working? |
cold or fine needle |
|
|
What are good induction agents with aortic stenosis? |
etomidate Can use propofol, but watch the BP |
|
|
What are bad induction agents with aortic stenosis? |
Ketamine because can cause tachycardia Rocuronium raises HR |
|
|
What are good gases to maintain the aortic stenosis pt? |
all the gases are good, can mix with nitrous, but always watch BP |
|
|
What is aortic regurgitation? |
dilation or lesions in the cusps |
|
|
Which is the more common aortic regurgitation? |
Chronic from rheumatic heart disease, connective tissue diseases. Can remain asymptomatic for years. |
|
|
What is the other form of aortic regurgitation? |
This less common form is acute and comes from trauma, endocarditis, and aortic dissection. |
|
|
What type of pt is it most likely to have aortic regurgitation? |
Marfan syndrome pt |
|
|
What happens with aortic regurgitation? |
You have regurgitant flow > volume overload > LV dilation > LV failure > decreased LV output (may lead to pulmonary edema) |
|
|
Where will you hear aortic regurgitation? |
3rd & 4th L intercostal space, parasternal line |
|
|
When will you hear aortic regurgitation? |
Holodiastolic(throughout diastole) High pitched, decrescendo |
|
|
What do we do that increases the intensity of aortic regurgitation? |
hand grip exercise |
|
|
How does aortic regurgitation present itself? |
Widened pulse pressure Corrigan's or water pressure pulses de Musset's sign Duroziez's sign Quincke's pulses Muller's sign |
|
|
What is Corrigan's or water pressure pulses? |
See pulsation in the carotid |
|
|
What is de Musset's sign? |
pt head moving with each heart beat |
|
|
What is Duroziez's sign? |
Bruit in the femoral area |
|
|
What is quinke's pulses? |
Look at capillary refill and see pulsation in the nailbeds. Sometimes see it in the pt's lips |
|
|
Muller's sign |
Uvula is pulsating |
|
|
What happens to the walls of the heart? |
Eccentric hypertrophy LV cavity increases in size, and you have dilation |
|
|
What in the PA catheter can show aortic regurgiation? |
Large P waves |
|
|
What kind of HR would be good for aortic regurgitation? |
80-90 to increase CO, shortens the diastolic time. |
|
|
What's a bad HR for aortic regurgitation? |
bradycardia, reduces CO and longer diastolic time that allows for backflow and overload LV. |
|
|
What kind of preload do we want for aortic regurgitation? |
Slightly elevated to maximize CO |
|
|
What kind of afterload do we want for aortic regurgitation? |
slightly controlled drop in SVR, which allows for forward cardiac flow and decreases regurgitation. |
|
|
What do you want to do with contractility in aortic regurgitation? |
Maintain it |
|
|
What kind of anesthesia can you use? |
Sedation General Regional (you can do peripheral or epidural) |
|
|
What gas should you use? |
Any, just don't drop HR or increase SVR |
|
|
What can nitrous do? |
Cause H/A |
|
|
How should you handle mecahnical ventilation for the aortic regurgitation pt? |
maintain normal oxygenation and carbon dioxide elimination. |
|
|
What can you use to treat bradycardia? |
Atropine and robinul |

