![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Positioning may not be enough for airway maintenance if... |
|
|
|
Face mask |
|
|
|
Endotracheal Tubes |
|
|
|
Why is red rubber not advised for use as an endotracheal tube? |
|
|
|
Types of Endotracheal Tubes (2) |
|
|
|
Cole Endotracheal tubes |
|
|
|
Murphy Endotrachealtubes |
|
|
|
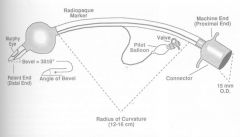
Murphy Endotracheal tubes |
|
|
|
Cole Endotracheal tubes |

|
|
|
Laryngoscope |
|
|
|
2 Types of laryngoscope blades |
|
|
|
Miller Blade |
Straight |
|
|
Bizarri-Guiffrida Blade |
Curved |
|
|
Horse,cow, sheep, and goat Airway Concerns |
|
|
|
Cat Airway Concerns |
|
|
|
Rabbit Airway Concerns |
|
|
|
Rodent Airway Concerns |
|
|
|
Swine Airway Concerns |
|
|
|
Ruminant Airway Concerns |
|

