![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What may happen to a species with low genetic diversity? |
|
|
|
Give an example of a factor that may lower genetic diversity in a population. |
|
|
|
What is a pedigree animal? |
An animal bred purely from animals from the same breed. |
|
|
What is a rare breed? |
A breed of farm animal that's not used in large-scale farming. |
|
|
Give an example of how the genetic diversity of a population could be increased |
Breeding programmes. |
|
|
Genetic .......... is used to measure genetic diversity |
polymorphism |
|
|
What is a locus on a chromosome? |
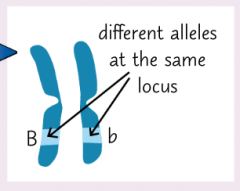
The point where alleles of the same gene are found at the same point. |
|
|
What does polymorphism describe? |
A locus that has two or more alleles. |
|
|
Working out the polymorphic gene loci in an organism gives you a measure of genetic diversity. State the formula used to calculate the proportion of polymorphic gene loci. |

|
|
|
State three factors affecting global biodiversity. |
|
|
|
State four factors that affect biodiversity due to human population growth |
|
|
|
How does habitat loss affect global biodiversity? |
|
|
|
How does over-exploitation affect global biodiversity? |
|
|
|
How does urbanisation affect global biodiversity? |
|
|
|
How does pollution affect global biodiversity? |
|
|
|
What is monoculture? |
The growing of a single variety of a single crop. |
|
|
How does monoculture in agriculture decrease global biodiversity? |
|
|
|
What is climate change? |
The variation of the earth's climate (e.g. changes in the temperature and rainfall patterns). |
|
|
Climate change occurs naturally, but the scientific consensus is that the climate change we are experiencing is due to humans. What is one of the causes of climate change due to humans? |
The increased emissions of greenhouse gases. |
|
|
Greenhouse gases cause .......... warming (increasing the global average ..........), which causes other types of climate change, e.g. changing ........ patterns. |
1. global 2. temperature 3. rainfall |
|
|
Climate change will affect .......... areas of the world in different ways - some places will get warmer, some ........, some wetter and others ........... . |
1. different 2. colder 3. drier |
|
|
Most species require a particular .......... . |
climate |
|
|
What can a change in climate do to a habitat? What may this result in? Give an example of a species this has affected. What would happen if a species cannot react fast enough to this change? |
|

