![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
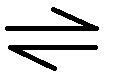
What does is symbol mean? |
The reaction is reversible |
|
|
What are the conditions for an equilibrium to be established? |
1. A closed system where reactants and products cannot escape 2. No more reactants added or products removed. If so, the equilibrium position shifts |
|
|
How can you tell when an equilibrium has been reached? |
The properties of the system do not change with time. This includes the density, concentration of reactants / products, colour and pressure |
|
|
What are the features of a dynamic equilibrium? Give the definition of a dynamic equilibrium. |
1. The rate of forward and backwards reactions are equal 2. The concentrations of reactants and products do not change Dynamic Equilibrium: A reversible reaction where the concentrations of reactants and products stays the same and the rates of the forward and backward reaction are equal |
|
|
State Le Chatelier's Principle |
A system at equilibrium will react to oppose any change imposed on it |
|
|
State the three factors that affect the position of equilibrium |
Concentration, Pressure and Temperature |
|
|
By Le Chatelier's principle, what would happen if the concentration of A was increased? A + B ⇌ C + D |
The position of equilibrium would shift to the right to make there be less reactants and more products, so there will be more products |
|
|
By Le Chatelier's principle, what would happen if the concentration of A was decreased? A + B ⇌ C + D |
The position of equilibrium would shift to the left to make more reactants and less products, so there will be fewer products |
|
|
By Le Chatelier's principle, what would happen in the following cases? 1. You add more of a chemical, increasing its concentration 2. You remove some of a chemical, decreasing its concentration 3. Increase the pressure of a gaseous reaction 4. Decrease the pressure of a gaseous reaction 5. Increase the temperature 6. Decrease the temperature |
1. The equilibrium moves to make less of it 2. The equilibrium moves to make more of it 3. The equilibrium moves to lower pressure 4. The equilibrium moves to increase pressure 5. The equilibrium moves to cool the reaction 6. The equilibrium moves to heat the reaction |
|
|
If the pressure is changed in an equilibrium that contains gasses (It must contain gasses) what will change? |
If pressure is increased, equilibrium moves to side with fewer moles to decrease pressure If pressure is decreased, equilibrium moves to the side with more moles to increase pressure |
|
|
If the temperature is changed in an equilibrium what will change? |
If the temperature is increased, the equilibrium shifts to the endothermic direction to absorb more heat If the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium shifts in the exothermic direction to give out more head |
|
|
How would you find the Equilibrium Constant Kc of the equation aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD ? |
Kc = the thingy of products PUT PRODUCTS ON TOP /(divided by) the thingy of reactants |
|
|
In production of Ammonia, what are the disadvantages of high pressures and temperatures?
|
A lot of energy is required to provide High Pressures, expensive. A strong pressure vessel is required for the reaction, which is also expensive. |
|
|
In production of Ethanol, what are the disadvantages of high pressures and low temperatures? |
High Pressure can cause ethene to polymerise. High pressures increase running costs as a lot of energy and a strong vessel are required. Low temperature will reduce the reaction rate. Use of steam in the reaction dilutes the catalyst. |
|
|
What are compromise conditions? |
Conditions which give an economical balance between yield, rate of reaction and cost |

